Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a simple harmonic motion
(a) the maximum potential energy equals the maximum kinetic energy
(b) the minimum potential energy equals the minimum kinetic energy
(c) the minimum potential energy equals the maximum kinetic energy
(d) the maximum potential energy equals the minimum kinetic energy
उत्तर
(a) the maximum potential energy equals the maximum kinetic energy
(b) the minimum potential energy equals the minimum kinetic energy
In SHM,
maximum kinetic energy = \[\frac{1}{2}k A^2\]
maximum potential energy =\[\frac{1}{2}k A^2\]
The minimum value of both kinetic and potential energy is zero.
Therefore, in a simple harmonic motion the maximum kinetic energy and maximum potential energy are equal. Also, the minimum kinetic energy and the minimum potential energy are equal.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define phase of S.H.M.
A particle executes simple harmonic motion Let P be a point near the mean position and Q be a point near an extreme. The speed of the particle at P is larger than the speed at Q. Still the particle crosses Pand Q equal number of times in a given time interval. Does it make you unhappy?
A pendulum clock gives correct time at the equator. Will it gain time or loose time as it is taken to the poles?
A hollow sphere filled with water is used as the bob of a pendulum. Assume that the equation for simple pendulum is valid with the distance between the point of suspension and centre of mass of the bob acting as the effective length of the pendulum. If water slowly leaks out of the bob, how will the time period vary?
A student says that he had applied a force \[F = - k\sqrt{x}\] on a particle and the particle moved in simple harmonic motion. He refuses to tell whether k is a constant or not. Assume that he was worked only with positive x and no other force acted on the particle.
A particle executes simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 10 cm and time period 6 s. At t = 0 it is at position x = 5 cm going towards positive x-direction. Write the equation for the displacement x at time t. Find the magnitude of the acceleration of the particle at t = 4 s.
A pendulum clock giving correct time at a place where g = 9.800 m/s2 is taken to another place where it loses 24 seconds during 24 hours. Find the value of g at this new place.
A simple pendulum is constructed by hanging a heavy ball by a 5.0 m long string. It undergoes small oscillations. (a) How many oscillations does it make per second? (b) What will be the frequency if the system is taken on the moon where acceleration due to gravitation of the moon is 1.67 m/s2?
A spherical ball of mass m and radius r rolls without slipping on a rough concave surface of large radius R. It makes small oscillations about the lowest point. Find the time period.
Assume that a tunnel is dug across the earth (radius = R) passing through its centre. Find the time a particle takes to cover the length of the tunnel if (a) it is projected into the tunnel with a speed of \[\sqrt{gR}\] (b) it is released from a height R above the tunnel (c) it is thrown vertically upward along the length of tunnel with a speed of \[\sqrt{gR}\]
A simple pendulum of length 1 feet suspended from the ceiling of an elevator takes π/3 seconds to complete one oscillation. Find the acceleration of the elevator.
A particle is subjected to two simple harmonic motions, one along the X-axis and the other on a line making an angle of 45° with the X-axis. The two motions are given by x = x0 sin ωt and s = s0 sin ωt. Find the amplitude of the resultant motion.
In a simple harmonic oscillation, the acceleration against displacement for one complete oscillation will be __________.
A simple pendulum is suspended from the roof of a school bus which moves in a horizontal direction with an acceleration a, then the time period is
State the laws of the simple pendulum?
Consider two simple harmonic motion along the x and y-axis having the same frequencies but different amplitudes as x = A sin (ωt + φ) (along x-axis) and y = B sin ωt (along y-axis). Then show that
`"x"^2/"A"^2 + "y"^2/"B"^2 - (2"xy")/"AB" cos φ = sin^2 φ`
and also discuss the special cases when
- φ = 0
- φ = π
- φ = `π/2`
- φ = `π/2` and A = B
- φ = `π/4`
Note: when a particle is subjected to two simple harmonic motions at right angle to each other the particle may move along different paths. Such paths are called Lissajous figures.
A spring is stretched by 5 cm by a force of 10 N. The time period of the oscillations when a mass of 2 kg is suspended by it is ______
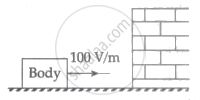
A body having specific charge 8 µC/g is resting on a frictionless plane at a distance 10 cm from the wall (as shown in the figure). It starts moving towards the wall when a uniform electric field of 100 V/m is applied horizontally toward the wall. If the collision of the body with the wall is perfectly elastic, then the time period of the motion will be ______ s.
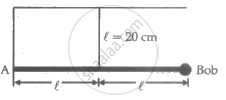
A weightless rigid rod with a small iron bob at the end is hinged at point A to the wall so that it can rotate in all directions. The rod is kept in the horizontal position by a vertical inextensible string of length 20 cm, fixed at its midpoint. The bob is displaced slightly, perpendicular to the plane of the rod and string. The period of small oscillations of the system in the form `(pix)/10` is ______ sec. and the value of x is ______.
(g = 10 m/s2)
Assume there are two identical simple pendulum clocks. Clock - 1 is placed on the earth and Clock - 2 is placed on a space station located at a height h above the earth's surface. Clock - 1 and Clock - 2 operate at time periods 4 s and 6 s respectively. Then the value of h is ______.
(consider the radius of earth RE = 6400 km and g on earth 10 m/s2)
