Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In ∆ABC, ray AD bisects ∠A and intersects BC in D. If BC = a, AC = b and AC = c, prove that \[DC = \frac{ab}{b + c}\]
उत्तर
Since BC = CD + BD
`⇒ CD =BC -BD`
`CD = a - (ac)/(b+c)`
`= (ab)/(b+c)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
the below given figure, a triangle ABC is drawn to circumscribe a circle of radius 3 cm, such that the segments BD and DC are respectively of lengths 6 cm and 9 cm. If the area of ΔABC is 54 cm2, then find the lengths of sides AB and AC.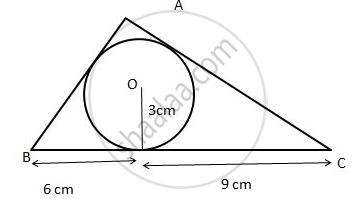
A girl of height 90 cm is walking away from the base of a lamp-post at a speed of 1.2m/sec. If the lamp is 3.6 m above the ground, find the length of her shadow after 4 seconds.
D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively of a ΔABC. In each of the following cases, determine whether DE║BC or not.
AD = 5.7cm, DB = 9.5cm, AE = 4.8cm and EC = 8cm.
A ladder is placed in such a way that its foot is at a distance of 15m from a wall and its top reaches a window 20m above the ground. Find the length of the ladder.
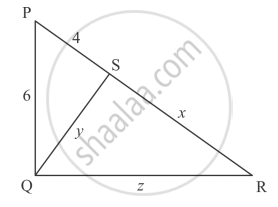
In each of the figures given below, an altitude is drawn to the hypotenuse by a right-angled triangle. The length of different line-segment are marked in each figure. Determine x, y, z in each case.
In ∆ABC, ∠A = 60°. Prove that BC2 = AB2 + AC2 − AB . AC.
In ∆ABC, AD is a median. Prove that AB2 + AC2 = 2AD2 + 2DC2.
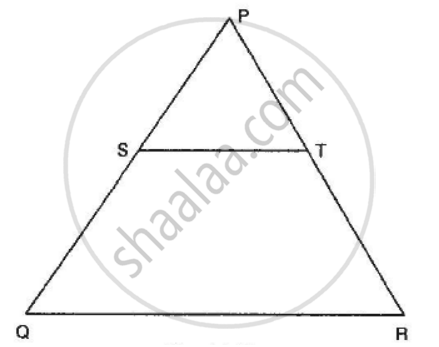
In the given figure, S and T are points on the sides PQ and PR respectively of ∆PQR such that PT = 2 cm, TR = 4 cm and ST is parallel to QR. Find the ratio of the areas of ∆PST and ∆PQR.
In a ∆ABC, ∠A = 90°, AB = 5 cm and AC = 12 cm. If AD ⊥ BC, then AD =
In the given figure, if ∠ADE = ∠ABC, then CE =