Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
From a lot of 30 bulbs which include 6 defectives, a sample of 4 bulbs is drawn at random with replacement. Find the probability distribution of the number of defective bulbs.
उत्तर १
It is given that out of 30 bulbs, 6 are defective.
⇒ Number of non-defective bulbs = 30 − 6 = 24
4 bulbs are drawn from the lot with replacement.
Let X be the random variable that denotes the number of defective bulbs in the selected bulbs.
∴ X can take the value 0, 1, 2, 3, 4.
∴ P (X = 0) = P (4 non-defective and 0 defective) = `""^4C_0 xx 4/5 xx 4/5 xx 4/5 xx 4/5 = 256/625`
P (X = 1) = P (3 non-defective and 1defective) =`""^4C_1 xx (1/5) xx (4/5)^3 = 256/625`
P (X = 2) = P (2 non-defective and 2defective) =`""^4C_2 xx (1/5)^2 xx (4/5)^2= 96/625`
P (X = 3) = P (1 non-defective and 3defective) =`""^4C_3 xx (1/5)^3xx (4/5) = 16/625`
P (X = 4) = P (0 non-defective and 4defective) =`""^4C_4 xx (1/5)^4xx (4/5)^0 = 1/625`
Therefore, the required probability distribution is as follows.
| X = x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P (X = x) | `256/625` | `256/625` | `96/625` | `16/625` | `1/625` |
उत्तर २
Here, the number of defective bulbs is the random variable.
Let the number of defective bulbs be denoted by X.
∴ X can take the value 0, 1, 2, 3, 4.
Since the draws are done with replacement, therefore the four draws are independent experiments.
Total number of bulbs is 30 which include 6 defectives.
∴ P (X = 0) = P (0) = P (all 4 non-defective bulbs)
`= 24/30 xx 24/30xx 24/30 xx 24/30 = 256/625`
P (X = 1) = P (1) = P (1 defective and 3 non-defective bulbs)
`= 6/30 xx 24/30 xx 24/30 xx 24/30 + 24/30 xx 24/30 xx 6/30 xx 24/30 + 24/30 xx 24/30 xx 6/30 xx 24/30 + 24/30 xx 24/30 xx 24/30 xx 24/30 xx 6/30 = 256/ 625`
P (X = 2) = P(2) = P (2 defective and 2 non-defective)
`= 6/30 xx 6/30 xx 24/30 xx 24/30 + 24/30 xx 6/30 xx 6/30 xx 24/30 + 24/30 xx 24/30 xx 6/30 xx6/30 + 6/30 xx 24/30 xx 6/30 xx24/30 + 6/30 xx 24/30 xx 24/30 xx 6/30 + 24/30 xx 6/30 xx 24/30 xx 6/30 = 96/625`
P (X = 3) = P (3) = P (3 defectives and 1 non-defective)
`= 6/30 xx 6/30 xx 6/30 xx 24/30 + 6/30 xx 6/30 xx ***24/30 xx6/30 + 6/30 xx 24/30 xx 6/30 xx6/30 + 24/30 xx6/30 xx6/30 xx6/30`
`= 16/625`
P (X = 4) = P (4) = P (all 4 defectives)
= `6/30 xx 6/30 xx 6/30 xx 6/30 = 1/625`
∴ The required probability distribution is
| X = x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P (X = x) | `(256)/625` | `256/625` | `96/625` | `16/625` | `1/625` |
उत्तर ३
Let X denotes the number of defective bulbs.
∴ Possible values of X are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4.
Let P(getting a defective bulb) = p = `6/30 = 1/5`
∴ q = 1 – p = `1 - 1/5 = 4/5`
∴ P(X = 0) = P(no defective bulb)
= qqqq
= q4
= `(4/5)^4`
= `256/625`
P(X = 1) = P(one defective bulb)
= qqqp + qqpq + qpqq + pqqq
= 4pq3
= `4 xx 1/5 xx (4/5)^3`
= `256/625`
P(X = 2) = P(two defective bulbs)
= ppqq + pqqp + qqpp + pqpq + qpqp + qppq
= 6p2q2
= `6(1/5)^2 (4/5)^2`
= `96/625`
P(X = 3) = P(three defective bulbs)
= pppq + ppqp + pqpp + qppp
= 4qp3
= `4(4/5)(1/5)^3`
= `16/625`
P(X = 4) = P(four defective bulbs)
= pppp
= p4
= `(1/5)^4`
= `1/625`
∴ Probability distribution of X is as follows:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(X = x) | `256/625` | `256/625` | `96/625` | `16/625` | `1/625` |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
then E(X)=....................
