Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State Gauss's law in electrostatics. Show, with the help of a suitable example along with the figure, that the outward flux due to a point charge 'q'. in vacuum within a closed surface, is independent of its size or shape and is given by `q/ε_0`
उत्तर
Statement: The electric flux linked with a closed surface is equal to `(1)/ε_0` times the net charge enclosed by a closed surface.
Mathematical expression :
`Ø_"E" = oint vec"E".dvec"s" = (1)/(ε_0) (q_"net")`
Consider two spherical surfaces of radius r and 2r respectively and a charge 1 is enclosed in it. According to gauss theorem, the total electric flux linked with a closed surface depends on the charge enclosed in it so
(a)
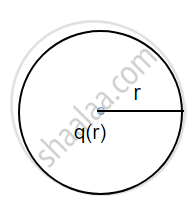
(b)
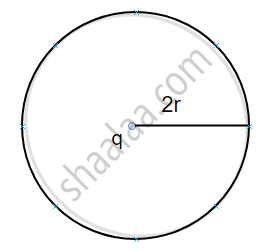
`Ø_E = q/ε_0 "and for fig"("b")`
`Ø_E = q/ε_0`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A thin conducting spherical shell of radius R has charge Q spread uniformly over its surface. Using Gauss’s law, derive an expression for an electric field at a point outside the shell.
Answer the following question.
State Gauss's law on electrostatics and drive expression for the electric field due to a long straight thin uniformly charged wire (linear charge density λ) at a point lying at a distance r from the wire.
The Gaussian surface ______.
Five charges q1, q2, q3, q4, and q5 are fixed at their positions as shown in figure. S is a Gaussian surface. The Gauss’s law is given by `oint_s E.ds = q/ε_0`
Which of the following statements is correct?
If `oint_s` E.dS = 0 over a surface, then ______.
- the electric field inside the surface and on it is zero.
- the electric field inside the surface is necessarily uniform.
- the number of flux lines entering the surface must be equal to the number of flux lines leaving it.
- all charges must necessarily be outside the surface.
If there were only one type of charge in the universe, then ______.
- `oint_s` E.dS ≠ 0 on any surface.
- `oint_s` E.dS = 0 if the charge is outside the surface.
- `oint_s` E.dS could not be defined.
- `oint_s` E.dS = `q/ε_0` if charges of magnitude q were inside the surface.
Refer to the arrangement of charges in figure and a Gaussian surface of radius R with Q at the centre. Then
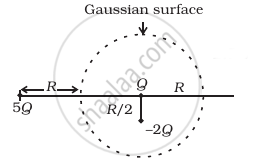
- total flux through the surface of the sphere is `(-Q)/ε_0`.
- field on the surface of the sphere is `(-Q)/(4 piε_0 R^2)`.
- flux through the surface of sphere due to 5Q is zero.
- field on the surface of sphere due to –2Q is same everywhere.
In finding the electric field using Gauss law the formula `|vec"E"| = "q"_"enc"/(epsilon_0|"A"|)` is applicable. In the formula ε0 is permittivity of free space, A is the area of Gaussian surface and qenc is charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface. This equation can be used in which of the following situation?
