Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Let i0 be the thermionic current from a metal surface when the absolute temperature of the surface is T0. The temperature is slowly increased and the thermionic current is measured as a function of temperature. Which of the following plots may represent the variation in (i/i0) against (T/T0)?
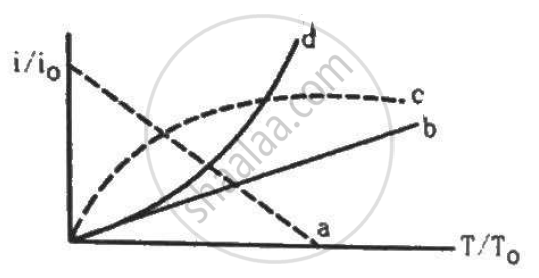
पर्याय
a
b
c
d
उत्तर
d
Since the thermionic current is directly proportional to the square of the temperature of the surface emitting thermions, the graph is parabolic.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the maximum frequency of X-rays produced by 30 kV electrons.
Find the (a) maximum frequency, and (b) minimum wavelength of X-rays produced by 30 kV electrons.
The work function of caesium metal is 2.14 eV. When light of frequency 6 × 1014 Hz is incident on the metal surface, photoemission of electrons occurs. What is the
(a) maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons,
(b) Stopping potential, and
(c) maximum speed of the emitted photoelectrons?
Why should gases be insulators at ordinary pressures and start conducting at very low pressures?
How does one explain the emission of electrons from a photosensitive surface with the help of Einstein's photoelectric equation?
The work function of the following metals is given : Na 2.75 ev, K = 2.3 eV, Mo = 4.17 eV and Ni = 5.15 eV. Which of these metals will not cause photoelectric emission for radiation of wavelength 3300 Å from a laser source placed 1 m away from these metals? What happens if the laser source is brought nearer and placed 50 cm away?
How will the thermionic current vary if the filament current is increased?
An isolated metal sphere is heated to a high temperature. Will it become positively charged due to thermionic emission?
The cathode of a diode valve is replaced by another cathode of double the surface area. Keeping the voltage and temperature conditions the same, will the place current decrease, increase or remain the same?
The constant A in the Richardson−Dushman equation for tungsten is 60 × 104 A m−2K−2. The work function of tungsten is 4.5 eV. A tungsten cathode with a surface area 2.0 × 10−5 m2 is heated by a 24 W electric heater. In steady state, the heat radiated by the heater and the cathode equals the energy input by the heater and the temperature becomes constant. Assuming that the cathode radiates like a blackbody, calculate the saturation current due to thermions. Take Stefan's Constant = 6 × 10−8 W m−2 K−1. Assume that the thermions take only a small fraction of the heat supplied.
The wavelength λe of an electron and λp of a photon of same energy E are related by
The wave associated with a moving particle of mass 3 × 10–6 g has the same wavelength as an electron moving with a velocity 6 × 106 ms–1. The velocity of the particle is
Emission of electrons by the absorption of heat energy is called ____________ emission.
Why do metals have a large number of free electrons?
In which case is electron emission from a metal not known?
Name the factors on which photoelectric emission from a surface depends.
The work function of a metal is 2.31 eV. Photoelectric emission occurs when the light of frequency 6.4 × 1014 Hz is incident on the metal surface. Calculate
- the energy of the incident radiation,
- the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electron and
- the stopping potential of the surface.
