Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The radius of the innermost electron orbit of a hydrogen atom is 5.3 × 10−11 m. What are the radii of the n = 2 and n = 3 orbits?
उत्तर
The radius of the innermost orbit of a hydrogen atom, r1 = 5.3 × 10−11 m.
Let r2 be the radius of the orbit at n = 2. It is related to the radius of the innermost orbit as:
`"r"_2 = ("n")^2 "r"_1`
= 4 × 5.3 × 10−11
= 2.12 × 10−10 m
For n = 3, we can write the corresponding electron radius as:
`"r"_3 = ("n")^2 "r"_1`
= 9 × 5.3 × 10−11
= 4.77 × 10−10 m
Hence, the radii of an electron for n = 2 and n = 3 orbits are 2.12 × 10−10 m and 4.77 × 10−10 m respectively.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(i) State Bohr's quantization condition for defining stationary orbits. How does the de Broglie hypothesis explain the stationary orbits?
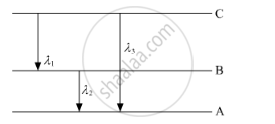
(ii) Find the relation between three wavelengths λ1, λ2 and λ3 from the energy-level diagram shown below.
The ratio of kinetic energy of an electron in Bohr’s orbit to its total energy in the same orbit is
(A) – 1
(B) 2
(C) 1/2
(D) – 0.5
Write the expression for Bohr’s radius in hydrogen atom ?
The numerical value of ionization energy in eV equals the ionization potential in volts. Does the equality hold if these quantities are measured in some other units?
Calculate angular momentum of an electron in the third Bohr orbit of a hydrogen atom.
How are various lines of Lyman series formed? Explain on the basis of Bohr’s theory.
The energy associated with the first orbit of He+ is ____________ J.
When an electric discharge is passed through hydrogen gas, the hydrogen molecules dissociate to produce excited hydrogen atoms. These excited atoms emit electromagnetic radiation of discrete frequencies which can be given by the general formula
`bar(v) = 109677 1/n_1^2 - 1/n_f^2`
What points of Bohr’s model of an atom can be used to arrive at this formula? Based on these points derive the above formula giving description of each step and each term.
Consider two different hydrogen atoms. The electron in each atom is in an excited state. Is it possible for the electrons to have different energies but same orbital angular momentum according to the Bohr model? Justify your answer.
Derive an expression for the frequency of radiation emitted when a hydrogen atom de-excites from level n to level (n – 1). Also show that for large values of n, this frequency equals to classical frequency of revolution of an electron.
When an electron falls from a higher energy to a lower energy level, the difference in the energies appears in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Why cannot it be emitted as other forms of energy?
The wavelength in Å of the photon that is emitted when an electron in Bohr orbit with n = 2 returns to orbit with n = 1 in H atom is ______ Å. The ionisation potential of the ground state of the H-atom is 2.17 × 10−11 erg.
An electron in H-atom makes a transition from n = 3 to n = 1. The recoil momentum of the H-atom will be ______.
A hydrogen atom in its first excited state absorbs a photon of energy x × 10-2 eV and exited to a higher energy state where the potential energy of electron is -1.08 eV. The value of x is ______.
In Bohr's atomic model of hydrogen, let K. P and E are the kinetic energy, potential energy and total energy of the electron respectively. Choose the correct option when the electron undergoes transitions to a higher level:
In Bohr's theory of hydrogen atom, the electron jumps from higher orbit n to lower orbit p. The wavelength will be minimum for the transition ______.
What is meant by ionisation energy?
The wavelength of the second line of the Balmer series in the hydrogen spectrum is 4861 Å. Calculate the wavelength of the first line of the same series.
How much is the angular momentum of an electron when it is orbiting in the second Bohr orbit of hydrogen atom?
The figure below is the Energy level diagram for the Hydrogen atom. Study the transitions shown and answer the following question:
- State the type of spectrum obtained.
- Name the series of spectrum obtained.

