Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If f : A → A, g : A → A are two bijections, then prove that fog is an injection ?
उत्तर
Injectivity of fog:
Let x and y be two elements of the domain (A), such that
(fog) (x) = (fog) (y)
⇒ f (g(x)) = f (g(y))
⇒ g (x) = g (y) (As, f is one-one)
⇒ x = y (As, g is one-one)
So, fog is an injection.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: N → N given by f(x) = x2
Following the case, state whether the function is one-one, onto, or bijective. Justify your answer.
f: R → R defined by f(x) = 1 + x2
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection : f : Z → Z given by f(x) = x3
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = sin2x + cos2x
Show that the logarithmic function f : R0+ → R given by f (x) loga x ,a> 0 is a bijection.
Let f = {(3, 1), (9, 3), (12, 4)} and g = {(1, 3), (3, 3) (4, 9) (5, 9)}. Show that gof and fog are both defined. Also, find fog and gof.
Find fog and gof if : f(x)= x + 1, g (x) = 2x + 3 .
If f(x) = |x|, prove that fof = f.
If f(x) = sin x and g(x) = 2x be two real functions, then describe gof and fog. Are these equal functions?
Let
f (x) =`{ (1 + x, 0≤ x ≤ 2) , (3 -x , 2 < x ≤ 3):}`
Find fof.
If A = {1, 2, 3, 4} and B = {a, b, c, d}, define any four bijections from A to B. Also give their inverse functions.
If f : A → A, g : A → A are two bijections, then prove that fog is a surjection ?
If f : C → C is defined by f(x) = x2, write f−1 (−4). Here, C denotes the set of all complex numbers.
Let f be a function from C (set of all complex numbers) to itself given by f(x) = x3. Write f−1 (−1).
If f : {5, 6} → {2, 3} and g : {2, 3} → {5, 6} are given by f = {(5, 2), (6, 3)} and g = {(2, 5), (3, 6)}, then find fog. [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
If a function g = {(1, 1), (2, 3), (3, 5), (4, 7)} is described by g(x) = \[\alpha x + \beta\] then find the values of \[\alpha\] and \[ \beta\] . [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
If f(x) = 4 −( x - 7)3 then write f-1 (x).
The function
The function \[f : R \to R\] defined by
\[f\left( x \right) = 6^x + 6^{|x|}\] is
Let \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{\alpha x}{x + 1}, x \neq - 1\] Then, for what value of α is \[f \left( f\left( x \right) \right) = x?\]
Let the function f: R → R be defined by f(x) = 4x – 1, ∀ x ∈ R. Then, show that f is one-one.
Let R be the set of real numbers and f: R → R be the function defined by f(x) = 4x + 5. Show that f is invertible and find f–1.
The domain of the function f: R → R defined by f(x) = `sqrt(x^2 - 3x + 2)` is ______
Let the function f: R → R be defined by f(x) = cosx, ∀ x ∈ R. Show that f is neither one-one nor onto
Let f: R → R be defined by f(x) = `1/x` ∀ x ∈ R. Then f is ______.
Let f: R → R be given by f(x) = tan x. Then f–1(1) is ______.
If f(x) = (4 – (x – 7)3}, then f–1(x) = ______.
If N be the set of all-natural numbers, consider f: N → N such that f(x) = 2x, ∀ x ∈ N, then f is ____________.
Let f : R → R, g : R → R be two functions such that f(x) = 2x – 3, g(x) = x3 + 5. The function (fog)-1 (x) is equal to ____________.
Range of `"f"("x") = sqrt((1 - "cos x") sqrt ((1 - "cos x")sqrt ((1 - "cos x")....infty))`
Raji visited the Exhibition along with her family. The Exhibition had a huge swing, which attracted many children. Raji found that the swing traced the path of a Parabola as given by y = x2.
Answer the following questions using the above information.
- Let f: {1,2,3,....} → {1,4,9,....} be defined by f(x) = x2 is ____________.
Prove that the function f is surjective, where f: N → N such that `f(n) = {{:((n + 1)/2",", if "n is odd"),(n/2",", if "n is even"):}` Is the function injective? Justify your answer.
If f: R→R is a function defined by f(x) = `[x - 1]cos((2x - 1)/2)π`, where [ ] denotes the greatest integer function, then f is ______.
The solution set of the inequation log1/3(x2 + x + 1) + 1 > 0 is ______.
Let a and b are two positive integers such that b ≠ 1. Let g(a, b) = Number of lattice points inside the quadrilateral formed by lines x = 0, y = 0, x = b and y = a. f(a, b) = `[a/b] + [(2a)/b] + ... + [((b - 1)a)/b]`, then the value of `[(g(101, 37))/(f(101, 37))]` is ______.
(Note P(x, y) is lattice point if x, y ∈ I)
(where [.] denotes greatest integer function)
Let f(n) = `[1/3 + (3n)/100]n`, where [n] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to n. Then `sum_(n = 1)^56f(n)` is equal to ______.
Write the domain and range (principle value branch) of the following functions:
f(x) = tan–1 x.
Which one of the following graphs is a function of x?
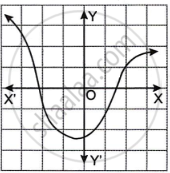 |
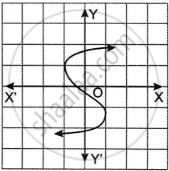 |
| Graph A | Graph B |
