Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The SI unit of the potential gradient is ______
पर्याय
V/cm
V-m
V/m
V-cm
उत्तर
The SI unit of the potential gradient is V/m.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A potentiometer wire has resistance of per unit length of 0.1 Ω/m. A cell of e.m.f. 1.5 V balances against a 300 cm length of the wire. Find the current in the potentiometer wire.
Write two factors by which current sensitivity of a potentiometer can be increased.
Figure shows a 2.0 V potentiometer used for the determination of internal resistance of a 1.5 V cell. The balance point of the cell in open circuit is 76.3 cm. When a resistor of 9.5 Ω is used in the external circuit of the cell, the balance point shifts to 64.8 cm length of the potentiometer wire. Determine the internal resistance of the cell.
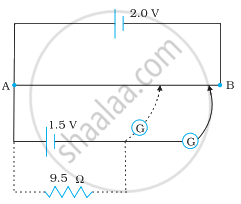
State the advantages of potentiometer over voltmeter.
SI unit of potential gradient is _______.
(a) V cm
(b) `V/"cm"`
(c) Vm
(d) `V/m`
State the principle of a potentiometer. Define potential gradient. Obtain an expression for potential gradient in terms of resistivity of the potentiometer wire.
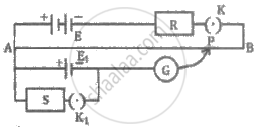
State the working principle of a potentiometer. With the help of the circuit diagram, explain how a potentiometer is used to compare the emf's of two primary cells. Obtain the required expression used for comparing the emfs.
Two students ‘X’ and ‘Y’ perform an experiment on potentiometer separately using the circuit given below:
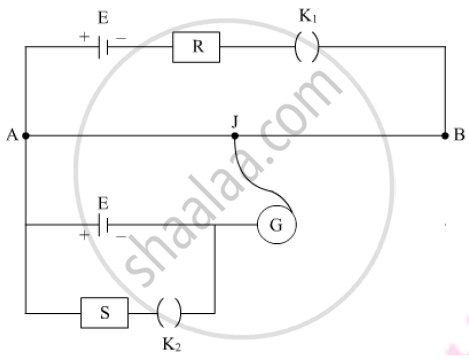
Keeping other parameters unchanged, how will the position of the null point be affected if
(i) ‘X’ increases the value of resistance R in the set-up by keeping the key K1 closed and the Key K2 opens?
(ii) ‘Y’ decreases the value of resistance S in the set-up, while the key K2 remains open and they K1 closed?
Justify.
Write the principle of working of a potentiometer. Describe briefly, with the help of a circuit diagram, how a potentiometer is used to determine the internal resistance of a given cell.
The net resistance of an ammeter should be small to ensure that _______________ .
Define potential gradient of the potentiometer wire.
How is potential gradient measured? Explain.
State the uses of a potentiometer.
Describe how a potentiometer is used to compare the EMFs of two cells by connecting the cells individually.
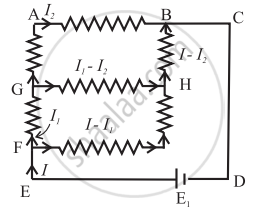
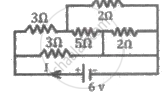
Find the equivalent resistance between the terminals of A and B in the network shown in the figure below given that the resistance of each resistor is 10 ohm.
Describe how a potentiometer is used to compare the emf's of two cells by the combination method.
The emf of a cell is balanced by a length of 120 cm of a potentiometer wire. When the cell is shunted by a resistance of 10 Ω, the balancing length is reduced by 20 cm. Find the internal resistance of the cell.
If the potential gradient of a wire decreases, then its length ______
What are the disadvantages of a potentiometer over a voltmeter?
A cell of e.m.f 1.5V and negligible internal resistance is connected in series with a potential meter of length 10 m and the total resistance of 20 Ω. What resistance should be introduced in the resistance box such that the potential drop across the potentiometer is one microvolt per cm of the wire?
Which of the following instruments is not a direct reading instrument?
In a potentiometer experiment, when the galvanometer shows no deflection, then no current flows through ____________.
The potentiometer is more sensitive, when ______.
The resistivity of potentiometer wire is 40 × 10-8 ohm - metre and its area of cross-section is 8 × 10-6 m2. If 0.2 ampere current is flowing through the wire, the potential gradient of the wire is ______.
A potentiometer wire has length L For given cell of emf E, the balancing length is `"L"/3` from 3 the positive end of the wire. If the length of the potentiometer wire is increased by 50%, then for the same cell, the balance point is obtained at length.
To determine the internal resistance of a cell by using potentiometer, the null point is at 1 m when cell is shunted by 3 Ω resistance and at a length 1.5 m when cell is shunted by 6 Ω resistance. The internal resistance of the cell is ______.
A cell of e.m.f. 'E' is connected across a resistance 'R'. The potential difference across the terminals of the cell is 90% ofE. The internal resistance of the cell is ______.
