Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Assume that the earth goes round the sun in a circular orbit with a constant speed of 30 kms
पर्याय
The average velocity of the earth from 1st jan, 90 to 30th June, 90 is zero.
The average acceleration during the above period is 60 km/s2.
The average speed from 1st Jan, 90 to 31st Dec, 90 is zero.
The instantaneous acceleration of the earth points towards the sun.
उत्तर
The instantaneous acceleration of the Earth points towards the Sun.
The speed is constant; therefore, there is no tangential acceleration and the direction of radial acceleration is towards the Sun. So, the instantaneous acceleration of the Earth points towards the Sun.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
You may have seen in a circus a motorcyclist driving in vertical loops inside a ‘death-well’ (a hollow spherical chamber with holes, so the spectators can watch from outside). Explain clearly why the motorcyclist does not drop down when he is at the uppermost point, with no support from below. What is the minimum speed required at the uppermost position to perform a vertical loop if the radius of the chamber is 25 m?
A smooth block loosely fits in a circular tube placed on a horizontal surface. The block moves in a uniform circular motion along the tube. Which wall (inner or outer) will exert a nonzero normal contact force on the block?
Water in a bucket is whirled in a vertical circle with string attached to it. The water does no fall down even when the bucket is inverted at the top of its path. We conclude that in this position
A motorcycle is going on an overbridge of radius R. The driver maintains a constant speed. As the motorcycle is ascending on the overbridge, the normal force on it
If the earth stop rotating, the apparent value of g on its surface will
A simple pendulum having a bob of mass m is suspended from the ceiling of a car used in a stunt film shooting. the car moves up along an inclined cliff at a speed v and makes a jump to leave the cliff and lands at some distance. Let R be the maximum height of the car from the top of the cliff. The tension in the string when the car is in air is
An object follows a curved path. The following quantities may remain constant during the motion
(a) speed
(b) velocity
(c) acceleration
(d) magnitude of acceleration.
Find the acceleration of a particle placed on the surface of the earth at the equator due to earth's rotation. The diameter of earth = 12800 km and it takes 24 hours for the earth to complete one revolution about its axis.
A ceiling fan has a diameter (of the circle through the outer edges of the three blades) of 120 cm and rpm 1500 at full speed. Consider a particle of mass 1 g sticking at the outer end of a blade. How much force does it experience when the fan runs at full speed? Who exerts this force on the particle? How much force does the particle exert on the blade along its surface?
A mosquito is sitting on an L.P. record disc rotating on a turn table at \[33\frac{1}{3}\] revolutions per minute. The distance of the mosquito from the centre of the turn table is 10 cm. Show that the friction coefficient between the record and the mosquito is greater than π2/81. Take g =10 m/s2.
The bob of a simple pendulum of length 1 m has mass 100 g and a speed of 1.4 m/s at the lowest point in its path. Find the tension in the string at this instant.
A turn of radius 20 m is banked for the vehicles going at a speed of 36 km/h. If the coefficient of static friction between the road and the tyre is 0.4, what are the possible speeds of a vehicle so that it neither slips down nor skids up?
A car goes on a horizontal circular road of radius R, the speed increasing at a constant rate \[\frac{\text{dv}}{\text{dt}} = a\] . The friction coefficient between the road and the tyre is μ. Find the speed at which the car will skid.
A block of mass m is kept on a horizontal ruler. The friction coefficient between the ruler and the block is μ. The ruler is fixed at one end and the block is at a distance L from the fixed end. The ruler is rotated about the fixed end in the horizontal plane through the fixed end. (a) What can the maximum angular speed be for which the block does not slip? (b) If the angular speed of the ruler is uniformly increased from zero at an angular acceleration α, at what angular speed will the block slip?
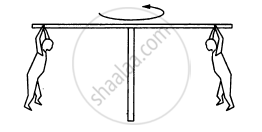
In a children's park a heavy rod is pivoted at the centre and is made to rotate about the pivot so that the rod always remains horizontal. Two kids hold the rod near the ends and thus rotate with the rod (In the following figure). Let the mass of each kid be 15 kg, the distance between the points of the rod where the two kids hold it be 3.0 m and suppose that the rod rotates at the rate of 20 revolutions per minute. Find the force of friction exerted by the rod on one of the kids.
A hemispherical bowl of radius R is rotated about its axis of symmetry which is kept vertical. A small block is kept in the bowl at a position where the radius makes an angle θ with the vertical. The block rotates with the bowl without any slipping. The friction coefficient between the block and the bowl surface is μ. Find the range of the angular speed for which the block will not slip.
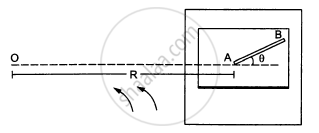
A table with smooth horizontal surface is fixed in a cabin that rotates with a uniform angular velocity ω in a circular path of radius R (In the following figure). A smooth groove AB of length L(<<R) is made the surface of the table. The groove makes an angle θ with the radius OA of the circle in which the cabin rotates. A small particle is kept at the point A in the groove and is released to move at the point A in the groove and is released to move along AB. Find the time taken by the particle to reach the point B.
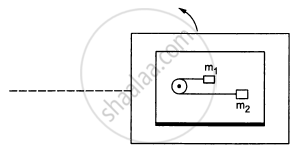
A table with smooth horizontal surface is placed in a circle of a large radius R (In the following figure). A smooth pulley of small radius is fastened to the table. Two masses m and 2m placed on the table are connected through a string going over the pulley. Initially the masses are held by a person with the string along the outward radius and then the system is released from rest (with respect to the cabin). Find the magnitude of the initial acceleration of the masses as seen from the cabin and the tension in the string.
A child starts running from rest along a circular track of radius r with constant tangential acceleration a. After time the feels that slipping of shoes on the ground has started. The coefficient of friction between shoes and the ground is [g = acceleration due to gravity].
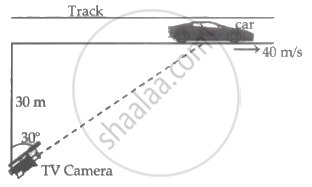
A racing car is travelling along a track at a constant speed of 40 m/s. A T.V. cameraman is recording the event from a distance of 30 m directly away from the track as shown in the figure. In order to keep the car under view in the position shown, the angular speed with which the camera should be rotated is ______.