Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a ∆ABC, perpendicular AD from A and BC meets BC at D. If BD = 8 cm, DC = 2 cm and AD = 4 cm, then
विकल्प
∆ABC is isosceles
∆ABC is equilateral
AC = 2AB
∆ABC is right-angled at A
उत्तर
Given: In ΔABC,`AD ⊥ BC`, BD = 8cm, DC = 2 cm and AD = 4cm.
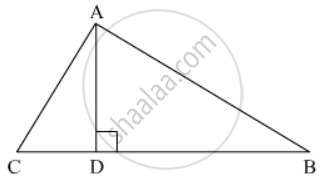
In ΔADC,
`AC^2=AD^2+DC^2`
`AC^2=4^2+2^2`
`AC^2=20`..............(1)
Similarly, in ΔADB
`AB^2=AD^2+BD^2`
`AB^2=4^2+8^2`
`AB^2=80`......................(2)
Now, In ΔABC
and
Hence, triangle ABC is right angled at A.
We got the result as (d)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the below figure, If AB || CD, find the value of x.
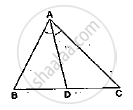
In a ΔABC, AD is the bisector of ∠A.
If AB = 5.6cm, BD = 3.2cm and BC = 6cm, find AC.
In the given figure, given that ∆ABC ∼ ∆PQR and quad ABCD ∼ quad PQRS. Determine the value of x, y, z in each case.
In each of the following figures, you find who triangles. Indicate whether the triangles are similar. Give reasons in support of your answer.
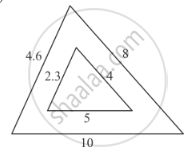
In each of the following figures, you find who triangles. Indicate whether the triangles are similar. Give reasons in support of your answer.
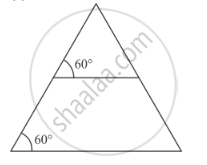
Corresponding sides of two triangles are in the ratio 2 : 3. If the area of the smaller triangle is 48 cm2, determine the area of the larger triangle.
Corresponding sides of two similar triangles are in the ratio 1 : 3. If the area of the smaller triangle in 40 cm2, find the area of the larger triangle.
In ∆ABC, ∠C is an obtuse angle. AD ⊥ BC and AB2 = AC2 + 3 BC2. Prove that BC = CD.
If the areas of two similar triangles ABC and PQR are in the ratio 9 : 16 and BC = 4.5 cm, what is the length of QR?
A man goes 24 m due west and then 7 m due north. How far is he from the starting point?
