Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distributions:
| xi : | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| pi : | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.3 |
उत्तर
| xi | pi | pixi | pixi2 |
| 2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.8 |
| 3 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 4.5 |
| 4 | 0.3 | 1.2 | 4.8 |
| `∑`pixi = 3.1
|
`∑`pixi2 = 10.1
|
\[\text{ Mean } = \sum p_i x_i = 3 . 1\]
\[\text{ Variance} = \sum p_i {x_i}^2 - \left( \text{ Mean} \right)^2 \]
\[ = 10 . 1 - \left( 3 . 1 \right)^2 \]
\[ = 10 . 1 - 9 . 61\]
\[ = 0 . 49\]
\[\text{ Step Deviation } = \sqrt{\text{ Variance}}\]
\[ = \sqrt{0 . 49}\]
\[ = 0 . 7\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
then E(X)=....................
State the following are not the probability distributions of a random variable. Give reasons for your answer.
| Y | -1 | 0 | 1 |
| P(Y) | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
An urn contains 5 red and 2 black balls. Two balls are randomly drawn. Let X represents the number of black balls. What are the possible values of X? Is X a random variable?
Find the probability distribution of number of heads in two tosses of a coin.
There are 4 cards numbered 1, 3, 5 and 7, one number on one card. Two cards are drawn at random without replacement. Let X denote the sum of the numbers on the two drawn cards. Find the mean 'and variance of X.
There are 4 cards numbered 1 to 4, one number on one card. Two cards are drawn at random without replacement. Let X denote the sum of the numbers on the two drawn cards. Find the mean and variance of X.
Find the probability distribution of the number of doublets in four throws of a pair of dice. Also find the mean and variance of this distribution.
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| Values of X : | −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P (X) : | 0.1 | k | 0.2 | 2k | 0.3 | k |
Find the value of k.
Two cards are drawn from a well shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of aces.
Find the probability distribution of the number of heads, when three coins are tossed.
Five defective mangoes are accidently mixed with 15 good ones. Four mangoes are drawn at random from this lot. Find the probability distribution of the number of defective mangoes.
Two dice are thrown together and the number appearing on them noted. X denotes the sum of the two numbers. Assuming that all the 36 outcomes are equally likely, what is the probability distribution of X?
An urn contains 4 red and 3 blue balls. Find the probability distribution of the number of blue balls in a random draw of 3 balls with replacement.
Let X represent the difference between the number of heads and the number of tails when a coin is tossed 6 times. What are the possible values of X?
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k |
\[\frac{k}{2}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{8}\]
|
Determine P(X ≤ 2) and P(X > 2) .
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution:
| xi : | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| pi: | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution:
| xi : | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| pi : | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
Two cards are selected at random from a box which contains five cards numbered 1, 1, 2, 2, and 3. Let X denote the sum and Y the maximum of the two numbers drawn. Find the probability distribution, mean and variance of X and Y.
Three cards are drawn at random (without replacement) from a well shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of number of red cards. Hence, find the mean of the distribution .
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| X : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| P (X) : | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.05 |
For the events E = {X : X is a prime number}, F = {X : X < 4}, the probability P (E ∪ F) is
A random variable X takes the values 0, 1, 2, 3 and its mean is 1.3. If P (X = 3) = 2 P (X = 1) and P (X = 2) = 0.3, then P (X = 0) is
Find the probability distribution of the number of doublets in three throws of a pair of dice and find its mean.
Verify whether the following function can be regarded as probability mass function (p.m.f.) for the given values of X :
| X | -1 | 0 | 1 |
| P(X = x) | -0.2 | 1 | 0.2 |
A card is drawn at random and replaced four times from a well shuftled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that -
(a) Two diamond cards are drawn.
(b) At least one diamond card is drawn.
The p.d.f. of r.v. of X is given by
f (x) = `k /sqrtx` , for 0 < x < 4 and = 0, otherwise. Determine k .
Determine c.d.f. of X and hence P (X ≤ 2) and P(X ≤ 1).
In a multiple choice test with three possible answers for each of the five questions, what is the probability of a candidate getting four or more correct answers by random choice?
Solve the following problem :
If a fair coin is tossed 4 times, find the probability that it shows 3 heads
Solve the following problem :
If a fair coin is tossed 4 times, find the probability that it shows head in the first 2 tosses and tail in last 2 tosses.
Find the probability distribution of the number of successes in two tosses of a die, where a success is defined as six appears on at least one die
Let X be a discrete random variable. The probability distribution of X is given below:
| X | 30 | 10 | – 10 |
| P(X) | `1/5` | `3/10` | `1/2` |
Then E(X) is equal to ______.
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k | `"k"/2` | `"k"/4` | `"k"/8` |
Determine P(X ≤ 2) and P(X > 2)
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k | `"k"/2` | `"k"/4` | `"k"/8` |
Find P(X ≤ 2) + P (X > 2)
Let X be a discrete random variable whose probability distribution is defined as follows:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"(x + 1), "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3"," 4),(2"k"x, "for" x = 5"," 6"," 7),(0, "Otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate Standard deviation of X.
Find the probability distribution of the number of successes in two toves of a die where a success is define as:- Six appeared on at least one die.
Box I contains 30 cards numbered 1 to 30 and Box II contains 20 cards numbered 31 to 50. A box is selected at random and a card is drawn from it. The number on the card is found to be a nonprime number. The probability that the card was drawn from Box I is ______.
Two numbers are selected from first six even natural numbers at random without replacement. If X denotes the greater of two numbers selected, find the probability distribution of X.
A primary school teacher wants to teach the concept of 'larger number' to the students of Class II.
To teach this concept, he conducts an activity in his class. He asks the children to select two numbers from a set of numbers given as 2, 3, 4, 5 one after the other without replacement.
All the outcomes of this activity are tabulated in the form of ordered pairs given below:
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| 2 | (2, 2) | (2, 3) | (2, 4) | |
| 3 | (3, 2) | (3, 3) | (3, 5) | |
| 4 | (4, 2) | (4, 4) | (4, 5) | |
| 5 | (5, 3) | (5, 4) | (5, 5) |
- Complete the table given above.
- Find the total number of ordered pairs having one larger number.
- Let the random variable X denote the larger of two numbers in the ordered pair.
Now, complete the probability distribution table for X given below.
X 3 4 5 P(X = x) - Find the value of P(X < 5)
- Calculate the expected value of the probability distribution.
Five numbers x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 are randomly selected from the numbers 1, 2, 3, ......., 18 and are arranged in the increasing order such that x1 < x2 < x3 < x4 < x5. What is the probability that x2 = 7 and x4 = 11?
Kiran plays a game of throwing a fair die 3 times but to quit as and when she gets a six. Kiran gets +1 point for a six and –1 for any other number.
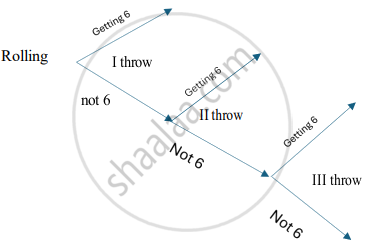
- If X denotes the random variable “points earned” then what are the possible values X can take?
- Find the probability distribution of this random variable X.
- Find the expected value of the points she gets.
