Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
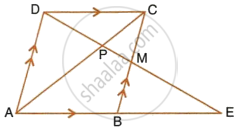
In the given figure, two chords AB and CD of a circle intersect each other at the point P (when produced) outside the circle. Prove that
(i) ΔPAC ∼ ΔPDB
(ii) PA.PB = PC.PD
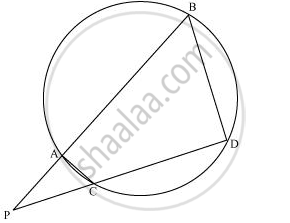
उत्तर
(i) In ΔPAC and ΔPDB,
∠P = ∠P (Common)
∠PAC = ∠PDB (Exterior angle of a cyclic quadrilateral is ∠PCA = ∠PBD equal to the opposite interior angle)
∴ ΔPAC ∼ ΔPDB
(ii)We know that the corresponding sides of similar triangles are proportional.
∴ PA/PD = AC/DB = PC/PB
=>PA/PD = PC/PB
∴ PA.PB = PC.PD
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In figure, considering triangles BEP and CPD, prove that BP × PD = EP × PC.
If a perpendicular is drawn from the vertex containing the right angle of a right triangle to the hypotenuse then prove that the triangle on each side of the perpendicular are similar to each other and to the original triangle. Also, prove that the square of the perpendicular is equal to the product of the lengths of the two parts of the hypotenuse
In ∆ABC, DE is parallel to base BC, with D on AB and E on AC. If `\frac{AD}{DB}=\frac{2}{3}` , find `\frac{BC}{DE}.`
Using Basic proportionality theorem, prove that a line drawn through the mid-points of one side of a triangle parallel to another side bisects the third side. (Recall that you have proved it in Class IX).
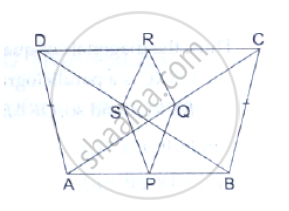
In the figure, PQRS is a parallelogram with PQ = 16 cm and QR = 10 cm. L is a point on PR such that RL : LP = 2 : 3. QL produced meets RS at M and PS produced at N.

Find the lengths of PN and RM.
On a map, drawn to a scale of 1 : 250000, a triangular plot PQR of land has the following measurements :
PQ = 3cm, QR = 4 cm and angles PQR = 90°
(i) the actual lengths of QR and PR in kilometer.
(ii) the actual area of the plot in sq . km.
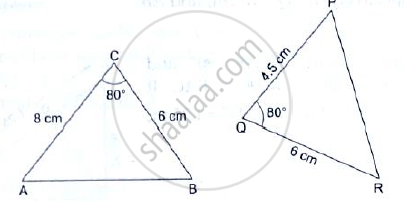
In each of the given pairs of triangles, find which pair of triangles are similar. State the similarity criterion and write the similarity relation in symbolic form:
In the given figure, if ∠ADE = ∠B, show that ΔADE ~ ΔABC. If AD = 3.8cm, AE = 3.6cm, BE = 2.1cm and BC = 4.2cm, find DE.
The corresponding sides of two similar triangles ABC and DEF are BC = 9.1cm and EF = 6.5cm. If the perimeter of ΔDEF is 25cm, find the perimeter of ΔABC.
In the given figure, ∠ABC = 90° and BD⊥AC. If AB = 5.7cm, BD = 3.8cm and CD = 5.4cm, find BC.
ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AD = BC. If P, Q, R, S be the midpoints of AB, AC, CD and BD respectively, show that PQRS is a rhombus.
ΔABC~ΔPQR and ar(ΔABC) = 4, ar(ΔPQR) . If BC = 12cm, find QR.
ΔABC is right angled at A and AD⊥BC. If BC = 13cm and AC = 5cm, find the ratio of the areas of ΔABC and ΔADC.
The length of a river in a map is 54cm. if lcm on the map represents 12500m on land, find the length of the river.
A triangle LMN has been reduced by scale factor 0.8 to the triangle L' M' N'. Calculate: the length of LM, if L' M' = 5.4 cm.
A triangle ABC is enlarged, about the point O as centre of enlargement, and the scale factor is 3. Find : A' B', if AB = 4 cm.
A line segment DE is drawn parallel to base BC of ΔABC which cuts AB at point D and AC at point E. If AB = 5BD and EC = 3.2 cm, find the length of AE.
In the following figure, M is mid-point of BC of a parallelogram ABCD. DM intersects the diagonal AC at P and AB produced at E. Prove that : PE = 2 PD
Prove that, if a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides, then the two sides are divided in the same ratio.
In ΔPQR, L and M are two points on the base QR, such that ∠LPQ = ∠QRP and ∠RPM = ∠RQP.
Prove that : (i) ΔPQL ∼ ΔRPM
(ii) QL. Rm = PL. PM
(iii) PQ2 = QR. QL.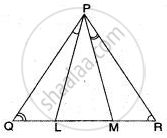
In the adjoining figure, the medians BD and CE of a ∆ABC meet at G. Prove that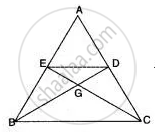
(i) ∆EGD ∼ ∆CGB and
(ii) BG = 2GD for (i) above.
In a quadrilateral PQRS, the diagonals PR and QS intersect each other at the point T. If PT:TR = QT :TS = 1:2, show that ΔPTQ - DRTS
The scale of a map is 1 : 50000. The area of a city is 40 sq km which is to be represented on the map. Find: The area of land represented on the map.
The scale of a map is 1 : 50000. The area of a city is 40 sq km which is to be represented on the map. Find: The length of a scale in km represented by 1cm on the map.
A map is drawn to scale of 1:20000. Find: The distance on the map representing 4km
In the adjacent figure, ∆ABC is right angled at C and DE ⊥ AB. Prove that ∆ABC ~ ∆ADE and hence find the lengths of AE and DE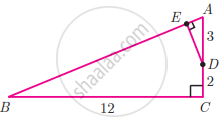
If ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF such that area of ∆ABC is 9 cm2 and the area of ∆DEF is 16 cm2 and BC = 2.1 cm. Find the length of EF.
ΔDEF ~ ΔABC. If DE : AB = 2 : 3 and ar ΔDEF is equal to 44 square units then ar (ΔABC) (square unit) is ______.
In a square of side 10 cm, its diagonal = ______.
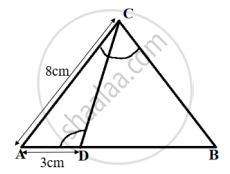
In the given figure, ∠ACB = ∠CDA, AC = 8cm, AD = 3cm, then BD is ______.