Probability distribution of X is given by
| X = x | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(X = x) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
Find P(X ≥ 2) and obtain cumulative distribution function of X
Of the students in a college, it is known that 60% reside in hostel and 40% are day scholars (not residing in hostel). Previous year results report that 30% of all students who reside in hostel attain A grade and 20% of day scholars attain A grade in their annual examination. At the end of the year, one student is chosen at random from the college and he has an A grade, what is the probability that the student is hostler?
State the following are not the probability distributions of a random variable. Give reasons for your answer.
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(X) | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | -0.1 | 0.3 |
State the following are not the probability distributions of a random variable. Give reasons for your answer.
| Y | -1 | 0 | 1 |
| P(Y) | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
State the following are not the probability distributions of a random variable. Give reasons for your answer.
| Z | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | -1 |
| P(Z) | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
Find the probability distribution of the number of successes in two tosses of a die, where a success is defined as
(i) number greater than 4
(ii) six appears on at least one die
A random variable X has the following probability distribution.
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| P(X) | 0 | k | 2k | 2k | 3k | k2 |
2k2 |
7k2 + k |
Determine
(i) k
(ii) P (X < 3)
(iii) P (X > 6)
(iv) P (0 < X < 3)
Two dice are thrown simultaneously. If X denotes the number of sixes, find the expectation of X.
Two numbers are selected at random (without replacement) from the first six positive integers. Let X denotes the larger of the two numbers obtained. Find E(X).
An urn contains 25 balls of which 10 balls bear a mark ‘X’ and the remaining 15 bear a mark ‘Y’. A ball is drawn at random from the urn, its mark is noted down and it is replaced. If 6 balls are drawn in this way, find the probability that
(i) all will bear ‘X’ mark.
(ii) not more than 2 will bear ‘Y’ mark.
(iii) at least one ball will bear ‘Y’ mark
(iv) the number of balls with ‘X’ mark and ‘Y’ mark will be equal.
Assume that the chances of the patient having a heart attack are 40%. It is also assumed that a meditation and yoga course reduce the risk of heart attack by 30% and prescription of certain drug reduces its chances by 25%. At a time a patient can choose any one of the two options with equal probabilities. It is given that after going through one of the two options the patient selected at random suffers a heart attack. Find the probability that the patient followed a course of meditation and yoga?
If the probability that a fluorescent light has a useful life of at least 800 hours is 0.9, find the probabilities that among 20 such lights at least 2 will not have a useful life of at least 800 hours. [Given : (0⋅9)19 = 0⋅1348]
There are 4 cards numbered 1, 3, 5 and 7, one number on one card. Two cards are drawn at random without replacement. Let X denote the sum of the numbers on the two drawn cards. Find the mean 'and variance of X.
Two numbers are selected at random (without replacement) from the first five positive integers. Let X denote the larger of the two numbers obtained. Find the mean and variance of X
Three persons A, B and C shoot to hit a target. If A hits the target four times in five trials, B hits it three times in four trials and C hits it two times in three trials, find the probability that:
1) Exactly two persons hit the target.
2) At least two persons hit the target.
3) None hit the target.
There are 4 cards numbered 1 to 4, one number on one card. Two cards are drawn at random without replacement. Let X denote the sum of the numbers on the two drawn cards. Find the mean and variance of X.
Which of the following distributions of probabilities of a random variable X are the probability distributions?
(i)
| X : | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | −1 |
| P (X) : | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
| X : | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| P (X) : | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
(iii)
| X : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P (X) : | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
(iv)
| X : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P (X) : | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.1 |
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| Values of X : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| P (X) : | a | 3a | 5a | 7a | 9a | 11a | 13a | 15a | 17a |
Determine:
(i) The value of a
(ii) P (X < 3), P (X ≥ 3), P (0 < X < 5).
The probability distribution function of a random variable X is given by
| xi : | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| pi : | 3c3 | 4c − 10c2 | 5c-1 |
where c > 0 Find: P (X < 2)
The probability distribution function of a random variable X is given by
| xi : | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| pi : | 3c3 | 4c − 10c2 | 5c-1 |
where c > 0 Find: P (1 < X ≤ 2)
Find the probability distribution of the number of heads, when three coins are tossed.
Four cards are drawn simultaneously from a well shuffled pack of 52 playing cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of aces.
Two dice are thrown together and the number appearing on them noted. X denotes the sum of the two numbers. Assuming that all the 36 outcomes are equally likely, what is the probability distribution of X?
Two cards are drawn successively with replacement from a well shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of kings.
