Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An urn contains 25 balls of which 10 balls bear a mark ‘X’ and the remaining 15 bear a mark ‘Y’. A ball is drawn at random from the urn, its mark is noted down and it is replaced. If 6 balls are drawn in this way, find the probability that
(i) all will bear ‘X’ mark.
(ii) not more than 2 will bear ‘Y’ mark.
(iii) at least one ball will bear ‘Y’ mark
(iv) the number of balls with ‘X’ mark and ‘Y’ mark will be equal.
उत्तर
Total number of balls in the urn = 25
Balls bearing mark ‘X’ = 10
Balls bearing mark ‘Y’ = 15
p = P (ball bearing mark ‘X’) =`10/25 = 2/5`
q = P (ball bearing mark ‘Y’) =`15/25 = 3/5`
Six balls are drawn with replacement. Therefore, the number of trials are Bernoulli trials.
Let Z be the random variable that represents the number of balls with ‘Y’ mark on them in the trials.
Clearly, Z has a binomial distribution with n = 6 and p = 2/5
∴ P (Z = z) = `""^nC_zp^(n-z)q^z`
(i) P (all will bear ‘X’ mark) = P (Z = 0) =`""^6C_0 (2/5)^6 = (2/5)^6`
(ii) P (not more than 2 bear ‘Y’ mark) = P (Z ≤ 2)
= P (Z = 0) + P (Z = 1) + P (Z = 2)
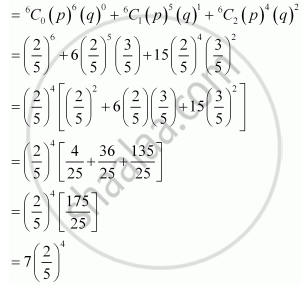
(iii) P (at least one ball bears ‘Y’ mark) = P (Z ≥ 1) = 1 − P (Z = 0)
`= 1 - (2/5)^6`
(iv) P (equal number of balls with ‘X’ mark and ‘Y’ mark) = P (Z = 3)
= C36 253 353
`= 20x8x27/15628`
`= 864/3125`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Of the students in a college, it is known that 60% reside in hostel and 40% are day scholars (not residing in hostel). Previous year results report that 30% of all students who reside in hostel attain A grade and 20% of day scholars attain A grade in their annual examination. At the end of the year, one student is chosen at random from the college and he has an A grade, what is the probability that the student is hostler?
Two dice are thrown simultaneously. If X denotes the number of sixes, find the expectation of X.
Two numbers are selected at random (without replacement) from positive integers 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7. Let X denote the larger of the two numbers obtained. Find the mean and variance of the probability distribution of X.
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| Values of X : | −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P (X) : | 0.1 | k | 0.2 | 2k | 0.3 | k |
Find the value of k.
Find the probability distribution of the number of heads, when three coins are tossed.
Two cards are drawn simultaneously from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of successes, when getting a spade is considered a success.
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k |
\[\frac{k}{2}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{8}\]
|
Determine the value of k .
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k |
\[\frac{k}{2}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{8}\]
|
Find P(X ≤ 2) + P(X > 2) .
For what value of k the following distribution is a probability distribution?
| X = xi : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P (X = xi) : | 2k4 | 3k2 − 5k3 | 2k − 3k2 | 3k − 1 |
If the probability distribution of a random variable X is as given below:
Write the value of P (X ≤ 2).
| X = xi : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P (X = xi) : | c | 2c | 4c | 4c |
A random variable has the following probability distribution:
| X = xi : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P (X = xi) : | k | 2k | 3k | 4k |
Write the value of P (X ≥ 3).
For the following probability density function (p. d. f) of X, find P(X < 1) and P(|x| < 1)
`f(x) = x^2/18, -3 < x < 3`
= 0, otherwise
Calculate `"e"_0^circ ,"e"_1^circ , "e"_2^circ` from the following:
| Age x | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| lx | 1000 | 880 | 876 |
| Tx | - | - | 3323 |
If the demand function is D = 150 - p2 - 3p, find marginal revenue, average revenue and elasticity of demand for price p = 3.
