Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a ∆ABC, AD is the bisector of ∠BAC. If AB = 8 cm, BD = 6 cm and DC = 3 cm. Find AC
पर्याय
4 cm
6 cm
3 cm
8 cm
उत्तर
Given: In a ΔABC, AD is the bisector of angle BAC. AB = 8cm, and DC = 3cm and BD = 6cm.
To find: AC
We know that the internal bisector of angle of a triangle divides the opposite side internally in the ratio of the sides containing the angle.
Hence,
`(AB)/(AC)=(BD)/(DC)`
`8/(AC)=6/3`
`8/(AC)=(8xx3)/6`
`AC= 4cm`
Hence we got the result `a`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
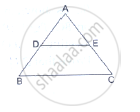
D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively of a ΔABC. In each of the following cases, determine whether DE║BC or not.
AB = 10.8cm, AD = 6.3cm, AC = 9.6cm and EC = 4cm.
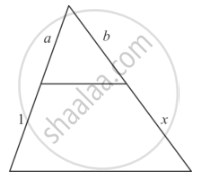
In each of the figures [(i)-(iv)] given below, a line segment is drawn parallel to one side of the triangle and the lengths of certain line-segment are marked. Find the value of x in each of the following :

In each of the figures [(i)-(iv)] given below, a line segment is drawn parallel to one side of the triangle and the lengths of certain line-segment are marked. Find the value of x in each of the following :
In the given figure, DE || BD. Determine AC and AE.

In each of the following figures, you find who triangles. Indicate whether the triangles are similar. Give reasons in support of your answer.
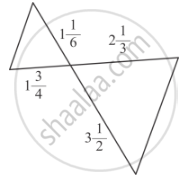
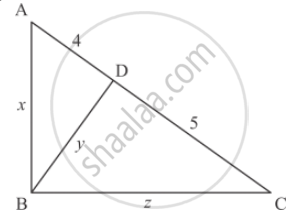
In each of the figures given below, an altitude is drawn to the hypotenuse by a right-angled triangle. The length of different line-segment are marked in each figure. Determine x, y, z in each case.
The diagonals of quadrilateral ABCD intersect at O. Prove that
`[A(∆"ACB")]/[A(∆"ACD")] = "BO"/"DO"`
In ∆ABC, ray AD bisects ∠A and intersects BC in D. If BC = a, AC = b and AC = c, prove that \[BD = \frac{ac}{b + c}\]
In ∆ABC, ray AD bisects ∠A and intersects BC in D. If BC = a, AC = b and AC = c, prove that \[DC = \frac{ab}{b + c}\]
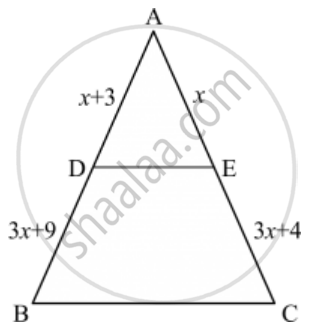
In the given figure, the value of x for which DE || AB is