Two cards are drawn simultaneously from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of successes, when getting a spade is considered a success.
Four balls are to be drawn without replacement from a box containing 8 red and 4 white balls. If X denotes the number of red balls drawn, then find the probability distribution of X.
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k |
\[\frac{k}{2}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{8}\]
|
Determine the value of k .
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k |
\[\frac{k}{2}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{8}\]
|
Determine P(X ≤ 2) and P(X > 2) .
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution:
| xi : | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| pi: | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution :
| xi : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| pi : | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution :
| xi: | 0 | 1 | 3 | 5 |
| pi : | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution :
| xi : | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| pi : | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution :
| xi : | -3 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| pi : | 0.05 | 0.45 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.05 |
A discrete random variable X has the probability distribution given below:
| X: | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
| P(X): | k | k2 | 2k2 | k |
Find the value of k.
A discrete random variable X has the probability distribution given below:
| X: | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
| P(X): | k | k2 | 2k2 | k |
Determine the mean of the distribution.
Find the mean variance and standard deviation of the following probability distribution
| xi : | a | b |
| pi : | p | q |
Two bad eggs are accidently mixed up with ten good ones. Three eggs are drawn at random with replacement from this lot. Compute the mean for the number of bad eggs drawn.
A fair coin is tossed four times. Let X denote the number of heads occurring. Find the probability distribution, mean and variance of X.
A fair die is tossed. Let X denote 1 or 3 according as an odd or an even number appears. Find the probability distribution, mean and variance of X.
A die is tossed twice. A 'success' is getting an odd number on a toss. Find the variance of the number of successes.
In a game, a man wins Rs 5 for getting a number greater than 4 and loses Rs 1 otherwise, when a fair die is thrown. The man decided to thrown a die thrice but to quit as and when he gets a number greater than 4. Find the expected value of the amount he wins/loses.
Write the values of 'a' for which the following distribution of probabilities becomes a probability distribution:
| X= xi: | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 |
| P(X= xi) : |
\[\frac{1 - a}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{1 + 2a}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{1 - 2a}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{1 + a}{4}\]
|
If X denotes the number on the upper face of a cubical die when it is thrown, find the mean of X.
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| X : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| P (X) : | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.05 |
For the events E = {X : X is a prime number}, F = {X : X < 4}, the probability P (E ∪ F) is
A random variable X takes the values 0, 1, 2, 3 and its mean is 1.3. If P (X = 3) = 2 P (X = 1) and P (X = 2) = 0.3, then P (X = 0) is
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
For the following probability distribution:
| X: | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 |
| P(X): | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
The value of E(X) is
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
For the following probability distribution:
| X : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(X) : |
\[\frac{1}{10}\]
|
\[\frac{1}{5}\]
|
\[\frac{3}{10}\]
|
\[\frac{2}{5}\]
|
The value of E(X2) is
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let X be a discrete random variable. Then the variance of X is
A pair of dice is thrown 4 times. If getting a doublet is considered a success, find the probability distribution of the number of successes and, hence, find its mean.
Five bad oranges are accidently mixed with 20 good ones. If four oranges are drawn one by one successively with replacement, then find the probability distribution of number of bad oranges drawn. Hence find the mean and variance of the distribution.
Three fair coins are tossed simultaneously. If X denotes the number of heads, find the probability distribution of X.
Calculate `"e"_0^circ ,"e"_1^circ , "e"_2^circ` from the following:
| Age x | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| lx | 1000 | 880 | 876 |
| Tx | - | - | 3323 |
Demand function x, for a certain commodity is given as x = 200 - 4p where p is the unit price. Find :
(a) elasticity of demand as function of p.
(b) elasticity of demand when p = 10 , interpret your result.
Using the truth table verify that p ∨ (q ∧ r) ≡ (p ∨ q) ∧ (p ∨ r).
If the demand function is D = 150 - p2 - 3p, find marginal revenue, average revenue and elasticity of demand for price p = 3.
Compute the age specific death rate for the following data :
| Age group (years) | Population (in thousands) | Number of deaths |
| Below 5 | 15 | 360 |
| 5-30 | 20 | 400 |
| Above 30 | 10 | 280 |
John and Mathew started a business with their capitals in the ratio 8 : 5. After 8 months, john added 25% of his earlier capital as further investment. At the same time, Mathew withdrew 20% of bis earlier capital. At the end of the year, they earned ₹ 52000 as profit. How should they divide the profit between them?
