Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
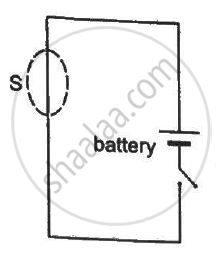
A closed surface S is constructed around a conducting wire connected to a battery and a switch in the following figure. As the switch is closed, the free electrons in the wire start moving along the wire. In any time interval, the number of electrons entering the closed surface S is equal to the number of electrons leaving it. On closing the switch, the flux of the electric field through the closed surface
(a) is increased
(b) is decreased
(c) remains unchanged
(d) remains zero
उत्तर
(c) remains unchanged
(d) remains zero
Initially, there is no charge in the closed surface. As the wire is neutral, the flux initially is zero. Now, if we connect the battery and a current flows through it, the flux remains zero, as the number of electrons entering the surface is equal to number of electrons leaving. That is, net charge enclosed is zero and so is the flux.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(i) If two similar large plates, each of area A having surface charge densities +σ and –σ are separated by a distance d in air, find the expressions for
(a) field at points between the two plates and on outer side of the plates. Specify the direction of the field in each case.
(b) the potential difference between the plates.
(c) the capacitance of the capacitor so formed.
(ii) Two metallic spheres of Radii R and 2R are charged so that both of these have same surface charge density σ. If they are connected to each other with a conducting wire, inn which direction will the charge flow and why?
plot a graph showing the variation of current density (j) versus the electric field (E) for two conductors of different materials. What information from this plot regarding the properties of the conducting material, can be obtained which can be used to select suitable materials for use in making (i) standard resistance and (ii) connecting wires in electric circuits?
Two identical circular loops 1 and 2 of radius R each have linear charge densities −λ and +λ C/m respectively. The loops are placed coaxially with their centres `Rsqrt3` distance apart. Find the magnitude and direction of the net electric field at the centre of loop 1.
Why is the potential inside a hollow spherical charged conductor constant and has the same value of as on its surface?
A metallic particle with no net charge is placed near a finite metal plate carrying a positive charge. The electric force on the particle will be
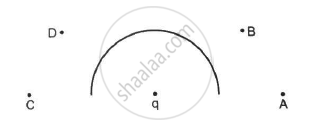
In the following figure shows a charge q placed at the centre of a hemisphere. A second charge Q is placed at one of the positions A, B, C and D. In which position(s) of this second charge, the flux of the electric field through the hemisphere remains unchanged?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
The electric field in a region is given by
`vec"E"= 3/5"E"_0 vec"i" + 4/5 "E"_0 vec "i" "with" " E"_0 = 2.0 xx 10^3 "N""C"^-1.`
Find the flux of this field through a rectangular surface of area 0⋅2 m2 parallel to the y-z plane.
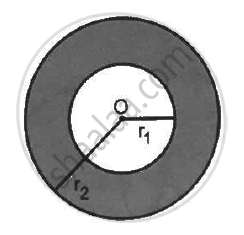
A charge Q is distributed uniformly within the material of a hollow sphere of inner and outer radii r1 and r2 (see the figure). Find the electric field at a point P at a distance x away from the centre for r1 < x < r. Draw a rough graph showing the electric field as a function of x for 0 < x < 2r2 (see the figure).
One end of a 10 cm long silk thread is fixed to a large vertical surface of a charged non-conducting plate and the other end is fastened to a small ball of mass 10 g and a charge of 4.0× 10-6 C. In equilibrium, the thread makes an angle of 60° with the vertical (a) Find the tension in the string in equilibrium. (b) Suppose the ball is slightly pushed aside and released. Find the time period of the small oscillations.
A uniform electric field of 10 N C−1 exists in the vertically downward direction. Find the increase in the electric potential as one goes up through a height of 50 cm.
A simple pendulum consists of a small sphere of mass m suspended by a thread of length l. The sphere carries a positive charge q. The pendulum is placed in a uniform electric field of strength E directed vertically downwards. Find the period of oscillation of the pendulum due to the electrostatic force acting on the sphere, neglecting the effect of the gravitational force.
Electric field at a point is defined as ______.
When a comb rubbed with dry hair attracts pieces of paper. This is because the ______.
The force per unit charge is known as ______.
A charge Q is applied to a conducting sphere of radius R. At the sphere's centre, the electric potential and electric field are respectively
Pick out the statement which is incorrect
