Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
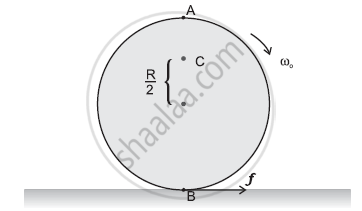
Explain why friction is necessary to make the disc in Figure roll in the direction indicated
(a) Give the direction of frictional force at B, and the sense of frictional torque, before perfect rolling begins.
(b) What is the force of friction after perfect rolling begins?
उत्तर १
A torque is required to roll the given disc. As per the definition of torque, the rotating force should be tangential to the disc. Since the frictional force at point B is along the tangential force at point A, a frictional force is required for making the disc roll.
(a) Force of friction acts opposite to the direction of velocity at point B. The direction of linear velocity at point B is tangentially leftward. Hence, frictional force will act tangentially rightward. The sense of frictional torque before the start of perfect rolling is perpendicular to the plane of the disc in the outward direction.
(b) Since frictional force acts opposite to the direction of velocity at point B, perfect rolling will begin when the velocity at that point becomes equal to zero. This will make the frictional force acting on the disc zero.
उत्तर २
To roll a disc, we require a torque, which can be provided only by a tangential force. As a force of friction is the only tangential force, in this case, it is necessary.
a)As frictional force at B opposes the velocity of point B, which is to the left, the frictional force must be to the right. The sense of frictional torque will be perpendicular to the plane of the disc and outwards.
(b)As frictional force at B decreases the velocity of the point of contact B with the surface, the perfect rolling begins only when a velocity of point B becomes zero. Also, force of friction would become zero at this stage.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A solid cylinder of mass 20 kg rotates about its axis with angular speed 100 rad s–1. The radius of the cylinder is 0.25 m. What is the kinetic energy associated with the rotation of the cylinder? What is the magnitude of the angular momentum of the cylinder about its axis?
The torque of a force \[\overrightarrow F \] about a point is defined as \[\overrightarrow\Gamma = \overrightarrow r \times \overrightarrow F.\] Suppose \[\overrightarrow r, \overrightarrow F\] and \[\overrightarrow \Gamma\] are all nonzero. Is \[r \times \overrightarrow\Gamma || \overrightarrow F\] always true? Is it ever true?
A flywheel of moment of inertia 5⋅0 kg-m2 is rotated at a speed of 60 rad/s. Because of the friction at the axle it comes to rest in 5⋅0 minutes. Find (a) the average torque of the friction (b) the total work done by the friction and (c) the angular momentum of the wheel 1 minute before it stops rotating.
What are the conditions in which force can not produce torque?
A Merry-go-round, made of a ring-like platform of radius R and mass M, is revolving with angular speed ω. A person of mass M is standing on it. At one instant, the person jumps off the round, radially away from the centre of the round (as seen from the round). The speed of the round afterwards is ______.
The net external torque on a system of particles about an axis is zero. Which of the following are compatible with it?
- The forces may be acting radially from a point on the axis.
- The forces may be acting on the axis of rotation.
- The forces may be acting parallel to the axis of rotation.
- The torque caused by some forces may be equal and opposite to that caused by other forces.
A uniform cube of mass m and side a is placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. A vertical force F is applied to the edge as shown in figure. Match the following (most appropriate choice):
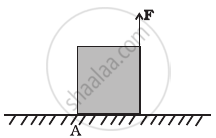
| (a) mg/4 < F < mg/2 | (i) Cube will move up. |
| (b) F > mg/2 | (ii) Cube will not exhibit motion. |
| (c) F > mg | (iii) Cube will begin to rotate and slip at A. |
| (d) F = mg/4 | (iv) Normal reaction effectively at a/3 from A, no motion. |
A rod of mass 'm' hinged at one end is free to rotate in a horizontal plane. A small bullet of mass m/4 travelling with speed 'u' hits the rod and attaches to it at its centre. Find the angular speed of rotation of rod just after the bullet hits the rod 3. [take length of the rod as 'l']
Angular momentum of a single particle moving with constant speed along the circular path ______.
A solid sphere is rotating in free space. If the radius of the sphere is increased while keeping the mass the same, which one of the following will not be affected?
