Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In ΔABC, AB = AC. D is a point in the interior of the triangle such that ∠DBC = ∠DCB. Prove that AD bisects ∠BAC of ΔABC.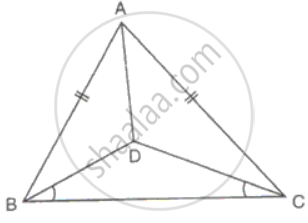
उत्तर
Since AB = AC
∠ABC = ∠ACB
But ∠DBC = ∠DBC
⇒ ∠ABD = ∠ACD
Now in ΔABD and ΔADC
AB = AC
AD = AD
∠ABD = ∠ACD
Therefore, ΔABD ≅ ΔADC ...(SSA criteria)
Hence, ∠BAD = ∠CAD
Thus, AD bisects ∠BAC.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If ΔDEF ≅ ΔBCA, write the part(s) of ΔBCA that correspond to ∠F
In a ΔABC, if AB = AC and ∠B = 70°, find ∠A.
In two right triangles one side an acute angle of one are equal to the corresponding side and angle of the othe Prove that the triangles are congruent.
ΔPQR and ΔABC is not congruent to ΔRPQ, then which of the following is not true:
Prove that:
(i) ∆ ABC ≅ ∆ ADC
(ii) ∠B = ∠D
Which of the following pairs of triangles are congruent? Give reasons
ΔABC;(AB = 5cm,BC = 7cm,CA = 9cm);
ΔKLM;(KL = 7cm,LM = 5cm,KM = 9cm).
In the given figure ABCD is a parallelogram, AB is Produced to L and E is a midpoint of BC. Show that:
a. DDCE ≅ DLDE
b. AB = BL
c. DC = `"AL"/(2)`
Two right-angled triangles ABC and ADC have the same base AC. If BC = DC, prove that AC bisects ∠BCD.
∆ABC and ∆PQR are congruent under the correspondence:
ABC ↔ RQP
Write the parts of ∆ABC that correspond to
(i) `bar"PQ"`
(ii)∠Q
(iii) `bar"RP"`
Given that ∆ABC ≅ ∆DEF List all the corresponding congruent sides
