Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
D is a point on the side BC of a ∆ABC such that AD bisects ∠BAC. Then ______.
पर्याय
BD = CD
BA > BD
BD > BA
CD > CA
उत्तर
D is a point on the side BC of a ∆ABC such that AD bisects ∠BAC. Then BA > BD.
Explanation:
Given, ∆ABC such that AD bisects ∠BAC
∴ ∠BAD = ∠CAD ...(i)
In ∆ACD, ∠BDA is an exterior angle.
∴ ∠BDA > ∠CAD [∵ Exterior angle > interior opposite angle] ...(i)
⇒ ∠BDA > ∠BAD ...[From equation (i)]
⇒ BA > BD ...[Side opposite to greater angle is greater]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
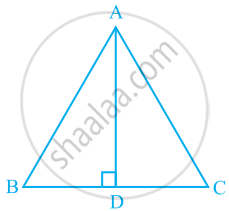
In ΔABC, AD is the perpendicular bisector of BC (see the given figure). Show that ΔABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC.
Which of the following statements are true (T) and which are false (F):
The bisectors of two equal angles of a triangle are equal
Fill in the blank to make the following statement true.
If two angles of a triangle are unequal, then the smaller angle has the........ side opposite to it.
In the given figure, the sides BC, CA and AB of a Δ ABC have been produced to D, E and F respectively. If ∠ACD = 105° and ∠EAF = 45°, find all the angles of the Δ ABC.
If the angles A, B and C of ΔABC satisfy the relation B − A = C − B, then find the measure of ∠B.
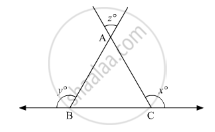
In the given figure, what is z in terms of x and y?
In ∆ABC, AB = AC and ∠B = 50°. Then ∠C is equal to ______.
M is a point on side BC of a triangle ABC such that AM is the bisector of ∠BAC. Is it true to say that perimeter of the triangle is greater than 2 AM? Give reason for your answer.
CDE is an equilateral triangle formed on a side CD of a square ABCD (Figure). Show that ∆ADE ≅ ∆BCE.
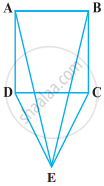
Show that in a quadrilateral ABCD, AB + BC + CD + DA < 2(BD + AC)
