Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the locus of a complex number, z = x + iy, satisfying the relation `|[ z -3i}/{z +3i]| ≤ sqrt2 `. Illustrate the locus of z in the Argand plane.
उत्तर
`|[ z -3i]/[z +3i]| ≤ sqrt2 `
⇒ `|[x + iy - 3i]/[x +iy +3i]| ≤ sqrt2 `
⇒ `|x + i (y - 3)| ≤ sqrt2 |x + i (y + 3)|`
⇒ `sqrt(x^2 + (y - 3)^2) ≤ sqrt2 sqrt(x^2 + (y + 3)^2)`
⇒ x2 + (y - 3)2 ≤ 2 (x2 + (y + 3)2)
⇒ x2 + y2 + 9 - 6y ≤ 2x2 + 2(y2 + 9 + 6y)
⇒ 2x2 + 2y2 + 18 + 12y - x2 - y2 - 9 + 6y ≥ 0
⇒ x2 + y2 + 9 + 18y ≥ 0
⇒ x2 + y2 + 18y + 9 + 81 ≥ 81
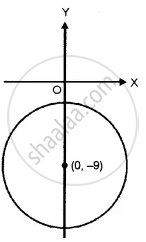
⇒ x2 + (y + 9)2 ≥ 72
⇒ (x - 0)2 + (y - (-9))2 ≥ ( 6√2)2
This represents a circle with centre (0, 9) and radius 6√2 units.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the sum of intercepts cut off by the plane `vecr.(2hati+hatj-k)-5=0` on the three axes
Prove that if a plane has the intercepts a, b, c and is at a distance of P units from the origin, then `1/a^2 + 1/b^2 + 1/c^2 = 1/p^2`
A variable plane which remains at a constant distance 3p from the origin cuts the coordinate axes at A, B, C. Show that the locus of the centroid of triangle ABC is `1/x^2 + 1/y^2 + 1/z^2 = 1/p^2`
Write the equation of the plane whose intercepts on the coordinate axes are 2, −3 and 4.
Reduce the equations of the following planes to intercept form and find the intercepts on the coordinate axes.
4x + 3y − 6z − 12 = 0
Reduce the equations of the following planes to intercept form and find the intercepts on the coordinate axes.
2x + 3y − z = 6
Reduce the equations of the following planes to intercept form and find the intercepts on the coordinate axes.
2x − y + z = 5
Find the equation of a plane which meets the axes at A, B and C, given that the centroid of the triangle ABC is the point (α, β, γ).
A plane meets the coordinate axes at A, B and C, respectively, such that the centroid of triangle ABC is (1, −2, 3). Find the equation of the plane.
Find the equation of the plane which contains the line of intersection of the planes x + 2y + 3z − 4 = 0 and 2x + y − z + 5 = 0 and which is perpendicular to the plane 5x + 3y − 6z+ 8 = 0.
Find the equation of the plane through the line of intersection of the planes x + 2y + 3z + 4 = 0 and x − y + z + 3 = 0 and passing through the origin.
Find the vector equation (in scalar product form) of the plane containing the line of intersection of the planes x − 3y + 2z − 5 = 0 and 2x − y + 3z − 1 = 0 and passing through (1, −2, 3).
Find the equation of the plane passing through the intersection of the planes 2x + 3y − z+ 1 = 0 and x + y − 2z + 3 = 0 and perpendicular to the plane 3x − y − 2z − 4 = 0.
Find the vector equation of the plane through the line of intersection of the planes x + y+ z = 1 and 2x + 3y + 4z = 5 which is perpendicular to the plane x − y + z = 0.
Find the equation of the plane which contains the line of intersection of the planes x \[+\] 2y \[+\] 3 \[z - \] 4 \[=\] 0 and 2 \[x + y - z\] \[+\] 5 \[=\] 0 and whose x-intercept is twice its z-intercept. Hence, write the equation of the plane passing through the point (2, 3, \[-\] 1) and parallel to the plane obtained above.
Find the length of the perpendicular from origin to the plane `vecr. (3i - 4j-12hatk)+39 = 0`
The intercepts made by the plane 2x – 3y + 5z + 4 = 0 on the coordinate axes are `-2, 4/3, (-4)/5`.
The equation of the plane which is parallel to 2x − 3y + z = 0 and which passes through (1, −1, 2) is:
The intercepts made on the coordinate axes by the plane 2x + y − 2z = 3 are:
