Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The linkage present in Lactose is ______.
पर्याय
α, β - 1, 2 - glycosidic linkage
α - 1, 4 - glycosidic linkage
β - 1, 4 - glycosidic linkage
α - 1, 4 - glycosidic linkage
उत्तर
The linkage present in Lactose is β - 1, 4 - glycosidic linkage.
Explanation:
Lactose is a disaccharide composed of glucose and galactose.
These two monosaccharides are joined by a β-1,4-glycosidic bond, where the hydroxyl group on carbon 1 of galactose (in the β-configuration) is linked to the hydroxyl group on carbon 4 of glucose.
This type of linkage is hydrolysed by the enzyme lactase in the human body during digestion.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give scientific reasons:
The disaccharide sucrose gives negative Tollens test while the disaccharide maltose gives a positive Tollens test.
Draw a neat diagram for the following:
Haworth formula of glucopyranose.
Write the name of the polysaccharide used for the commercial preparation of glucose.
Write chemical reaction for following conversions
glucose into gluconic acid
By which of the following process formation of glycosidic bond occurs?
Identify the given structure 'P' and 'Q'.
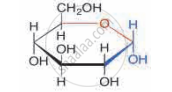
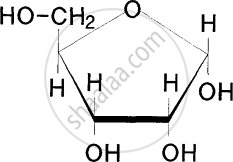
Which enzymes would work sequentially on potatoes consumed by an individual?
The reserve food material in animals is ____________.
Identify a non-reducing carbohydrate from the following.
Monosaccharides are ______ in nature.
Identify the CORRECT combination.
Prolonged heating of glucose with hot HI results in the formation of ____________.
Which element among the following is not present in saccharine?
Which one of the following carbohydrates is insoluble in water?
Which one of the following is NOT soluble in water?
Identify the number of secondary carbon atoms in glucose.
Identify the number of oxygen atoms present in saccharic acid?
Which among the following is a product of hydrolysis of one mole raffinose?
Which one of the following rotates the plane polarized light towards left?
α-D (+) Glucose and β-D (+) glucose are ____________.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active?
Is the following sugar, D-sugar or L-sugar?
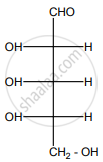
The molecule of glucose is also called ______.
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called ______.
Which carbon atoms of fructose are bonded together through oxygen forming fructofuranose?
Starch and cellulose are compounds made up of many units of ______.
Consider the following reaction
\[\ce{A <-[Br2 - H2O] Glucose ->[HNO3] B}\]
Here, 'A' and 'B' are respectively.
Identify the product obtained in the following conversion.
\[\ce{Glucose ->[(O)][Br2 water] Product}\]
Explain the hydrolysis of sucrose.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