Three different aeroplanes are to be assigned to carry three cargo consignments with a view to maximize profit. The profit matrix (in lakhs of ₹) is as follows :
| Aeroplanes | Cargo consignments | ||
| C1 | C2 | C3 | |
| A1 | 1 | 4 | 5 |
| A2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| A3 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
How should the cargo consignments be assigned to the aeroplanes to maximize the profit?
A fair coin is tossed 12 times. Find the probability of getting at least 2 heads .
If random variable X has probability distribution function.
f(x) = `c/x`, 1 < x < 3, c > 0, find c, E(x) and Var(X)
If p : It is a day time , q : It is warm
Give the verbal statements for the following symbolic statements :
(a) p ∧ ∼ q (b) p v q (c) p ↔ q
Find the premium on a property worth ₹12,50,000 at 3% if the property is fully insured.
The following table gives the age of the husbands and of the wives :
| Age of wives (in years) |
Age of husbands (in years) |
|||
| 20-30 | 30- 40 | 40- 50 | 50- 60 | |
| 15-25 | 5 | 9 | 3 | - |
| 25-35 | - | 10 | 25 | 2 |
| 35-45 | - | 1 | 12 | 2 |
| 45-55 | - | - | 4 | 16 |
| 55-65 | - | - | - | 4 |
Find the marginal frequency distribution of the age of husbands.
The p.m.f. of a random variable X is
`"P"(x) = 1/5` , for x = I, 2, 3, 4, 5
= 0 , otherwise.
Find E(X).
The defects on a plywood sheet occur at random with an average of the defect per 50 sq. ft. What Is the probability that such sheet will have-
(a) No defects
(b) At least one defect
[Use e-1 = 0.3678]
The probability that a bomb dropped from an aeroplane will strike a target is `1/5`, If four bombs are dropped, find the probability that :
(a) exactly two will strike the target,
(b) at least one will strike the target.
Amit and Rohit started a business by investing ₹20,000 each. After 3 months Amit withdrew ₹5,000 and Rohit put in ₹5,000 additionally. How should a profit of ₹12,800 be divided between them at the end of the year?
A random variable X has the following probability distribution :
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| P(X) | C | 2C | 2C | 3C | C2 | 2C2 | 7C2+C |
Find the value of C and also calculate the mean of this distribution.
An urn contains 5 red and 2 black balls. Two balls are drawn at random. X denotes number of black balls drawn. What are possible values of X?
Solve the following :
Identify the random variable as either discrete or continuous in each of the following. Write down the range of it.
20 white rats are available for an experiment. Twelve rats are male. Scientist randomly selects 5 rats number of female rats selected on a specific day
The p.d.f. of a continuous r.v. X is given by
f (x) = `1/ (2a)` , for 0 < x < 2a and = 0, otherwise. Show that `P [X < a/ 2] = P [X >( 3a)/ 2]` .
The p.d.f. of r.v. of X is given by
f (x) = `k /sqrtx` , for 0 < x < 4 and = 0, otherwise. Determine k .
Determine c.d.f. of X and hence P (X ≤ 2) and P(X ≤ 1).
A random variable X has the following probability distribution :
| x = x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 7 | |||
| P(X=x) | 0 | k | 2k | 2k | 3k | k2 | 2k2 | 7k2 + k |
Determine (i) k
(ii) P(X> 6)
(iii) P(0<X<3).
Determine whether each of the following is a probability distribution. Give reasons for your answer.
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| P(x) | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
Determine whether each of the following is a probability distribution. Give reasons for your answer.
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(x) | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | –0.1 | 0.3 |
Determine whether each of the following is a probability distribution. Give reasons for your answer.
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| P(x) | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
Determine whether each of the following is a probability distribution. Give reasons for your answer.
| z | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | -1 |
| P(z) | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4. | 0.05 | 0.05 |
Determine whether each of the following is a probability distribution. Give reasons for your answer.
| y | –1 | 0 | 1 |
| P(y) | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
Find the probability distribution of the number of successes in two tosses of a die if success is defined as getting a number greater than 4.
10 balls are marked with digits 0 to 9. If four balls are selected with replacement. What is the probability that none is marked 0?
Defects on plywood sheet occur at random with the average of one defect per 50 Sq.ft. Find the probability that such a sheet has no defect
Solve the following problem :
Following is the probability distribution of a r.v.X.
| X | – 3 | – 2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X = x) | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.1 |
Find the probability that X is positive.
Solve the following problem :
Following is the probability distribution of a r.v.X.
| x | – 3 | – 2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X = x) | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.1 |
Find the probability that X is even.
