Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Depict the equipotential surfaces for a system of two identical positive point charges placed a distance(d) apart?
उत्तर
An equipotential surface is a surface with a constant value of the potential at all points on the surface.
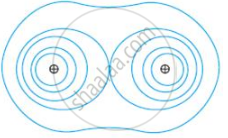
Equipotential surfaces for two identical positive charges.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The top of the atmosphere is at about 400 kV with respect to the surface of the earth, corresponding to an electric field that decreases with altitude. Near the surface of the earth, the field is about 100 Vm−1. Why then do we not get an electric shock as we step out of our house into the open? (Assume the house to be a steel cage so there is no field inside!)
What is the geometrical shape of equipotential surfaces due to a single isolated charge?
Define equipotential surface.
Statement - 1: For practical purpose, the earth is used as a reference at zero potential in electrical circuits.
Statement - 2: The electrical potential of a sphere of radius R with charge Q uniformly distributed on the surface is given by `Q/(4piepsilon_0R)`.
Assertion: Electric field is discontinuous across the surface of a spherical charged shell.
Reason: Electric potential is continuous across the surface of a spherical charged shell.
The diagrams below show regions of equipotentials.
(i) |
(ii)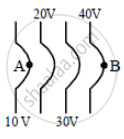 |
(iii) |
(iv) |
A positive charge is moved from A to B in each diagram.
Equipotential surfaces ______.
Which of the following is NOT the property of equipotential surface?
The work done to move a charge along an equipotential from A to B ______.
- cannot be defined as `- int_A^B E.dl`
- must be defined as `- int_A^B E.dl`
- is zero.
- can have a non-zero value.
Draw equipotential surfaces for (i) an electric dipole and (ii) two identical positive charges placed near each other.
