Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In triangles ABC and PQR, AB = AC, ∠C = ∠P and ∠B = ∠Q. The two triangles are ______.
पर्याय
isosceles but not congruent
isosceles and congruent
congruent but not isosceles
neither congruent nor isosceles
उत्तर
In triangles ABC and PQR, AB = AC, ∠C = ∠P and ∠B = ∠Q. The two triangles are isosceles but not congruent.
Explanation:
In triangle ABC,
AB = AC ...[Given]
∠C = ∠B ...[Angle opposite to equal sides are equal]
So, in triangle ABC is an isosceles triangle.
∠B = ∠Q ...[Given]
∠C = ∠P
∠P = ∠Q ...[Since, ∠C = ∠B]
QR = PR ...[Sides opposite to equal angles are equal]
So, in triangle PQR is also an isosceles triangle.
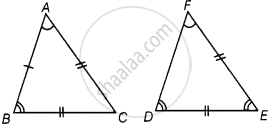
Hence, both triangle are isosceles but not congruent.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a ΔABC, if ∠A=l20° and AB = AC. Find ∠B and ∠C.
Two lines AB and CD intersect at O such that BC is equal and parallel to AD. Prove that the lines AB and CD bisect at O.
Which of the following statements are true (T) and which are false (F):
The bisectors of two equal angles of a triangle are equal
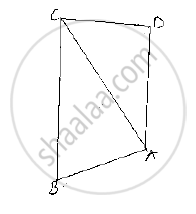
In Fig. 10.131, prove that: (i) CD + DA + AB + BC > 2AC (ii) CD + DA + AB > BC
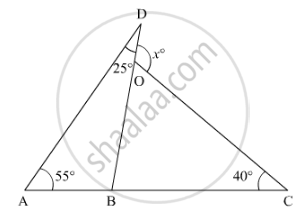
In the given figure, the value of x is ______.
In ∆ABC, AB = AC and ∠B = 50°. Then ∠C is equal to ______.
In ∆PQR, ∠R = ∠P and QR = 4 cm and PR = 5 cm. Then the length of PQ is ______.
D is a point on the side BC of a ∆ABC such that AD bisects ∠BAC. Then ______.
It is given that ∆ABC ≅ ∆FDE and AB = 5 cm, ∠B = 40° and ∠A = 80°. Then which of the following is true?
In a triangle ABC, D is the mid-point of side AC such that BD = `1/2` AC. Show that ∠ABC is a right angle.
