Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
There is a staircase as shown in the given figure, connecting points A and B. Measurements of steps are marked in the figure. Find the straight line distance between A and B.

उत्तर
We are given the following figure with the related information
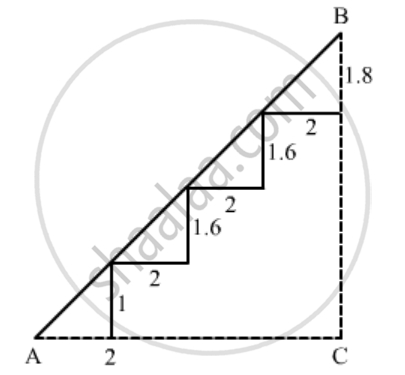
In the above figure complete the triangle ABC with right angled at C
So
AC = 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 8 and
BC = 1 + 1.6 + 1.6 + 1.8 = 6
Using Pythagoras theorem for triangle ABC to find
`AB^2=AC^2+BC^2`
`=8^2+6^2`
`=100`
`⇒ AB=10`
Hence the distance between A and B is 10 cm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In ∆ABC, P and Q are points on sides AB and AC respectively such that PQ || BC. If AP = 3 cm, PB = 5 cm and AC = 8 cm, find AQ.
Prove that in an equilateral triangle, three times the square of a side is equal to four times the square of its altitudes.
In ∆ABC, AD is a median. Prove that AB2 + AC2 = 2AD2 + 2DC2.
In ∆ABC, ∠ABC = 135°. Prove that AC2 = AB2 + BC2 + 4 ar (∆ABC)
In a triangle ABC, N is a point on AC such that BN ⊥ AC. If BN2 = AN . NC, prove that ∠B = 90°.
Two poles of height 6 m and 11 m stand vertically upright on a plane ground. If the distance between their foot is 12 m, the distance between their tops is
In a ∆ABC, AD is the bisector of ∠BAC. If AB = 6 cm, AC = 5 cm and BD = 3 cm, then DC =
In a ∆ABC, AD is the bisector of ∠BAC. If AB = 8 cm, BD = 6 cm and DC = 3 cm. Find AC
In an equilateral triangle ABC if AD ⊥ BC, then
∆ABC is an isosceles triangle in which ∠C = 90. If AC = 6 cm, then AB =
