Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
the below given figure, a triangle ABC is drawn to circumscribe a circle of radius 3 cm, such that the segments BD and DC are respectively of lengths 6 cm and 9 cm. If the area of ΔABC is 54 cm2, then find the lengths of sides AB and AC.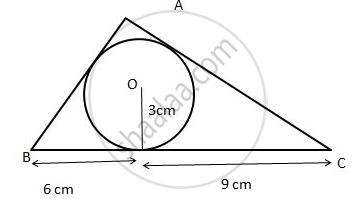
उत्तर
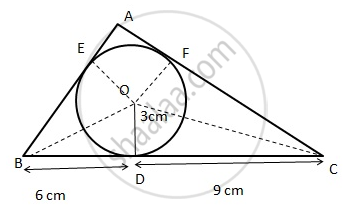
Given : OD = 3cm
Construction : Join OA, OB and X
Proof : Area of the ΔABC = area of ΔOBC + area of ΔOAC + arc of ∠ OAB.
BD = 6 cm : BE = 6 cm ( equal tangents )
DC = 9 cm : CF = 9 cm ( equal tangents )
AB = AF + FB = 6 + x = 6 + 3 = 9.
संबंधित प्रश्न
A vertical stick of length 6 m casts a shadow 4 m long on the ground and at the same time a tower casts a shadow 28 m long. Find the height of the tower.
In each of the following figures, you find who triangles. Indicate whether the triangles are similar. Give reasons in support of your answer.
In each of the following figures, you find who triangles. Indicate whether the triangles are similar. Give reasons in support of your answer.
In ∆PQR, M and N are points on sides PQ and PR respectively such that PM = 15 cm and NR = 8 cm. If PQ = 25 cm and PR = 20 cm state whether MN || QR.
In the given figure,
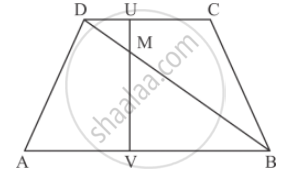
AB || DC prove that
(i) ∆DMU ∼ ∆BMV
In ∆ABC, ray AD bisects ∠A and intersects BC in D. If BC = a, AC = b and AC = c, prove that \[DC = \frac{ab}{b + c}\]
In ∆ABC, ∠C is an obtuse angle. AD ⊥ BC and AB2 = AC2 + 3 BC2. Prove that BC = CD.
In the adjoining figure, DE is parallel to BC and AD = 1 cm, BD = 2 cm. What is the ratio of the area of ∆ABC to the area of ∆ADE?
If in ∆ABC and ∆DEF, \[\frac{AB}{DE} = \frac{BC}{FD}\], then ∆ABC ∼ ∆DEF when
∆ABC ∼ ∆DEF, ar(∆ABC) = 9 cm2, ar(∆DEF) = 16 cm2. If BC = 2.1 cm, then the measure of EF is
