Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The p.d.f. of a continuous r.v. X is given by
f (x) = `1/ (2a)` , for 0 < x < 2a and = 0, otherwise. Show that `P [X < a/ 2] = P [X >( 3a)/ 2]` .
उत्तर
P (`X< a /2`) = ` int_(-∞)^(a/2) f (x) dx`
=` int_(-∞)^0 f (x) dx+ int_(-∞)^(a/2) f (x) dx`
= 0+ ` int_(0)^(a/2) 1/(2a) dx`
= `1/(2a) int_(0)^(a/2) 1 dx = 1/(2a)[x]_0^(a/2)`
= `1/(2a) [a/2-0] = 1/4` .......(1)
P `[X >( 3a)/ 2] = int_((3a)/2)^(∞) f(x) dx`
= `int_((3a)/2)^(*2a) f(x) dx + int_(2a)^(∞) f(x) dx`
= `int_((3a)/2)^(2a) 1/(2a) dx + 0`
= `1/(2a) int_((3a)/2)^(2a) 1 dx = 1/(2a)[x]_((3a)/2)^(2a)`
= `1/(2a)[2a-(3a)/2] = 1/(2a)(a/2) = 1/4` ......(2)
From (1) and (2), we get
`P [X < a/ 2] = P [X >( 3a)/ 2]`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
From a lot of 25 bulbs of which 5 are defective a sample of 5 bulbs was drawn at random with replacement. Find the probability that the sample will contain -
(a) exactly 1 defective bulb.
(b) at least 1 defective bulb.
State the following are not the probability distributions of a random variable. Give reasons for your answer.
| Y | -1 | 0 | 1 |
| P(Y) | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
An urn contains 5 red and 2 black balls. Two balls are randomly drawn. Let X represents the number of black balls. What are the possible values of X? Is X a random variable?
Find the probability distribution of number of heads in two tosses of a coin.
From a lot of 30 bulbs which include 6 defectives, a sample of 4 bulbs is drawn at random with replacement. Find the probability distribution of the number of defective bulbs.
Two numbers are selected at random (without replacement) from the first six positive integers. Let X denotes the larger of the two numbers obtained. Find E(X).
A random variable X ~ N (0, 1). Find P(X > 0) and P(X < 0).
Let, X denote the number of colleges where you will apply after your results and P(X = x) denotes your probability of getting admission in x number of colleges. It is given that
where k is a positive constant. Find the value of k. Also find the probability that you will get admission in (i) exactly one college (ii) at most 2 colleges (iii) at least 2 colleges.
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| Values of X : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| P (X) : | a | 3a | 5a | 7a | 9a | 11a | 13a | 15a | 17a |
Determine:
(i) The value of a
(ii) P (X < 3), P (X ≥ 3), P (0 < X < 5).
The probability distribution function of a random variable X is given by
| xi : | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| pi : | 3c3 | 4c − 10c2 | 5c-1 |
where c > 0 Find: P (1 < X ≤ 2)
Let X be a random variable which assumes values x1, x2, x3, x4 such that 2P (X = x1) = 3P(X = x2) = P (X = x3) = 5 P (X = x4). Find the probability distribution of X.
Two cards are drawn from a well shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of aces.
Two dice are thrown together and the number appearing on them noted. X denotes the sum of the two numbers. Assuming that all the 36 outcomes are equally likely, what is the probability distribution of X?
Two cards are drawn successively with replacement from well shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of aces.
Two cards are drawn simultaneously from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of successes, when getting a spade is considered a success.
From a lot of 10 bulbs, which includes 3 defectives, a sample of 2 bulbs is drawn at random. Find the probability distribution of the number of defective bulbs.
Four balls are to be drawn without replacement from a box containing 8 red and 4 white balls. If X denotes the number of red balls drawn, then find the probability distribution of X.
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distributions:
| xi : | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| pi : | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.3 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution :
| xi : | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| pi : | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution :
| xi : | -3 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| pi : | 0.05 | 0.45 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.05 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution :
| xi : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| pi : |
\[\frac{1}{6}\]
|
\[\frac{5}{18}\]
|
\[\frac{2}{9}\]
|
\[\frac{1}{6}\]
|
\[\frac{1}{9}\]
|
\[\frac{1}{18}\]
|
A pair of fair dice is thrown. Let X be the random variable which denotes the minimum of the two numbers which appear. Find the probability distribution, mean and variance of X.
