Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram for concave mirror when the object is between centre of curvature and focus.
उत्तर
When the object is between the centre of curvature and the focus of a concave mirror

Here, Object AB is kept between C and F
First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis
So, it passes through focus after reflection
We draw another ray which passes through Center of Curvature
So, the ray will go back along the same path after reflection
Where both reflected rays meet is point A'
And the image formed is A'B'
This image is formed between beyong Center(C)
We can say that
Image is in Front of the mirror (Real image)
Image is Inverted
Image is larger than the object (Magnified)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
"A concave mirror of focal length 15 cm can form a magnified, erect as well as inverted image of an object placed in front of it." Justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror in both the cases for obtaining the images.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the refracted ray in each of the following cases:-
A ray of light incident on a concave lens is
(i) passing through its optical centre.
(ii) parallel to its principal axis.
(iii) directed towards its principal focus.
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
Will the image be smaller or larger than the object? Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case.
A student has obtained the image of a distant object with a concave mirror to determine its focal length. If he has selected a well-illuminated red building as object, which of the following correctly describes the features of the image formed?
(A) Virtual, inverted and diminished image in red shade
(B) Real, erect and diminished image in pink shade
(C) Real, inverted and diminished image in red shade
(D) Virtual, erect and enlarged image in red shade
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror. Mark the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
Name the mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a focal length of -15 cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be ______.
A ray of light is incident on a plane mirror making an angle of 90° with the mirror surface. The angle of reflection for this ray of light will be:
(a) 45°
(b) 90°
(c) 0°
(d) 60°
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Parallel rays of light are reflected by a concave mirror to a point called the ..........
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The focal length of a concave mirror is the distance from the ......... to the mirror.
Which kind of mirror is used in the headlights of a car? Why is it used for this purpose?
State where an object must be placed so that the image formed by a concave mirror is:
(b) at infinity.
(c) the same size as the object.
The real image formed by a concave mirror is larger than the object when object is:
(a) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
(b) at a distance less than the focal length
(c) between focus and centre of curvature
(d) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
The real image formed by a concave mirror is smaller than the object if the object is:
(a) between centre of curvature and focus
(b) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
(c) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
(d) at a distance equal to focal length
According to the "New Cartesian Singh Convention" for mirrors, what sign has been given to the focal length of:
a convex mirror?
According to New Cartesian Sign Convention:
(a) focal length of concave mirror is positive and that of convex mirror is negative
(b) focal length of both concave and convex mirrors is positive
(c) focal length of both concave and convex mirrors is negative
(d) focal length of concave mirror is negative and that of convex mirror is positive
Describe the nature of image formed when the object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm
At what distance from a concave mirror focal length 10 cm should an object 2 cm long be placed in order to get an erect image 6 cm tall?
A converging mirror forms a real image of height 4 cm of an object of height 1 cm placed 20 cm away from the mirror:
- Calculate the image distance.
- What is the focal length of the mirror?
A concave mirror has a focal length of 4 cm and an object 2 cm tall is placed 9 cm away from it. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed.
A concave mirror produces three times enlarged virtual image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Calculate the radius of curvature of the mirror.
How far should an object be placed from the pole of a converging mirror of focal length 20cm to form a real image of the size exactly `1/4`th the size of the object?
Why does a beam of light when it enters glass at an angle? Why does it not bend if it inters the glass at right angles?
In the following diagram. MM' is a concave mirror and AB is an object. Draw on your answer-sheet a ray diagram to show the formation of image of this object.
A student obtained a sharp inverted image of a distant tree on a screen placed in front of the concave mirror. He then removed the screen and tried to look into the mirror. He would now see
(A) a very blurred image on the wall opposite to the mirror
(B) an erect and magnified image of the tree in the mirror
(C) no image as the screen has been removed
(D) a highly diminished inverted image of the tree at the focus of the mirror.
A student has to determine the focal length of a concave mirror by obtaining the image of a distant object on a screen. For getting best result he should focus
(A) a distant tree or an electric pole
(B) a well-illuminated distant building
(C) well-lit grills of the nearest window
(D) a burning candle laced at the distant edge of the laboratory table
Draw the ray diagram and also state the position, the relative size and the nature of image formed by a concave mirror when the object is placed at the centre of curvature of the mirror.
A _____________ mirror is used by a dentist.
Choose the correct option from given alternative:
Consider the following properties of virtual images:
(A) cannot be projected on the screen
(B) are formed by both concave and convex lens
(C) are always erect
(D) are always inverted
The mirror used by the ophthalmologist to examine the eye is _______.
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in figure?

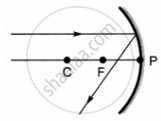 |
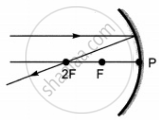 |
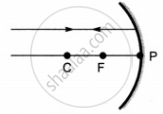 |
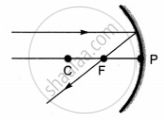 |
| A | B | C | D |
Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
In the headlights of motor vehicles, ______ mirrors are used as reflectors.
______ mirrors make things look larger when objects are placed close to them.
The image formed by a concave mirror is real, inverted and of the same size as that of the object, the position of the object should be ______.
A student took three concave mirrors of different focal lengths and performed the experiment to see the image formation by placing an object at different distance with these mirrors as shown in the following table.
| Case No. | Object-distance | Focal length |
| I | 45 cm | 20 cm |
| II | 30 cm | 15 cm |
| III | 20 cm | 30 cm |
Now answer the following questions:
(a) List two properties of the image formed in Case I.
(b) In which one of the cases given in the table, the mirror will form real image of same size and why?
(c) Name the type of mirror used by dentists. Given reason why do they use such type of mirrors.
OR
(c) Look at the table and identify the situation (object distance and focal length) which resembles the situation in which concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Floodlights
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Head lamps of a car
