Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
ABCD is a trapezium with AB parallel to DC. A line parallel to AC intersects AB at X and BC at Y.
Prove that the area of ∆ADX = area of ∆ACY.
उत्तर
Join CX, DX and AY.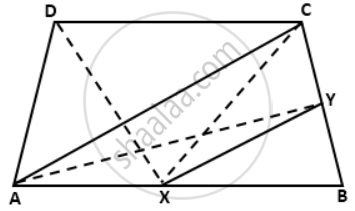 Now, triangles ADX and ACX are on the same base AX and between the parallels AB and DC.
Now, triangles ADX and ACX are on the same base AX and between the parallels AB and DC.
∴ A( ΔADX ) = A( ΔACX ) ….(i)
Also, triangles ACX and ACY are on the same base AC and between the parallels AC and XY.
∴ A( ΔACX ) = A( ΔACY ) ….(ii)
From (i) and (ii), we get
A( ΔADX ) = A( ΔACY )
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the given figure, ABCD is a parallelogram; BC is produced to point X.
Prove that: area ( Δ ABX ) = area (`square`ACXD )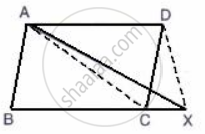
In the following, AC // PS // QR and PQ // DB // SR.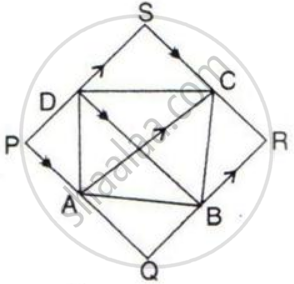
Prove that: Area of quadrilateral PQRS = 2 x Area of the quad. ABCD.
In the given figure, diagonals PR and QS of the parallelogram PQRS intersect at point O and LM is parallel to PS. Show that: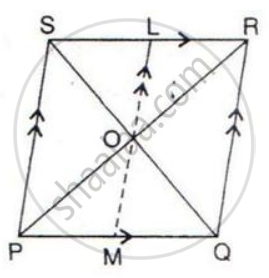
(i) 2 Area (POS) = Area (// gm PMLS)
(ii) Area (POS) + Area (QOR) = Area (// gm PQRS)
(iii) Area (POS) + Area (QOR) = Area (POQ) + Area (SOR).
In parallelogram ABCD, P is a point on side AB and Q is a point on side BC.
Prove that:
(i) ΔCPD and ΔAQD are equal in the area.
(ii) Area (ΔAQD) = Area (ΔAPD) + Area (ΔCPB)
In the given figure, M and N are the mid-points of the sides DC and AB respectively of the parallelogram ABCD.
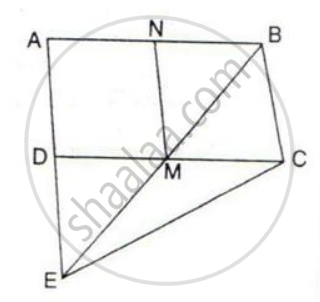
If the area of parallelogram ABCD is 48 cm2;
(i) State the area of the triangle BEC.
(ii) Name the parallelogram which is equal in area to the triangle BEC.
ABCD is a parallelogram in which BC is produced to E such that CE = BC and AE intersects CD at F.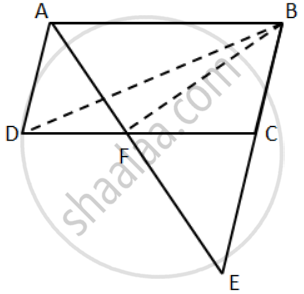
If ar.(∆DFB) = 30 cm2; find the area of parallelogram.
E, F, G, and H are the midpoints of the sides of a parallelogram ABCD.
Show that the area of quadrilateral EFGH is half of the area of parallelogram ABCD.
The given figure shows a parallelogram ABCD with area 324 sq. cm. P is a point in AB such that AP: PB = 1:2
Find The area of Δ APD.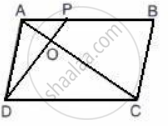
In parallelogram ABCD, P is the mid-point of AB. CP and BD intersect each other at point O. If the area of ΔPOB = 40 cm2, and OP: OC = 1:2, find:
(i) Areas of ΔBOC and ΔPBC
(ii) Areas of ΔABC and parallelogram ABCD.
Show that:
The ratio of the areas of two triangles on the same base is equal to the ratio of their heights.