A fair die is tossed. Let X denote 1 or 3 according as an odd or an even number appears. Find the probability distribution, mean and variance of X.
A fair coin is tossed four times. Let X denote the longest string of heads occurring. Find the probability distribution, mean and variance of X.
In a game, a man wins Rs 5 for getting a number greater than 4 and loses Rs 1 otherwise, when a fair die is thrown. The man decided to thrown a die thrice but to quit as and when he gets a number greater than 4. Find the expected value of the amount he wins/loses.
A random variable has the following probability distribution:
| X = xi : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| P (X = xi) : | 0 | 2 p | 2 p | 3 p | p2 | 2 p2 | 7 p2 | 2 p |
The value of p is
If X is a random-variable with probability distribution as given below:
| X = xi : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P (X = xi) : | k | 3 k | 3 k | k |
The value of k and its variance are
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let X be a discrete random variable. Then the variance of X is
For the following probability density function (p. d. f) of X, find P(X < 1) and P(|x| < 1)
`f(x) = x^2/18, -3 < x < 3`
= 0, otherwise
Using the truth table verify that p ∨ (q ∧ r) ≡ (p ∨ q) ∧ (p ∨ r).
The following data gives the marks of 20 students in mathematics (X) and statistics (Y) each out of 10, expressed as (x, y). construct ungrouped frequency distribution considering single number as a class :
(2, 7) (3, 8) (4, 9) (2, 8) (2, 8) (5, 6) (5 , 7) (4, 9) (3, 8) (4, 8) (2, 9) (3, 8) (4, 8) (5, 6) (4, 7) (4, 7) (4, 6 ) (5, 6) (5, 7 ) (4, 6 )
Find mean and standard deviation of the continuous random variable X whose p.d.f. is given by f(x) = 6x(1 - x);= (0); 0 < x < 1(otherwise)
A fair coin is tossed 12 times. Find the probability of getting at least 2 heads .
Alex spends 20% of his income on food items and 12% on conveyance. If for the month of June 2010, he spent ₹900 on conveyance, find his expenditure on food items during the same month.
The p.m.f. of a random variable X is
`"P"(x) = 1/5` , for x = I, 2, 3, 4, 5
= 0 , otherwise.
Find E(X).
Amit and Rohit started a business by investing ₹20,000 each. After 3 months Amit withdrew ₹5,000 and Rohit put in ₹5,000 additionally. How should a profit of ₹12,800 be divided between them at the end of the year?
A card is drawn at random and replaced four times from a well shuftled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that -
(a) Two diamond cards are drawn.
(b) At least one diamond card is drawn.
The p.d.f. of r.v. of X is given by
f (x) = `k /sqrtx` , for 0 < x < 4 and = 0, otherwise. Determine k .
Determine c.d.f. of X and hence P (X ≤ 2) and P(X ≤ 1).
Determine whether each of the following is a probability distribution. Give reasons for your answer.
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| P(x) | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
Determine whether each of the following is a probability distribution. Give reasons for your answer.
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| P(x) | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
A sample of 4 bulbs is drawn at random with replacement from a lot of 30 bulbs which includes 6 defective bulbs. Find the probability distribution of the number of defective bulbs.
A coin is biased so that the head is 3 times as likely to occur as tail. Find the probability distribution of number of tails in two tosses.
A die is thrown 4 times. If ‘getting an odd number’ is a success, find the probability of at most 2 successes.
The probability that a bulb produced by a factory will fuse after 200 days of use is 0.2. Let X denote the number of bulbs (out of 5) that fuse after 200 days of use. Find the probability of X ≤ 1
The probability that a bulb produced by a factory will fuse after 200 days of use is 0.2. Let X denote the number of bulbs (out of 5) that fuse after 200 days of use. Find the probability of (i) X = 0, (ii) X ≤ 1, (iii) X > 1, (iv) X ≥ 1.
10 balls are marked with digits 0 to 9. If four balls are selected with replacement. What is the probability that none is marked 0?
Defects on plywood sheet occur at random with the average of one defect per 50 Sq.ft. Find the probability that such a sheet has no defect
State whether the following is True or False :
If r.v. X assumes the values 1, 2, 3, ……. 9 with equal probabilities, E(x) = 5.
Solve the following problem :
Following is the probability distribution of a r.v.X.
| X | – 3 | – 2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X = x) | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.1 |
Find the probability that X is positive.
