Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Can two states of an ideal gas be connected by an isothermal process as well as an adiabatic process?
उत्तर
For two states to be connected by an isothermal process,
P1V1 = P2V2 ... (i)
For the same two states to be connected by an adiabatic process,
P1V1γ = P2V2γ ...(ii)
If both the equations hold simultaneously then, on dividing eqaution (ii) by (i) we get
V1γ-1 = V2γ-1
Let the gas be monatomic. Then,
γ =`5/3`
`=> "V"_1^ (2/3)= "V"_2^(2/3)`
⇒ V1 = V2
If this condition is met, then the two states can be connected by an isothermal as well as an adiabatic process.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A metre long narrow bore held horizontally (and closed at one end) contains a 76 cm long mercury thread, which traps a 15 cm column of air. What happens if the tube is held vertically with the open end at the bottom?
Given below are densities of some solids and liquids. Give rough estimates of the size of their atoms:
| Substance | Atomic Mass (u) | Density (103 Kg m-3) |
| Carbon (diamond) | 12.01 | 2.22 |
| Gold | 197.00 | 19.32 |
| Nitrogen (liquid) | 14.01 | 1.00 |
| Lithium | 6.94 | 0.53 |
| Fluorine (liquid) | 19.00 | 1.14 |
[Hint: Assume the atoms to be ‘tightly packed’ in a solid or liquid phase, and use the known value of Avogadro’s number. You should, however, not take the actual numbers you obtain for various atomic sizes too literally. Because of the crudeness of the tight packing approximation, the results only indicate that atomic sizes are in the range of a few Å].
Does a solid also have two kinds of molar heat capacities Cp and Cv? If yes, is Cp > Cv? Or is Cp − Cv = R?
In a real gas, the internal energy depends on temperature and also on volume. The energy increases when the gas expands isothermally. Examining the derivation of Cp − Cv = R, find whether Cp − Cv will be more than R, less than R or equal to R for a real gas.
Show that the slope of the p−V diagram is greater for an adiabatic process compared to an isothermal process.
In an isothermal process on an ideal gas, the pressure increases by 0.5%. The volume decreases by about
Two samples A and B are initially kept in the same state. Sample A is expanded through an adiabatic process and the sample B through an isothermal process. The final volumes of the samples are the same. The final pressures in A and B are pA and pBrespectively.
Let ∆Wa and ∆Wb be the work done by the systems A and B, respectively, in the previous question.
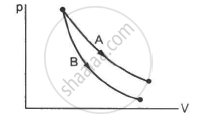
Consider the processes A and B shown in the figure. It is possible that
An ideal gas expands from 100 cm3 to 200 cm3 at a constant pressure of 2.0 × 105 Pa when 50 J of heat is supplied to it. Calculate (a) the change in internal energy of the gas (b) the number of moles in the gas if the initial temperature is 300 K (c) the molar heat capacity Cp at constant pressure and (d) the molar heat capacity Cv at constant volume.
In Joly's differential steam calorimeter, 3 g of an ideal gas is contained in a rigid closed sphere at 20°C. The sphere is heated by steam at 100°C and it is found that an extra 0.095 g of steam has condensed into water as the temperature of the gas becomes constant. Calculate the specific heat capacity of the gas in J g−1 K−1. The latent heat of vaporisation of water = 540 cal g−1
Air (γ = 1.4) is pumped at 2 atm pressure in a motor tyre at 20°C. If the tyre suddenly bursts, what would be the temperature of the air coming out of the tyre? Neglect any mixing with the atmospheric air.
The speed of sound in hydrogen at 0°C is 1280 m s−1. The density of hydrogen at STP is 0.089 kg m−3. Calculate the molar heat capacities Cp and Cv of hydrogen.
Molar specific heat of water is C = 74.7 J/mol K, its value in cal/g K is ______.
If at same temperature and pressure, the densities for two diatomic gases are respectively d1 and d2 then the ratio of velocities of sound in these gases will be ______.
