Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If `vec"a"` and `vec"b"` are the position vectors of A and B, respectively, find the position vector of a point C in BA produced such that BC = 1.5 BA.
उत्तर
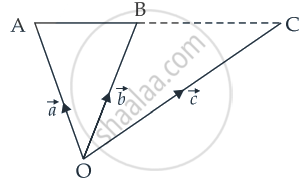
Given that BC = 1.5 BA
⇒ `"BC"/"BA"` = 1.5 = `3/2`
⇒ `(vec"c" - vec"b")/(vec"a" - vec"b") = 3/2`
⇒ `2vec"c" - 2vec"b" = 3vec"a" - 3vec"b"`
⇒ `2vec"c" = 3vec"a" - 3vec"b" + 2vec"b"`
⇒ `2vec"c" = 3vec"a" - vec"b"`
∴ `vec"c" = (3vec"a" - vec"b")/2`
Hence, the required vector is `vec"c" = (3vec"a" - vec"b")/2`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the direction ratios of a vector perpendicular to the two lines whose direction ratios are -2, 1, -1, and -3, -4, 1.
If `bara, barb, barc` are position vectors of the points A, B, C respectively such that `3bara+ 5barb-8barc = 0`, find the ratio in which A divides BC.
`veca and -veca` are collinear.
Two collinear vectors having the same magnitude are equal.
Find the direction cosines of the vector joining the points A (1, 2, -3) and B (-1, -2, 1) directed from A to B.
Show that the vector `hati + hatj + hatk` is equally inclined to the axes OX, OY, and OZ.
Find the position vector of a point R which divides the line joining two points P and Q whose position vectors are `hati + 2hatj - hatk` and `-hati + hatj + hatk` respectively, externally in the ratio 2:1.
Find the position vector of the mid point of the vector joining the points P (2, 3, 4) and Q (4, 1, – 2).
Express \[\vec{AB}\] in terms of unit vectors \[\hat{i}\] and \[\hat{j}\], when the points are A (4, −1), B (1, 3)
Find \[\left| \vec{A} B \right|\] in each case.
Find the angle between the vectors \[\vec{a} = 2 \hat{i} - 3 \hat{j} + \hat{k} \text{ and } \vec{b} = \hat{i} + \hat{j} - 2 \hat{k}\]
Dot product of a vector with \[\hat{i} + \hat{j} - 3\hat{k} , \hat{i} + 3\hat{j} - 2 \hat{k} \text{ and } 2 \hat{i} + \hat{j} + 4 \hat{k}\] are 0, 5 and 8 respectively. Find the vector.
The adjacent sides of a parallelogram are represented by the vectors \[\vec{a} = \hat{i} + \hat{j} - \hat{k}\text{ and }\vec{b} = - 2 \hat{i} + \hat{j} + 2 \hat{k} .\]
Find unit vectors parallel to the diagonals of the parallelogram.
If \[\hat{a} \text{ and } \hat{b}\] are unit vectors inclined at an angle θ, prove that \[\cos\frac{\theta}{2} = \frac{1}{2}\left| \hat{a} + \hat{b} \right|\]
Show that the vector \[\hat{i} + \hat{j} + \hat{k}\] is equally inclined to the coordinate axes.
For any two vectors \[\vec{a} \text{ and } \vec{b}\] show that \[\left( \vec{a} + \vec{b} \right) \cdot \left( \vec{a} - \vec{b} \right) = 0 \Leftrightarrow \left| \vec{a} \right| = \left| \vec{b} \right|\]
If \[\vec{p} = 5 \hat{i} + \lambda \hat{j} - 3 \hat{k} \text{ and } \vec{q} = \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} - 5 \hat{k} ,\] then find the value of λ, so that \[\vec{p} + \vec{q}\] and \[\vec{p} - \vec{q}\] are perpendicular vectors.
Show that the vectors \[\vec{a} = 3 \hat{i} - 2 \hat{j} + \hat{k} , \vec{b} = \hat{i} - 3 \hat{j} + 5 \hat{k} , \vec{c} = 2 \hat{i} + \hat{j} - 4 \hat{k}\] form a right-angled triangle.
Find the magnitude of two vectors \[\vec{a} \text{ and } \vec{b}\] that are of the same magnitude, are inclined at 60° and whose scalar product is 1/2.
Find the unit vector in the direction of vector \[\overrightarrow{PQ} ,\]
where P and Q are the points (1, 2, 3) and (4, 5, 6).
Show that the points \[A \left( 2 \hat{i} - \hat{j} + \hat{k} \right), B \left( \hat{i} - 3 \hat{j} - 5 \hat{k} \right), C \left( 3 \hat{i} - 4 \hat{j} - 4 \hat{k} \right)\] are the vertices of a right angled triangle.
Find the value of x for which \[x \left( \hat{i} + \hat{j} + \hat{k} \right)\] is a unit vector.
Show that the vectors \[2 \hat{i} - 3 \hat{j} + 4 \hat{k}\text{ and }- 4 \hat{i} + 6 \hat{j} - 8 \hat{k}\] are collinear.
Find the sine of the angle between the vectors `vec"a" = 3hat"i" + hat"j" + 2hat"k"` and `vec"b" = 2hat"i" - 2hat"j" + 4hat"k"`.
The altitude through vertex C of a triangle ABC, with position vectors of vertices `veca, vecb, vecc` respectively is:
Area of rectangle having vertices A, B, C and D will position vector `(- hati + 1/2hatj + 4hatk), (hati + 1/2hatj + 4hatk) (hati - 1/2hatj + 4hatk)` and `(-hati - 1/2hatj + 4hatk)` is
Assertion (A): If a line makes angles α, β, γ with positive direction of the coordinate axes, then sin2 α + sin2 β + sin2 γ = 2.
Reason (R): The sum of squares of the direction cosines of a line is 1.
A line l passes through point (– 1, 3, – 2) and is perpendicular to both the lines `x/1 = y/2 = z/3` and `(x + 2)/-3 = (y - 1)/2 = (z + 1)/5`. Find the vector equation of the line l. Hence, obtain its distance from the origin.
