Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A particle is going in a spiral path as shown in figure with constant speed.
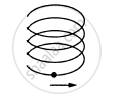
पर्याय
The velocity of the particle is constant.
The acceleration of the particle is constant.
The magnitude of acceleration is constant.
The magnitude of acceleration is decreasing continuously.
उत्तर
The magnitude of acceleration is constant.
As the pitch and radius of the path is constant, it shows that the magnitude of tangential and radial acceleration is also constant.
Hence, the magnitude of total acceleration is constant.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A smooth block loosely fits in a circular tube placed on a horizontal surface. The block moves in a uniform circular motion along the tube. Which wall (inner or outer) will exert a nonzero normal contact force on the block?
A particle is kept fixed on a turntable rotating uniformly. As seen from the ground the particle goes in a circle, its speed is 20 cm/s and acceleration is 20 cm/s2. The particle is now shifted to a new position to make the radius half of the original value. The new value of the speed and acceleration will be
Water in a bucket is whirled in a vertical circle with string attached to it. The water does no fall down even when the bucket is inverted at the top of its path. We conclude that in this position
A stone of mass m tied to a string of length l is rotated in a circle with the other end of the string as the centre. The speed of the stone is v. If the string breaks, the stone will move
A motorcycle is going on an overbridge of radius R. The driver maintains a constant speed. As the motorcycle is ascending on the overbridge, the normal force on it
An object follows a curved path. The following quantities may remain constant during the motion
(a) speed
(b) velocity
(c) acceleration
(d) magnitude of acceleration.
A scooter weighing 150 kg together with its rider moving at 36 km/hr is to take a turn of a radius 30 m. What horizontal force on the scooter is needed to make the turn possible ?
What is the radius of curvature of the parabola traced out by the projectile in the previous problem at a point where the particle velocity makes an angle θ/2 with the horizontal?
A block of mass m moves on a horizontal circle against the wall of a cylindrical room of radius R. The floor of the room on which the block moves is smooth but the friction coefficient between the wall and the block is μ. The block is given an initial speed v0. As a function of the speed v writes
(a) the normal force by the wall on the block,
(b) the frictional force by a wall, and
(c) the tangential acceleration of the block.
(d) Integrate the tangential acceleration \[\left( \frac{dv}{dt} = v\frac{dv}{ds} \right)\] to obtain the speed of the block after one revolution.
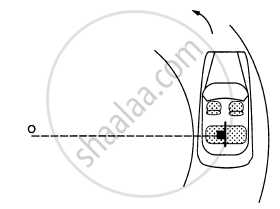
A car moving at a speed of 36 km/hr is taking a turn on a circular road of radius 50 m. A small wooden plate is kept on the seat with its plane perpendicular to the radius of the circular road (In the following figure). A small block of mass 100 g is kept on the seat which rests against the plate. the friction coefficient between the block and the plate is. (a) Find the normal contact force exerted by the plate on the block. (b) The plate is slowly turned so that the angle between the normal to the plate and the radius of the road slowly increases. Find the angle at which the block will just start sliding on the plate.
A particle of mass 1 kg, tied to a 1.2 m long string is whirled to perform the vertical circular motion, under gravity. The minimum speed of a particle is 5 m/s. Consider the following statements.
P) Maximum speed must be `5sqrt5` m/s.
Q) Difference between maximum and minimum tensions along the string is 60 N.
Select the correct option.
Choose the correct option.
Select correct statement about the formula (expression) of moment of inertia (M.I.) in terms of mass M of the object and some of its distance parameter/s, such as R, L, etc.
A body slides down a smooth inclined plane having angle θ and reaches the bottom with velocity v. If a body is a sphere, then its linear velocity at the bottom of the plane is
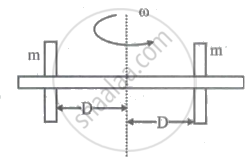
Two identical masses are connected to a horizontal thin (massless) rod as shown in the figure. When their distance from the pivot is D, a torque τ produces an angular acceleration of α1. The masses are now repositioned so that they are 2D from the pivot. The same torque produces an angular acceleration α2 which is given by ______
A body of M.I. 2 kg m2 rotates with an angular velocity of 20 rad/s. When an external torque of 0.5 N m acts on it in the opposite direction, the number of revolutions it makes before it comes to rest is ____________.
In negotiating curve on a flat road, a cyclist leans inwards by an angle e with the vertical in order to ______.
A body is moving along a circular track of radius 100 m with velocity 20 m/s. Its tangential acceleration is 3 m/s2 then its resultant accelaration will be ______.
A person driving a car suddenly applies the brakes on seeing a child on the road ahead. If he is not wearing seat belt, he falls forward and hits his head against the steering wheel. Why?
When a body slides down from rest along a smooth inclined plane making an angle of 45° with the horizontal, it takes time T. When the same body slides down from rest along a rough inclined plane making the same angle and through the same distance, it is seen to take time pT, where p is some number greater than 1. Calculate the co-efficient of friction between the body and the rough plane.