Find mean and standard deviation of the continuous random variable X whose p.d.f. is given by f(x) = 6x(1 - x);= (0); 0 < x < 1(otherwise)
If X ∼ N (4,25), then find P(x ≤ 4)
The p.m.f. of a random variable X is
`"P"(x) = 1/5` , for x = I, 2, 3, 4, 5
= 0 , otherwise.
Find E(X).
Determine whether each of the following is a probability distribution. Give reasons for your answer.
| y | –1 | 0 | 1 |
| P(y) | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
A coin is biased so that the head is 3 times as likely to occur as tail. Find the probability distribution of number of tails in two tosses.
A die is thrown 4 times. If ‘getting an odd number’ is a success, find the probability of at least 3 successes
A die is thrown 4 times. If ‘getting an odd number’ is a success, find the probability of at most 2 successes.
Defects on plywood sheet occur at random with the average of one defect per 50 Sq.ft. Find the probability that such a sheet has no defect
Solve the following problem :
If a fair coin is tossed 4 times, find the probability that it shows 3 heads
Solve the following problem :
A computer installation has 3 terminals. The probability that any one terminal requires attention during a week is 0.1, independent of other terminals. Find the probabilities that 0
Solve the following problem :
A computer installation has 3 terminals. The probability that any one terminal requires attention during a week is 0.1, independent of other terminals. Find the probabilities that 1 terminal requires attention during a week.
Solve the following problem :
In a large school, 80% of the students like mathematics. A visitor asks each of 4 students, selected at random, whether they like mathematics.
Calculate the probabilities of obtaining an answer yes from all of the selected students.
Let a pair of dice be thrown and the random variable X be the sum of the numbers that appear on the two dice. Find the mean or expectation of X and variance of X
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k | `"k"/2` | `"k"/4` | `"k"/8` |
Determine the value of k.
Let X be a discrete random variable whose probability distribution is defined as follows:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"(x + 1), "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3"," 4),(2"k"x, "for" x = 5"," 6"," 7),(0, "Otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate E(X)
Let X be a discrete random variable whose probability distribution is defined as follows:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"(x + 1), "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3"," 4),(2"k"x, "for" x = 5"," 6"," 7),(0, "Otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate Standard deviation of X.
The probability distribution of a random variable x is given as under:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"x^2, "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3),(2"k"x, "for" x = 4"," 5"," 6),(0, "otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate P(X ≥ 4)
For the following probability distribution:
| X | – 4 | – 3 | – 2 | – 1 | 0 |
| P(X) | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
E(X) is equal to ______.
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| x | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| P(x) | k | 2k | 2k | 3k | k2 | 2k2 | 7k2 + k |
Find:
- k
- P(X < 3)
- P(X > 4)
A large chain retailer purchases an electric device from the manufacturer. The manufacturer indicates that the defective rate of the device is 10%. The inspector of the retailer randomly selects 4 items from a shipment. Complete the following activity to find the probability that the inspector finds at most one defective item in the 4 selected items.
Solution:
Here, n = 4
p = probability of defective device = 10% = `10/100 = square`
∴ q = 1 - p = 1 - 0.1 = `square`
X ∼ B(4, 0.1)
`P(X=x)=""^n"C"_x p^x q^(n-x)= ""^4"C"_x (0.1)^x (0.9)^(4 - x)`
P[At most one defective device] = P[X ≤ 1]
= P[X=0] + P[X=1]
= `square+square`
∴ P[X ≤ 1] = `square`
A primary school teacher wants to teach the concept of 'larger number' to the students of Class II.
To teach this concept, he conducts an activity in his class. He asks the children to select two numbers from a set of numbers given as 2, 3, 4, 5 one after the other without replacement.
All the outcomes of this activity are tabulated in the form of ordered pairs given below:
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| 2 | (2, 2) | (2, 3) | (2, 4) | |
| 3 | (3, 2) | (3, 3) | (3, 5) | |
| 4 | (4, 2) | (4, 4) | (4, 5) | |
| 5 | (5, 3) | (5, 4) | (5, 5) |
- Complete the table given above.
- Find the total number of ordered pairs having one larger number.
- Let the random variable X denote the larger of two numbers in the ordered pair.
Now, complete the probability distribution table for X given below.
X 3 4 5 P(X = x) - Find the value of P(X < 5)
- Calculate the expected value of the probability distribution.
