Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the following are not the probability distributions of a random variable. Give reasons for your answer.
| Y | -1 | 0 | 1 |
| P(Y) | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
उत्तर
It is known that the sum of all the probabilities in a probability distribution is one.
Sum of the probabilities = 0.6 + 0.1 + 0.2 = 0.9 ≠ 1
Therefore, the given table is not a probability distribution of random variables.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the following are not the probability distributions of a random variable. Give reasons for your answer.
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(X) | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | -0.1 | 0.3 |
Find the probability distribution of the number of successes in two tosses of a die, where a success is defined as
(i) number greater than 4
(ii) six appears on at least one die
A random variable X has the following probability distribution.
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| P(X) | 0 | k | 2k | 2k | 3k | k2 |
2k2 |
7k2 + k |
Determine
(i) k
(ii) P (X < 3)
(iii) P (X > 6)
(iv) P (0 < X < 3)
There are 4 cards numbered 1 to 4, one number on one card. Two cards are drawn at random without replacement. Let X denote the sum of the numbers on the two drawn cards. Find the mean and variance of X.
Four cards are drawn simultaneously from a well shuffled pack of 52 playing cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of aces.
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k |
\[\frac{k}{2}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{8}\]
|
Find P(X ≤ 2) + P(X > 2) .
Let, X denote the number of colleges where you will apply after your results and P(X = x) denotes your probability of getting admission in x number of colleges. It is given that
where k is a positive constant. Find the value of k. Also find the probability that you will get admission in (i) exactly one college (ii) at most 2 colleges (iii) at least 2 colleges.
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distributions:
| xi : | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| pi : | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.3 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution:
| xi : | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| pi: | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
A pair of fair dice is thrown. Let X be the random variable which denotes the minimum of the two numbers which appear. Find the probability distribution, mean and variance of X.
A fair coin is tossed four times. Let X denote the longest string of heads occurring. Find the probability distribution, mean and variance of X.
Two cards are selected at random from a box which contains five cards numbered 1, 1, 2, 2, and 3. Let X denote the sum and Y the maximum of the two numbers drawn. Find the probability distribution, mean and variance of X and Y.
If the probability distribution of a random variable X is given by Write the value of k.
| X = xi : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P (X = xi) : | 2k | 4k | 3k | k |
A random variable has the following probability distribution:
| X = xi : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P (X = xi) : | k | 2k | 3k | 4k |
Write the value of P (X ≥ 3).
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| X : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| P (X) : | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.05 |
For the events E = {X : X is a prime number}, F = {X : X < 4}, the probability P (E ∪ F) is
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let X be a discrete random variable. Then the variance of X is
Demand function x, for a certain commodity is given as x = 200 - 4p where p is the unit price. Find :
(a) elasticity of demand as function of p.
(b) elasticity of demand when p = 10 , interpret your result.
Verify the following function, which can be regarded as p.m.f. for the given values of X :
| X = x | -1 | 0 | 1 |
| P(x) | -0.2 | 1 | 0.2 |
Three different aeroplanes are to be assigned to carry three cargo consignments with a view to maximize profit. The profit matrix (in lakhs of ₹) is as follows :
| Aeroplanes | Cargo consignments | ||
| C1 | C2 | C3 | |
| A1 | 1 | 4 | 5 |
| A2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| A3 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
How should the cargo consignments be assigned to the aeroplanes to maximize the profit?
The expenditure Ec of a person with income I is given by Ec = (0.000035) I2 + (0. 045) I. Find marginal propensity to consume (MPC) and average propensity to consume (APC) when I = 5000.
The p.m.f. of a random variable X is
`"P"(x) = 1/5` , for x = I, 2, 3, 4, 5
= 0 , otherwise.
Find E(X).
Solve the following:
Identify the random variable as either discrete or continuous in each of the following. Write down the range of it.
A highway safety group is interested in studying the speed (km/hrs) of a car at a check point.
The p.d.f. of a continuous r.v. X is given by
f (x) = `1/ (2a)` , for 0 < x < 2a and = 0, otherwise. Show that `P [X < a/ 2] = P [X >( 3a)/ 2]` .
A random variable X has the following probability distribution :
| x = x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 7 | |||
| P(X=x) | 0 | k | 2k | 2k | 3k | k2 | 2k2 | 7k2 + k |
Determine (i) k
(ii) P(X> 6)
(iii) P(0<X<3).
Determine whether each of the following is a probability distribution. Give reasons for your answer.
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| P(x) | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
There are 10% defective items in a large bulk of items. What is the probability that a sample of 4 items will include not more than one defective item?
Solve the following problem :
Following is the probability distribution of a r.v.X.
| x | – 3 | – 2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X = x) | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.1 |
Find the probability that X is even.
Solve the following problem :
If a fair coin is tossed 4 times, find the probability that it shows 3 heads
Solve the following problem :
A computer installation has 3 terminals. The probability that any one terminal requires attention during a week is 0.1, independent of other terminals. Find the probabilities that 1 terminal requires attention during a week.
Find the probability distribution of the number of successes in two tosses of a die, where a success is defined as six appears on at least one die
A discrete random variable X has the probability distribution given as below:
| X | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
| P(X) | k | k2 | 2k2 | k |
Determine the mean of the distribution.
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k | `"k"/2` | `"k"/4` | `"k"/8` |
Find P(X ≤ 2) + P (X > 2)
Two probability distributions of the discrete random variable X and Y are given below.
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | `1/5` | `2/5` | `1/5` | `1/5` |
| Y | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(Y) | `1/5` | `3/10` | `2/10` | `1/10` |
Prove that E(Y2) = 2E(X).
Let X be a discrete random variable whose probability distribution is defined as follows:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"(x + 1), "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3"," 4),(2"k"x, "for" x = 5"," 6"," 7),(0, "Otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate Standard deviation of X.
The probability distribution of a random variable x is given as under:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"x^2, "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3),(2"k"x, "for" x = 4"," 5"," 6),(0, "otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate E(3X2)
A random variable x has to following probability distribution.
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| P(x) | 0 | k | 2k | 2k | 3k | k2 | 2k2 | 7k2 + k |
Determine
Box I contains 30 cards numbered 1 to 30 and Box II contains 20 cards numbered 31 to 50. A box is selected at random and a card is drawn from it. The number on the card is found to be a nonprime number. The probability that the card was drawn from Box I is ______.
Five numbers x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 are randomly selected from the numbers 1, 2, 3, ......., 18 and are arranged in the increasing order such that x1 < x2 < x3 < x4 < x5. What is the probability that x2 = 7 and x4 = 11?
Kiran plays a game of throwing a fair die 3 times but to quit as and when she gets a six. Kiran gets +1 point for a six and –1 for any other number.
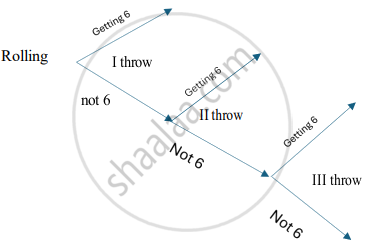
- If X denotes the random variable “points earned” then what are the possible values X can take?
- Find the probability distribution of this random variable X.
- Find the expected value of the points she gets.
