Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The work function of caesium metal is 2.14 eV. When light of frequency 6 × 1014 Hz is incident on the metal surface, photoemission of electrons occurs. What is the
(a) maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons,
(b) Stopping potential, and
(c) maximum speed of the emitted photoelectrons?
उत्तर
Work function of caesium metal, `phi_"o"` = 2.14 eV
Frequency of light, v = 6.0 × 1014 Hz
(a) The maximum kinetic energy is given by the photoelectric effect as:
`"K" = "hv" - phi_"o"`
Where,
h = Planck’s constant = 6.626 × 10−34 Js
∴ K = `(6.626 xx 10^34 xx 6 xx 10^14)/(1.6 xx 10^(-19)) - 2.14`
= 2.485 − 2.140
= 0.345 eV
Hence, the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons is 0.345 eV.
(b) For stopping potential `"V"_"o"`, we can write the equation for kinetic energy as:
`"K" = "eV"_"o"`
∴ `"V"_"o" = "K"/"e"`
= `(0.345 xx 1.6 xx 10^(-19))/(1.6 xx 10^(-19))`
= 0.345 V
Hence, the stopping potential of the material is 0.345 V.
(c) Maximum speed of the emitted photoelectrons = v
Hence, the relation for kinetic energy can be written as:
`"K" = 1/2 "mv"^2`
Where,
m = Mass of an electron = 9.1 × 10−31 kg
`"v"^2 = (2"K")/"m"`
= `(2 xx 0.345 xx 1.6 xx 10^(-19))/(9.1 xx 10^(-31))`
= 0.1104 × 1012
∴ v = 3.323 × 105 m/s
= 332.3 km/s
Hence, the maximum speed of the emitted photoelectrons is 332.3 km/s.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why should gases be insulators at ordinary pressures and start conducting at very low pressures?
The work function of the following metals is given : Na 2.75 ev, K = 2.3 eV, Mo = 4.17 eV and Ni = 5.15 eV. Which of these metals will not cause photoelectric emission for radiation of wavelength 3300 Å from a laser source placed 1 m away from these metals? What happens if the laser source is brought nearer and placed 50 cm away?
Would you prefer a material with a high melting point or a low melting point to be used as a cathode in a diode?
A diode value is connected to a battery and a load resistance. The filament is heated, so that a constant current is obtained in the circuit. As the cathode continuously emits electrons, does it become more and more positively charged?
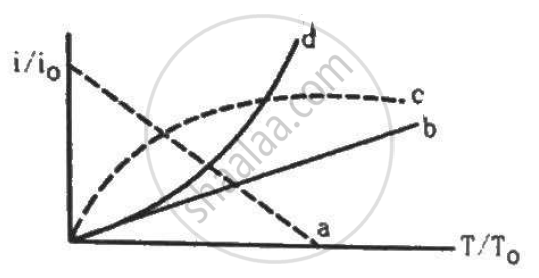
Let i0 be the thermionic current from a metal surface when the absolute temperature of the surface is T0. The temperature is slowly increased and the thermionic current is measured as a function of temperature. Which of the following plots may represent the variation in (i/i0) against (T/T0)?
The work function of aluminum is 4⋅2 eV. If two photons each of energy 2⋅5 eV are incident on its surface, will the emission of electrons take place? Justify your answer.
The wavelength λe of an electron and λp of a photon of same energy E are related by
Emission of electrons by the absorption of heat energy is called ____________ emission.
Define the work function of a metal. Give its unit.
A 150 W lamp emits light of the mean wavelength of 5500 Å. If the efficiency is 12%, find out the number of photons emitted by the lamp in one second.
In which case is electron emission from a metal not known?
Consider Figure for photoemission.
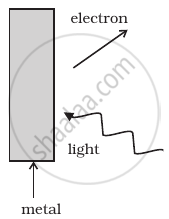
How would you reconcile with momentum conservation? Note light (photons) have momentum in a different direction than the emitted electrons.
Give an example each of a metal from which photoelectric emission takes place when irradiated by
- UV light
- visible light.
Name the factors on which photoelectric emission from a surface depends.
The work function of a metal is 2.31 eV. Photoelectric emission occurs when the light of frequency 6.4 × 1014 Hz is incident on the metal surface. Calculate
- the energy of the incident radiation,
- the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electron and
- the stopping potential of the surface.
