Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram for concave mirror when the object is between centre of curvature and focus.
उत्तर
When the object is between the centre of curvature and the focus of a concave mirror

Here, Object AB is kept between C and F
First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis
So, it passes through focus after reflection
We draw another ray which passes through Center of Curvature
So, the ray will go back along the same path after reflection
Where both reflected rays meet is point A'
And the image formed is A'B'
This image is formed between beyong Center(C)
We can say that
Image is in Front of the mirror (Real image)
Image is Inverted
Image is larger than the object (Magnified)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An object of height 5 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 10 cm. If the distance of the object from the optical centre of the lens is 20 cm, determine the position, nature and size of the image formed using the lens formula.
State two positions in which a concave mirror produces a magnified image of a given object. List two differences between the two images.
Draw ray diagrams to show the principal focus of a concave mirror.
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of light which are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the nature and position of the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm.
List four specific characteristics of the images of the objects formed by convex mirrors.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification −1 on a screen placed at a distance of 40 cm from the mirror:
(i) Write the type of mirror.
(ii) What is the nature of the image formed?
(iii) How far is the object located from the mirror?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror. Mark the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
Name the mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
Which type of mirror is used by a dentist?
For what position of an object, a concave mirror forms a real image equal in size to the object?
Which mirror is used as a torch reflector? Draw a labelled diagram to show how a torch reflector can be used to produce a parallel beam of light. Where is the bulb placed in relation to the torch reflector?
With the help of a labelled ray diagram, describe how a converging mirror can be used to give an enlarged upright image of an object.
Draw ray-diagrams to show the formation of images when the object is places in front of a concave mirror (converging mirror):
(i) between its pole and focus
(ii) between its centre of curvature and focus
A concave mirror has a focal length of 25 cm. At which of the following distance should a person hold his face from this concave mirror so that it may act as a shaving mirror?
(a) 45 cm
(b) 20 cm
(c) 25 cm
(d) 30 cm
Give reason for your choice.
Describe the nature of image formed when the object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
State two characteristics of the image formed.
If an object of 10 cm height is placed at a distance of 36 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm, find the position, nature and height of the image.
An object 3 cm high is placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror which produces a virtual image 4.5 cm high:
(i) What is the focal length of the mirror?
(ii) What is the position of image?
(iii) Draw a ray-diagram to show the formation of image.
How far should an object be placed from the pole of a converging mirror of focal length 20cm to form a real image of the size exactly `1/4`th the size of the object?
At what distance from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm should an object be placed so that:
its virtual image is formed 20 cm from the mirror?
With the help of a labelled diagram, explain how a concave lens diverges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the concave lens on the diagram.
If the radius of curvature of a concave mirror is 20 cm, its focal length is:
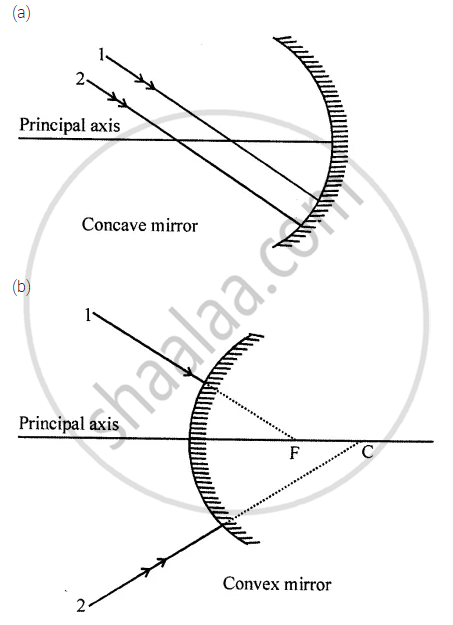
Complete the following diagrams in figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2 if F is the focus and C is the centre of curvature.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed between the pole and focus of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed on the principal axis of a convex mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image. What happens to the image as the object is moved away from the mirror?
To construct ray diagram we use two light rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection. Use these rays to locate the image of an object placed between centre of curvature and focus of a concave mirror.
A _____________ mirror is used by a dentist.
List four characteristics of the image formed by a concave mirror of focal length 40 cm when the object is placed in front of it at a distance of 20 cm from its pole.
Give any two applications of a concave and convex mirror.
State whether true or false. If false, correct the statement.
When an object is at the centre of curvature of concave mirror the image formed will be virtual and erect.
A 10 mm long awl pin is placed vertically in front of a concave mirror. A 5 mm long image of the awl pin is formed at 30 cm in front of the mirror. The focal length of this mirror is ______.
Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
The mirror having reflection surface curved outward ______.
The image formed by concave mirror is real, inverted and of the same size as that of the object. The position of object should be ______.
______ mirrors make things look larger when objects are placed close to them.
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Floodlights
