Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a ∆ABC, perpendicular AD from A and BC meets BC at D. If BD = 8 cm, DC = 2 cm and AD = 4 cm, then
पर्याय
∆ABC is isosceles
∆ABC is equilateral
AC = 2AB
∆ABC is right-angled at A
उत्तर
Given: In ΔABC,`AD ⊥ BC`, BD = 8cm, DC = 2 cm and AD = 4cm.
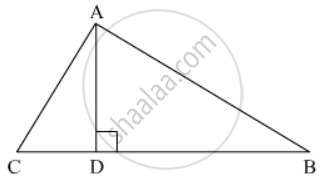
In ΔADC,
`AC^2=AD^2+DC^2`
`AC^2=4^2+2^2`
`AC^2=20`..............(1)
Similarly, in ΔADB
`AB^2=AD^2+BD^2`
`AB^2=4^2+8^2`
`AB^2=80`......................(2)
Now, In ΔABC
and
Hence, triangle ABC is right angled at A.
We got the result as (d)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A vertical stick of length 6 m casts a shadow 4 m long on the ground and at the same time a tower casts a shadow 28 m long. Find the height of the tower.
In a ΔABC, AD is the bisector of ∠A.
If AB = 5.6cm, BD = 3.2cm and BC = 6cm, find AC.
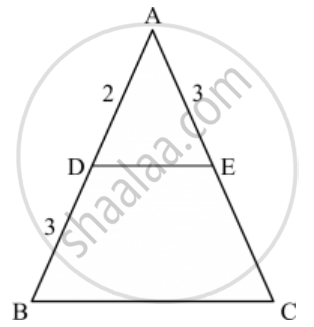
In each of the figures [(i)-(iv)] given below, a line segment is drawn parallel to one side of the triangle and the lengths of certain line-segment are marked. Find the value of x in each of the following :

What values of x will make DE || AB in the given figure?
The diagonals of quadrilateral ABCD intersect at O. Prove that
`[A(∆"ACB")]/[A(∆"ACD")] = "BO"/"DO"`
In the figure given below DE || BC. If AD = 2.4 cm, DB = 3.6 cm, AC = 5 cm. Find AE.
The areas of two similar triangles are 169 cm2 and 121 cm2 respectively. If the longest side of the larger triangle is 26 cm, what is the length of the longest side of the smaller triangle?
In a ∆ABC, ∠A = 90°, AB = 5 cm and AC = 12 cm. If AD ⊥ BC, then AD =
In the given figure, if ∠ADE = ∠ABC, then CE =
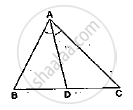
If ABC is an isosceles triangle and D is a point of BC such that AD ⊥ BC, then
