Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The position vector of a particle in a circular motion about the origin sweeps out equal area in equal time. Its
(a) velocity remains constant
(b) speed remains constant
(c) acceleration remains constant
(d) tangential acceleration remains constant.
उत्तर
(b) speed remains constant
(d) tangential acceleration remains constant
If the speed is constant, the position vector of the particle sweeps out equal area in equal time in circular motion.
Also, for constant speed, tangential acceleration is zero, i.e., constant.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
You may have seen in a circus a motorcyclist driving in vertical loops inside a ‘death-well’ (a hollow spherical chamber with holes, so the spectators can watch from outside). Explain clearly why the motorcyclist does not drop down when he is at the uppermost point, with no support from below. What is the minimum speed required at the uppermost position to perform a vertical loop if the radius of the chamber is 25 m?
A thin circular loop of radius R rotates about its vertical diameter with an angular frequency ω. Show that a small bead on the wire loop remains at its lowermost point for `omega <= sqrt(g/R)` .What is the angle made by the radius vector joining the centre to the bead with the vertical downward direction for `omega = sqrt("2g"/R)` ?Neglect friction.
A smooth block loosely fits in a circular tube placed on a horizontal surface. The block moves in a uniform circular motion along the tube. Which wall (inner or outer) will exert a nonzero normal contact force on the block?
When a particle moves in a circle with a uniform speed
A particle is kept fixed on a turntable rotating uniformly. As seen from the ground the particle goes in a circle, its speed is 20 cm/s and acceleration is 20 cm/s2. The particle is now shifted to a new position to make the radius half of the original value. The new value of the speed and acceleration will be
A stone of mass m tied to a string of length l is rotated in a circle with the other end of the string as the centre. The speed of the stone is v. If the string breaks, the stone will move
A train A runs from east to west and another train B of the same mass runs from west to east at the same speed along the equator. A presses the track with a force F1 and B presses the track with a force F2.
A simple pendulum having a bob of mass m is suspended from the ceiling of a car used in a stunt film shooting. the car moves up along an inclined cliff at a speed v and makes a jump to leave the cliff and lands at some distance. Let R be the maximum height of the car from the top of the cliff. The tension in the string when the car is in air is
An object follows a curved path. The following quantities may remain constant during the motion
(a) speed
(b) velocity
(c) acceleration
(d) magnitude of acceleration.
A particle moves in a circle of radius 1.0 cm at a speed given by v = 2.0 t where v is cm/s and t in seconds.
(a) Find the radial acceleration of the particle at t = 1 s.
(b) Find the tangential acceleration at t = 1 s.
(c) Find the magnitude of the acceleration at t = 1 s.
A ceiling fan has a diameter (of the circle through the outer edges of the three blades) of 120 cm and rpm 1500 at full speed. Consider a particle of mass 1 g sticking at the outer end of a blade. How much force does it experience when the fan runs at full speed? Who exerts this force on the particle? How much force does the particle exert on the blade along its surface?
A motorcycle has to move with a constant speed on an over bridge which is in the form of a circular arc of radius R and has a total length L. Suppose the motorcycle starts from the highest point.(a) What can its maximum velocity be for which the contact with the road is not broken at the highest point? (b) If the motorcycle goes at speed 1/√2 times the maximum found in part (a), where will it lose the contact with the road? (c) What maximum uniform speed can it maintain on the bridge if it does not lose contact anywhere on the bridge?
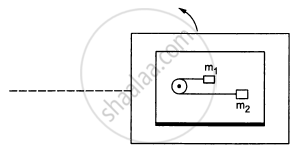
A table with smooth horizontal surface is placed in a circle of a large radius R (In the following figure). A smooth pulley of small radius is fastened to the table. Two masses m and 2m placed on the table are connected through a string going over the pulley. Initially the masses are held by a person with the string along the outward radius and then the system is released from rest (with respect to the cabin). Find the magnitude of the initial acceleration of the masses as seen from the cabin and the tension in the string.
When seen from below, the blades of a ceiling fan are seen to be revolving anticlockwise and their speed is decreasing. Select the correct statement about the directions of its angular velocity and angular acceleration.
A particle performs uniform circular motion in a horizontal plane. The radius of the circle is 10 cm. If the centripetal force F is kept constant but the angular velocity is halved, the new radius of the path will be ______.
A body of M.I. 2 kg m2 rotates with an angular velocity of 20 rad/s. When an external torque of 0.5 N m acts on it in the opposite direction, the number of revolutions it makes before it comes to rest is ____________.
In negotiating curve on a flat road, a cyclist leans inwards by an angle e with the vertical in order to ______.
A person driving a car suddenly applies the brakes on seeing a child on the road ahead. If he is not wearing seat belt, he falls forward and hits his head against the steering wheel. Why?
A block of 200 g mass moves with a uniform speed in a horizontal circular groove, with vertical side walls of radius 20 cm. If the block takes 40 s to complete one round, the normal force by the side walls of the groove is ______.
Which of the following statements is FALSE for a particle moving in a circle with a constant angular speed?
