Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
D, E, and F are the mid-points of the sides AB, BC and CA of an isosceles ΔABC in which AB = BC.
Prove that ΔDEF is also isosceles.
उत्तर
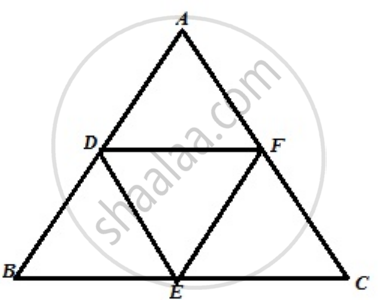
DF =
DE =
EF =
EF =
From equation (i) & (ii)
DF = EF
Hence, DEF is also isosceles triangle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
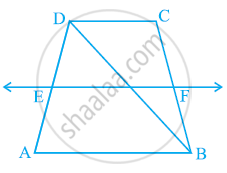
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC, BD is a diagonal and E is the mid-point of AD. A line is drawn through E parallel to AB intersecting BC at F (see the given figure). Show that F is the mid-point of BC.
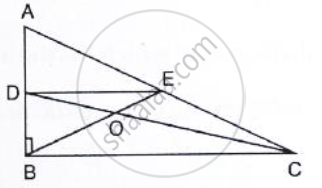
In Fig. below, triangle ABC is right-angled at B. Given that AB = 9 cm, AC = 15 cm and D,
E are the mid-points of the sides AB and AC respectively, calculate
(i) The length of BC (ii) The area of ΔADE.
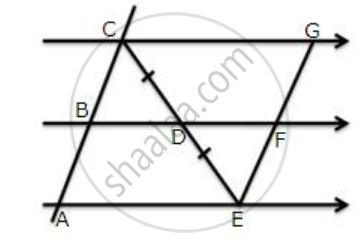
ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AD = BC. E, F, G and H are the mid-points of AB, BD, CD and Ac respectively. Prove that EFGH is a rhombus.

Use the following figure to find:
(i) BC, if AB = 7.2 cm.
(ii) GE, if FE = 4 cm.
(iii) AE, if BD = 4.1 cm
(iv) DF, if CG = 11 cm.
ABCD is a kite in which BC = CD, AB = AD. E, F and G are the mid-points of CD, BC and AB respectively. Prove that: The line drawn through G and parallel to FE and bisects DA.
In ΔABC, D, E and F are the midpoints of AB, BC and AC.
Show that AE and DF bisect each other.
In ΔABC, D, E and F are the midpoints of AB, BC and AC.
If AE and DF intersect at G, and M and N are the midpoints of GB and GC respectively, prove that DMNF is a parallelogram.
In ΔABC, the medians BE and CD are produced to the points P and Q respectively such that BE = EP and CD = DQ. Prove that: Q A and P are collinear.
In AABC, D and E are two points on the side AB such that AD = DE = EB. Through D and E, lines are drawn parallel to BC which meet the side AC at points F and G respectively. Through F and G, lines are drawn parallel to AB which meet the side BC at points M and N respectively. Prove that BM = MN = NC.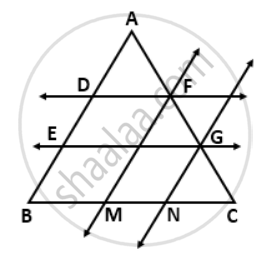
P, Q, R and S are respectively the mid-points of the sides AB, BC, CD and DA of a quadrilateral ABCD such that AC ⊥ BD. Prove that PQRS is a rectangle.