Solve the following problem :
Find the probability of the number of successes in two tosses of a die, where success is defined as number greater than 4.
Solve the following problem :
The probability that a bomb will hit the target is 0.8. Find the probability that, out of 5 bombs, exactly 2 will miss the target.
Solve the following problem :
A large chain retailer purchases an electric device from the manufacturer. The manufacturer indicates that the defective rate of the device is 10%. The inspector of the retailer randomly selects 4 items from a shipment. Find the probability that the inspector finds at most one defective item in the 4 selected items.
Solve the following problem :
The probability that a machine will produce all bolts in a production run within the specification is 0.9. A sample of 3 machines is taken at random. Calculate the probability that all machines will produce all bolts in a production run within the specification.
Solve the following problem :
In a large school, 80% of the students like mathematics. A visitor asks each of 4 students, selected at random, whether they like mathematics.
Calculate the probabilities of obtaining an answer yes from all of the selected students.
Solve the following problem :
In a large school, 80% of the students like mathematics. A visitor asks each of 4 students, selected at random, whether they like mathematics.
Find the probability that the visitor obtains the answer yes from at least 3 students.
A random variable X has the following probability distribution
| X | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(x) | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
Then the variance of this distribution is
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k | `"k"/2` | `"k"/4` | `"k"/8` |
Determine P(X ≤ 2) and P(X > 2)
Two biased dice are thrown together. For the first die P(6) = `1/2`, the other scores being equally likely while for the second die, P(1) = `2/5` and the other scores are equally likely. Find the probability distribution of ‘the number of ones seen’.
Two probability distributions of the discrete random variable X and Y are given below.
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | `1/5` | `2/5` | `1/5` | `1/5` |
| Y | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(Y) | `1/5` | `3/10` | `2/10` | `1/10` |
Prove that E(Y2) = 2E(X).
The random variable X can take only the values 0, 1, 2. Given that P(X = 0) = P(X = 1) = p and that E(X2) = E[X], find the value of p
Let X be a discrete random variable whose probability distribution is defined as follows:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"(x + 1), "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3"," 4),(2"k"x, "for" x = 5"," 6"," 7),(0, "Otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate Standard deviation of X.
The probability distribution of a random variable x is given as under:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"x^2, "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3),(2"k"x, "for" x = 4"," 5"," 6),(0, "otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate E(X)
The probability distribution of a random variable x is given as under:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"x^2, "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3),(2"k"x, "for" x = 4"," 5"," 6),(0, "otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate E(3X2)
The probability distribution of a discrete random variable X is given below:
| X | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| P(X) | `5/"k"` | `7/"k"` | `9/"k"` | `11/"k"` |
The value of k is ______.
A bag contains 1 red and 3 white balls. Find the probability distribution of the number of red balls if 2 balls are drawn at random from the bag one-by-one without replacement.
Find the probability distribution of the number of successes in two toves of a die where a success is define as:- Six appeared on at least one die.
A person throws two fair dice. He wins ₹ 15 for throwing a doublet (same numbers on the two dice), wins ₹ 12 when the throw results in the sum of 9, and loses ₹ 6 for any other outcome on the throw. Then the expected gain/loss (in ₹) of the person is ______.
Find the mean of number randomly selected from 1 to 15.
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| x | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| P(x) | k | 2k | 2k | 3k | k2 | 2k2 | 7k2 + k |
Find:
- k
- P(X < 3)
- P(X > 4)
Two numbers are selected from first six even natural numbers at random without replacement. If X denotes the greater of two numbers selected, find the probability distribution of X.
A box contains 30 fruits, out of which 10 are rotten. Two fruits are selected at random one by one without replacement from the box. Find the probability distribution of the number of unspoiled fruits. Also find the mean of the probability distribution.
Five numbers x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 are randomly selected from the numbers 1, 2, 3, ......., 18 and are arranged in the increasing order such that x1 < x2 < x3 < x4 < x5. What is the probability that x2 = 7 and x4 = 11?
Kiran plays a game of throwing a fair die 3 times but to quit as and when she gets a six. Kiran gets +1 point for a six and –1 for any other number.
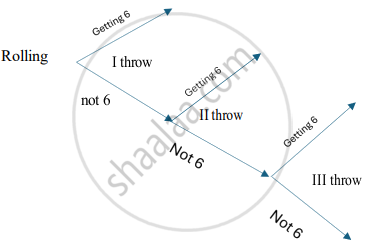
- If X denotes the random variable “points earned” then what are the possible values X can take?
- Find the probability distribution of this random variable X.
- Find the expected value of the points she gets.