Solve the following problem :
Following is the probability distribution of a r.v.X.
| x | – 3 | – 2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X = x) | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.1 |
Find the probability that X is even.
Solve the following problem :
If a fair coin is tossed 4 times, find the probability that it shows head in the first 2 tosses and tail in last 2 tosses.
Solve the following problem :
The probability that a lamp in the classroom will burn is 0.3. 3 lamps are fitted in the classroom. The classroom is unusable if the number of lamps burning in it is less than 2. Find the probability that the classroom cannot be used on a random occasion.
Solve the following problem :
It is observed that it rains on 10 days out of 30 days. Find the probability that it rains on exactly 3 days of a week.
A random variable X has the following probability distribution
| X | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(x) | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
Then the variance of this distribution is
Find the probability distribution of the number of doublets in three throws of a pair of dice
Find the mean and variance of the number randomly selected from 1 to 15
Let X be a discrete random variable. The probability distribution of X is given below:
| X | 30 | 10 | – 10 |
| P(X) | `1/5` | `3/10` | `1/2` |
Then E(X) is equal to ______.
A discrete random variable X has the probability distribution given as below:
| X | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
| P(X) | k | k2 | 2k2 | k |
Find the value of k
Consider the probability distribution of a random variable X:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(X) | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.15 |
Calculate `"V"("X"/2)`
Consider the probability distribution of a random variable X:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(X) | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.15 |
Variance of X.
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k | `"k"/2` | `"k"/4` | `"k"/8` |
Determine P(X ≤ 2) and P(X > 2)
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k | `"k"/2` | `"k"/4` | `"k"/8` |
Find P(X ≤ 2) + P (X > 2)
The probability distribution of a discrete random variable X is given as under:
| X | 1 | 2 | 4 | 2A | 3A | 5A |
| P(X) | `1/2` | `1/5` | `3/25` | `1/10` | `1/25` | `1/25` |
Calculate: The value of A if E(X) = 2.94
The probability distribution of a discrete random variable X is given below:
| X | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| P(X) | `5/"k"` | `7/"k"` | `9/"k"` | `11/"k"` |
The value of k is ______.
A bag contains 1 red and 3 white balls. Find the probability distribution of the number of red balls if 2 balls are drawn at random from the bag one-by-one without replacement.
If the p.m.f of a r. v. X is
P(x) = `c/x^3`, for x = 1, 2, 3
= 0, otherwise
then E(X) = ______.
Box I contains 30 cards numbered 1 to 30 and Box II contains 20 cards numbered 31 to 50. A box is selected at random and a card is drawn from it. The number on the card is found to be a nonprime number. The probability that the card was drawn from Box I is ______.
Find the mean of number randomly selected from 1 to 15.
Two balls are drawn at random one by one with replacement from an urn containing equal number of red balls and green balls. Find the probability distribution of number of red balls. Also, find the mean of the random variable.
A primary school teacher wants to teach the concept of 'larger number' to the students of Class II.
To teach this concept, he conducts an activity in his class. He asks the children to select two numbers from a set of numbers given as 2, 3, 4, 5 one after the other without replacement.
All the outcomes of this activity are tabulated in the form of ordered pairs given below:
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| 2 | (2, 2) | (2, 3) | (2, 4) | |
| 3 | (3, 2) | (3, 3) | (3, 5) | |
| 4 | (4, 2) | (4, 4) | (4, 5) | |
| 5 | (5, 3) | (5, 4) | (5, 5) |
- Complete the table given above.
- Find the total number of ordered pairs having one larger number.
- Let the random variable X denote the larger of two numbers in the ordered pair.
Now, complete the probability distribution table for X given below.
X 3 4 5 P(X = x) - Find the value of P(X < 5)
- Calculate the expected value of the probability distribution.
Kiran plays a game of throwing a fair die 3 times but to quit as and when she gets a six. Kiran gets +1 point for a six and –1 for any other number.
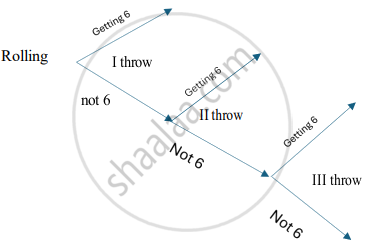
- If X denotes the random variable “points earned” then what are the possible values X can take?
- Find the probability distribution of this random variable X.
- Find the expected value of the points she gets.
