Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
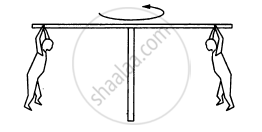
In a children's park a heavy rod is pivoted at the centre and is made to rotate about the pivot so that the rod always remains horizontal. Two kids hold the rod near the ends and thus rotate with the rod (In the following figure). Let the mass of each kid be 15 kg, the distance between the points of the rod where the two kids hold it be 3.0 m and suppose that the rod rotates at the rate of 20 revolutions per minute. Find the force of friction exerted by the rod on one of the kids.
उत्तर
Given :
\[\text {Frequency of rod }= n = 20 \text{ rev} \text{ per } \min\]
\[ \Rightarrow \text{ n} = \frac{20}{60} = \frac{1}{3}\text{rev/s}\]
Therefore, we have :
angular velocity of rod ,
\[\text { Angular velocity of rod }= \omega = 2\pi n = \frac{2\pi}{3}\text{rad/s}\]
Mass of each kid = \[\text{m = 15 kg}\]
Radius = \[r = \frac{3}{2} = 1 . 5 \text{m}\]
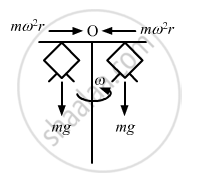
\[\therefore \text { Frictional force }= F = \text{mr }\omega^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow F = 15 \times (1 . 5) \times \frac{(2\pi )^2}{9}\]
\[ = 5 \times (0 . 5) \times 4 \pi^2 = 10 \pi^2 N\]
Thus, the force of frictional on one of the kids is 10 \[\pi\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A stone of mass 0.25 kg tied to the end of a string is whirled round in a circle of radius 1.5 m with a speed of 40 rev/min in a horizontal plane. What is the tension in the string? What is the maximum speed with which the stone can be whirled around if the string can withstand a maximum tension of 200 N?
Water in a bucket is whirled in a vertical circle with string attached to it. The water does no fall down even when the bucket is inverted at the top of its path. We conclude that in this position
A motorcycle is going on an overbridge of radius R. The driver maintains a constant speed. As the motorcycle is ascending on the overbridge, the normal force on it
The position vector of a particle in a circular motion about the origin sweeps out equal area in equal time. Its
(a) velocity remains constant
(b) speed remains constant
(c) acceleration remains constant
(d) tangential acceleration remains constant.
A particle moves in a circle of radius 1.0 cm at a speed given by v = 2.0 t where v is cm/s and t in seconds.
(a) Find the radial acceleration of the particle at t = 1 s.
(b) Find the tangential acceleration at t = 1 s.
(c) Find the magnitude of the acceleration at t = 1 s.
A scooter weighing 150 kg together with its rider moving at 36 km/hr is to take a turn of a radius 30 m. What horizontal force on the scooter is needed to make the turn possible ?
A simple pendulum is suspended from the ceiling of a car taking a turn of radius 10 m at a speed of 36 km/h. Find the angle made by he string of the pendulum with the vertical if this angle does not change during the turn. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Suppose the amplitude of a simple pendulum having a bob of mass m is θ0. Find the tension in the string when the bob is at its extreme position.
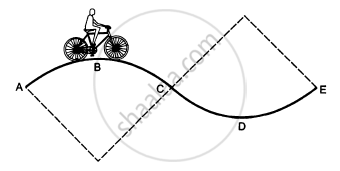
A track consists of two circular parts ABC and CDE of equal radius 100 m and joined smoothly as shown in figure. Each part subtends a right angle at its centre. A cycle weighing 100 kg together with the rider travels at a constant speed of 18 km/h on the track. (a) Find the normal contact force by the road on the cycle when it is at B and at D. (b) Find the force of friction exerted by the track on the tyres when the cycle is at B, C and. (c) Find the normal force between the road and the cycle just before and just after the cycle crosses C. (d) What should be the minimum friction coefficient between the road and the tyre, which will ensure that the cyclist can move with constant speed? Take g = 10 m/s2.
A particle is projected with a speed u at an angle θ with the horizontal. Consider a small part of its path near the highest position and take it approximately to be a circular arc. What is the radius of this circular circle? This radius is called the radius of curvature of the curve at the point.
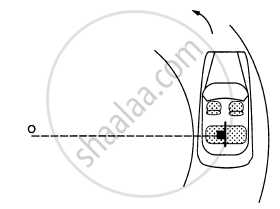
A car moving at a speed of 36 km/hr is taking a turn on a circular road of radius 50 m. A small wooden plate is kept on the seat with its plane perpendicular to the radius of the circular road (In the following figure). A small block of mass 100 g is kept on the seat which rests against the plate. the friction coefficient between the block and the plate is. (a) Find the normal contact force exerted by the plate on the block. (b) The plate is slowly turned so that the angle between the normal to the plate and the radius of the road slowly increases. Find the angle at which the block will just start sliding on the plate.
A person stands on a spring balance at the equator. If the speed of earth's rotation is increased by such an amount that the balance reading is half the true weight, what will be the length of the day in this case?
A particle of mass 1 kg, tied to a 1.2 m long string is whirled to perform the vertical circular motion, under gravity. The minimum speed of a particle is 5 m/s. Consider the following statements.
P) Maximum speed must be `5sqrt5` m/s.
Q) Difference between maximum and minimum tensions along the string is 60 N.
Select the correct option.
Angular displacement (θ) of a flywheel varies with time as θ = at + bt2 + ct3 then angular acceleration is given by ____________.
An engine requires 5 seconds to go from a speed of 600 r.p.m. to 1200 r.p.m. How many revolutions does it make in this period?
A body of mass m is performing a UCM in a circle of radius r with speed v. The work done by the centripetal force in moving it through `(2/3)`rd of the circular path is ______.
In negotiating curve on a flat road, a cyclist leans inwards by an angle e with the vertical in order to ______.
An engine is moving on a c1rcular path of radius 200 m with speed of 15 m/s. What will be the frequency heard by an observer who is at rest at the centre of the circular path, when engine blows the whistle with frequency 250 Hz?
Find the angular acceleration of a particle in circular motion which slows down from 300 r.p.m. to 0 r.p.m. in 20 s.
