Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a ∆ABC, ∠A = 90°, AB = 5 cm and AC = 12 cm. If AD ⊥ BC, then AD =
पर्याय
\[\frac{13}{2}cm\]
- \[\frac{60}{13}cm\]
- \[\frac{13}{60}cm\]
- \[\frac{2\sqrt{15}}{13}cm\]
उत्तर
Given: In ΔABC `∠ A=90^o, AD⊥ BC`,, AC = 12cm, and AB = 5cm.
To find: AD
We know that the ratio of areas of two similar triangles is equal to the ratio of squares of their corresponding sides.
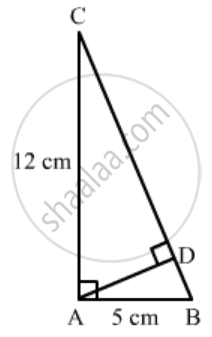
In ∆ACB and ∆ADC,
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
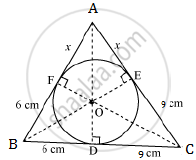
In the below figure, a triangle ABC is drawn to circumscribe a circle of radius 3 cm, such that the segments BD and DC are respectively of lengths 6 cm and 9 cm. If the area of Δ ABC is 54 cm2, then find the lengths of sides AB and AC.
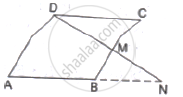
M is a point on the side BC of a parallelogram ABCD. DM when produced meets AB produced at N. Prove that
(1)` (DM)/(MN)=(DC)/(BN)`
(2)` (DN)/(DM)=(AN)/(DC)`
In the given figure,
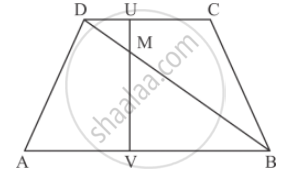
AB || DC prove that
(i) ∆DMU ∼ ∆BMV
In ∆ABC, ray AD bisects ∠A and intersects BC in D. If BC = a, AC = b and AC = c, prove that \[DC = \frac{ab}{b + c}\]
In ∆ABC, ∠A = 60°. Prove that BC2 = AB2 + AC2 − AB . AC.
In triangles ABC and DEF, ∠A = ∠E = 40°, AB : ED = AC : EF and ∠F = 65°, then ∠B =
In a ∆ABC, AD is the bisector of ∠BAC. If AB = 6 cm, AC = 5 cm and BD = 3 cm, then DC =
The areas of two similar triangles are 121 cm2 and 64 cm2 respectively. If the median of the first triangle is 12.1 cm, then the corresponding median of the other triangle is
In the given figure, if PB || CF and DP || EF, then \[\frac{AD}{DE} =\]
In a ∆ABC, perpendicular AD from A and BC meets BC at D. If BD = 8 cm, DC = 2 cm and AD = 4 cm, then
