Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the mechanism of cleansing action of soaps.
Explain with diagram the mechanism of the cleansing action of soaps.
उत्तर १
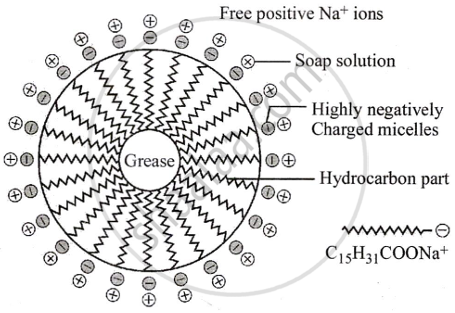
Mechanism of cleansing actum of soaps
Soap and detergents have two parts, a long chain, of hydrocarbon tail soluble in oil and other part (head) soluble in water
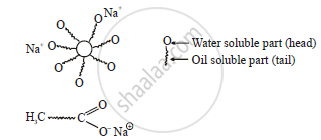
- When soap is added to an oily part of cloth as a vessel, the hydrocarbon part of the soap dissolves in oil and the ionic end of the soap dissolves in water.
- The soap molecules form micelles where one of the molecules is towards the oil droplet, while the ionic end faces outside.
- This results in an emulsion in water.
- The soap micelles assist in dissolving the dirt in water. Thus we can wash our clothes.
उत्तर २
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain cationic detergents.
Write the chemical equation for preparing sodium soap from Glyceryl palmitate . Structural formulae of the compounds are given below.
(C15H31COO)3C3H5 – Glyceryl palmitate
Write the chemical equation for preparing sodium soap from glyceryl oleate . Structural formulae of the compounds are given below.
(C17H32COO)3C3H5 – Glyceryl oleate
Why do soaps not work in hard water?
Can you use soaps and synthetic detergents to check the hardness of water?
Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
Write balanced chemical equations for the action of hydrogen bromide on styrene in the presence of a peroxide
Write balanced chemical equations for the action of methyl bromide on silver propanoate
How soap is prepared?
Glycerol is added to soap. It functions ______.
If soap has high alkali content it irritates skin. How can the amount of excess alkali be determined? What can be the source of excess alkali?
What is the difference between bathing soap and washing soaps?
How are transparent soaps manufactured?
What are fillers and what role these fillers play in soap?
Match the soaps given in Column I with items given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Soap chips | (a) dried miniature soap bubbles |
| (ii) Soap granules | (b) small broken pieces of soap formed from melted soaps |
| (iii) Soap powder | (c) soap powder + abrasives + builders \[\ce{(Na2CO3,Na3PO4)}\] |
| (iv) Scouring soap | (d) soap powder + builders like \[\ce{Na2CO3}\] and \[\ce{Na3PO4}\] |
Match the detergents given in Column I with their uses given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
(i) 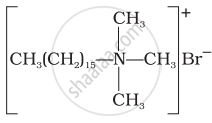 |
(a) Dishwashing powder |
(ii) 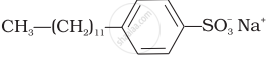 |
(b) Laundry soap |
| (iii) \[\ce{C17H33CO\overset{-}{O}\overset{+}{N}a + Na2CO3 + Rosin}\] | (c) Hair conditioners |
| (iv) \[\ce{CH3(CH2)16COO(CH2CH2O)nCH2CH2OH}\] | (d) Toothpaste |
Assertion: Transparent soaps are made by dissolving soaps in ethanol.
Reason: Ethanol makes things invisible.
Assertion: Sodium chloride is added to precipitate soap after saponification.
Reason: Hydrolysis of esters of long-chain fatty acids by alkali produces soap in colloidal form.
Which of the following is not a correct statement?
Green chemistry in day-to-day life is in the use of ______.
