Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A motorcycle is going on an overbridge of radius R. The driver maintains a constant speed. As the motorcycle is ascending on the overbridge, the normal force on it
पर्याय
increases
decreases
remains the same
fluctuates.
उत्तर

The normal force on the motorcycle , \[\text{N = mg}\cos\theta - \frac{\text{mv}^2}{R}\]
As the motorcycle is ascending on the overbridge, θ decreases (from \[\frac{\pi}{2}\] to 0).
So, normal force increases with decrease in θ.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A disc revolves with a speed of `33 1/3` rev/min, and has a radius of 15 cm. Two coins are placed at 4 cm and 14 cm away from the centre of the record. If the co-efficient of friction between the coins and the record is 0.15, which of the coins will revolve with the record?
A thin circular loop of radius R rotates about its vertical diameter with an angular frequency ω. Show that a small bead on the wire loop remains at its lowermost point for `omega <= sqrt(g/R)` .What is the angle made by the radius vector joining the centre to the bead with the vertical downward direction for `omega = sqrt("2g"/R)` ?Neglect friction.
Assume that the earth goes round the sun in a circular orbit with a constant speed of 30 kms
The position vector of a particle in a circular motion about the origin sweeps out equal area in equal time. Its
(a) velocity remains constant
(b) speed remains constant
(c) acceleration remains constant
(d) tangential acceleration remains constant.
A stone is fastened to one end of a string and is whirled in a vertical circle of radius R. Find the minimum speed the stone can have at the highest point of the circle.
A hemispherical bowl of radius R is rotated about its axis of symmetry which is kept vertical. A small block is kept in the bowl at a position where the radius makes an angle θ with the vertical. The block rotates with the bowl without any slipping. The friction coefficient between the block and the bowl surface is μ. Find the range of the angular speed for which the block will not slip.
A particle is projected with a speed u at an angle θ with the horizontal. Consider a small part of its path near the highest position and take it approximately to be a circular arc. What is the radius of this circular circle? This radius is called the radius of curvature of the curve at the point.
A car moving at a speed of 36 km/hr is taking a turn on a circular road of radius 50 m. A small wooden plate is kept on the seat with its plane perpendicular to the radius of the circular road (In the following figure). A small block of mass 100 g is kept on the seat which rests against the plate. the friction coefficient between the block and the plate is. (a) Find the normal contact force exerted by the plate on the block. (b) The plate is slowly turned so that the angle between the normal to the plate and the radius of the road slowly increases. Find the angle at which the block will just start sliding on the plate.
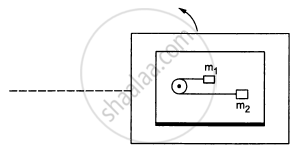
A table with smooth horizontal surface is placed in a circle of a large radius R (In the following figure). A smooth pulley of small radius is fastened to the table. Two masses m and 2m placed on the table are connected through a string going over the pulley. Initially the masses are held by a person with the string along the outward radius and then the system is released from rest (with respect to the cabin). Find the magnitude of the initial acceleration of the masses as seen from the cabin and the tension in the string.
Choose the correct option.
Select correct statement about the formula (expression) of moment of inertia (M.I.) in terms of mass M of the object and some of its distance parameter/s, such as R, L, etc.
In a certain unit, the radius of gyration of a uniform disc about its central and transverse axis is `sqrt2.5`. Its radius of gyration about a tangent in its plane (in the same unit) must be ______.
In non-uniform circular motion, the ratio of tangential to radial acceleration is (r = radius, a = angular acceleration and v = linear velocity)
Two particles A and B are located at distances rA and rB respectively from the centre of a rotating disc such that rA > rB. In this case, if angular velocity ω of rotation is constant, then ______
A child starts running from rest along a circular track of radius r with constant tangential acceleration a. After time the feels that slipping of shoes on the ground has started. The coefficient of friction between shoes and the ground is [g = acceleration due to gravity].
The real force 'F' acting on a particle of mass ' m' performing circular motion acts along the radius of circle 'r' and is directed towards the centre of circle. The square root of the magnitude of such force is (T = periodic time).
A body of M.I. 2 kg m2 rotates with an angular velocity of 20 rad/s. When an external torque of 0.5 N m acts on it in the opposite direction, the number of revolutions it makes before it comes to rest is ____________.
An engine is moving on a c1rcular path of radius 200 m with speed of 15 m/s. What will be the frequency heard by an observer who is at rest at the centre of the circular path, when engine blows the whistle with frequency 250 Hz?
Which of the following statements is FALSE for a particle moving in a circle with a constant angular speed?
Find the angular acceleration of a particle in circular motion which slows down from 300 r.p.m. to 0 r.p.m. in 20 s.
