Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the adjoining figure, ΔABC is right-angled at B and ∠A = 450. If AC = 3`sqrt(2)`cm, find (i) BC, (ii) AB.
उत्तर
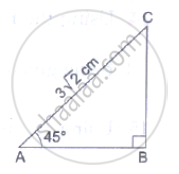
From the right-angled ΔABC, we have:
`(BC)/(AC) = sin 45^0`
⇒ `(BC)/(3sqrt(2)) = 1/sqrt(2) `⇒ BC = 3cm
Also, `(AB)/(AC) = cos 45^0`
⇒` (AB)/(3sqrt(2)) = 1/sqrt(2)` ⇒ AB = 3 cm
∴ BC = 3 cm and AB = 3 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If A = B = 60°, verify that sin (A − B) = sin A cos B − cos A sin B
If sin A = `9/41` find all the values of cos A and tan A
Evaluate:
`(sin^2 30^0 + 4 cot^2 45^0-sec^2 60^0)(cosec^2 45^0 sec^2 30^0)`
Show that:
(i)` (1-sin 60^0)/(cos 60^0)=(tan60^0-1)/(tan60^0+1)`
Verify each of the following:
(iv) `2 sin 45^0 cos 45^0`
If 5 cos θ = 3, evaluate : `(co secθ – cot θ)/(co secθ + cot θ)`
In each of the following, one trigonometric ratio is given. Find the values of the other trigonometric.
sinB = `sqrt(3)/(2)`
If cosec θ = `(29)/(20)`, find the value of: cosec θ - `(1)/("cot" θ)`
If sin θ = `"a"/sqrt("a"^2 + "b"^2)`, then show that b sin θ = a cos θ
Statement A (Assertion): For 0 < θ ≤ 90°, cosec θ – cot θ and cosec θ + cot θ are reciprocal of each other.
Statement R (Reason): cosec2 θ – cot2 θ = 1
