Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
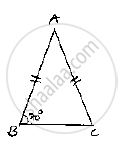
In a ΔABC, if AB = AC and ∠B = 70°, find ∠A.
उत्तर
Consider , ΔABC we have `∠B=70^@` and AB =AC
Since, AB A C ABC is an isosceles triangle
⇒ ∠B=∠C [Angles opposite to equal sides are equal]
⇒`∠B = ∠C = 70^@`
And also,
Sum of angles in a triangle `180^@`
⇒ `∠A+∠B+∠C=180^@`
⇒`∠A+70^@+70^@=180^@`
⇒`∠A+140^@=180^@`
⇒`∠A=180^@-140^@⇒∠A=40^@`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a squared sheet, draw two triangles of equal areas such that
The triangles are not congruent.
What can you say about their perimeters?
In an isosceles triangle, if the vertex angle is twice the sum of the base angles, then the measure of vertex angle of the triangle is
State, whether the pairs of triangles given in the following figures are congruent or not:

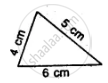
State, whether the pairs of triangles given in the following figures are congruent or not:
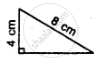
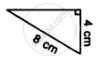
Which of the following pairs of triangles are congruent? Give reasons
ΔABC;(AB = 8cm,BC = 6cm,∠B = 100°);
ΔPQR;(PQ = 8cm,RP = 5cm,∠Q = 100°).
In the figure, RT = TS, ∠1 = 2∠2 and ∠4 = 2∠3. Prove that ΔRBT ≅ ΔSAT.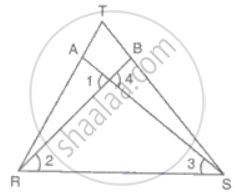
In ΔABC, AB = AC. D is a point in the interior of the triangle such that ∠DBC = ∠DCB. Prove that AD bisects ∠BAC of ΔABC.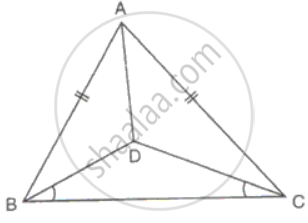
In ΔABC, AB = AC, BM and Cn are perpendiculars on AC and AB respectively. Prove that BM = CN.
Which of the following rule is not sufficient to verify the congruency of two triangles
“If two sides and an angle of one triangle are equal to two sides and an angle of another triangle, then the two triangles must be congruent.” Is the statement true? Why?