The length of a wire of a potentiometer is 100 cm, and the e.m.f of its standard cell is E volt. It is employed to measure the e.m.f of a battery whose internal resistance is 0.5 `Omega` If the balance point is obtained at `l`= 30 cm from the positive end, the e.m.f of the battery is ____________.
where 'i' is the current in the potentiometer
In the given figure, battery E is balanced on 55 cm length of potentiometer wire but when a resistance of 10 `Omega` is connected in parallel with the battery, then it balances on 50 cm length of the potentiometer wire. The internal resistance r of the battery is ____________.
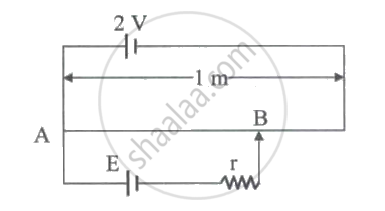
A potentiometer is used to measure the potential difference between A and B, the null point is obtained at 0.9 m. Now the potential difference between A and C is measured, the null point is obtained at 0.3 m. The ratio `E_2/E_1` is (E1 > E2) ______

The current drawn from the battery in the given network is ______
(Internal resistance of the battery is neglected)
A wire has a length of 2m and a resistance of 10Ω. It is connected in series with a resistance of 990Ω and a cell of e.m.f. 2V. The potential gradient along the wire will be ______
In the experiment to determine the internal resistance of a cell (E1) using a potentiometer, the resistance drawn from the resistance box is 'R'. The potential difference across the balancing length of the wire is equal to the terminal potential difference (V) of the cell. The value of internal resistance (r) of the cell is ______
If the length of potentiometer wire is increased, then the length of the previously obtained balance point will ______.
Two students X and Y perform potentiometer experiment separately and null point was obtained as shown in diagram. During the experiment, ______.
- X increases the value of R (resistance)
- Y decreases the value of S (resistance)
The position of null point obtained by students X and Y respectively.
A potentiometer wire of length 'L' and a resistance 'r' are connected in series with a battery of E.M.F. 'E0' and a resistance 'r1'. A cell of unknown E.M.F, 'E' is balanced at a length 'ℓ' of the potentiometer wire. The unknown E.M.F. E is given by ______
In the potentiometer experiment, the balancing length with a cell E1 of unknown e.m.f. is 'ℓ1' cm. By shunting the cell with resistance R Ω, the balancing length becomes `ℓ_1/2` cm, the internal resistance (r) of a cell is ______
A potentiometer is an accurate and versatile device to make electrical measurements of E.M.F. because the method involves ______.
The best instrument for accurate measurement of EMF of a cell is ____________.
Three resistance each of 4Ω are connected to from a triangle. The resistance b / w two terminal is
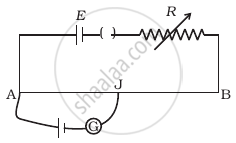
AB is a potentiometer wire (Figure). If the value of R is increased, in which direction will the balance point J shift?
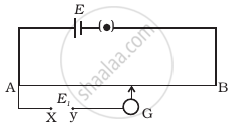
While doing an experiment with potentiometer (Figure) it was found that the deflection is one sided and (i) the deflection decreased while moving from one end A of the wire to the end B; (ii) the deflection increased. while the jockey was moved towards the end B.
- Which terminal + or – ve of the cell E1, is connected at X in case (i) and how is E1 related to E?
- Which terminal of the cell E1 is connected at X in case (ii)?
In an experiment with a potentiometer, VB = 10V. R is adjusted to be 50Ω (Figure). A student wanting to measure voltage E1 of a battery (approx. 8V) finds no null point possible. He then diminishes R to 10Ω and is able to locate the null point on the last (4th) segment of the potentiometer. Find the resistance of the potentiometer wire and potential drop per unit length across the wire in the second case.
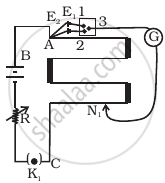
Potential difference between the points A and B in the circuit shown is 16 V, then potential difference across 2Ω resistor is ______ V. volt. (VA > VB)

A Daniel cell is balanced on 125 cm lengths of a potentiometer wire. Now the cell is short circuited by a resistance 2 Ω and the balance is obtained at 100 cm. The internal resistance of the Daniel cell is ______.
In a potentiometer arrangement, a cell of emf 1.20 V gives a balance point at 36 cm length of wire. This cell is now replaced by another cell of emf 1.80 V. The difference in balancing length of potentiometer wire in above conditions will be ______ cm.
Two cells of same emf but different internal resistances r1 and r2 are connected in series with a resistance R. The value of resistance R, for which the potential difference across second cell is zero, is ______.
In balanced meter bridge, the resistance of bridge wire is 0.1 Ω cm. Unknown resistance X is connected in left gap and 6 Ω in right gap, null point divides the wire in the ratio 2:3. Find the current drawn from the battery of 5 V having negligible resistance.
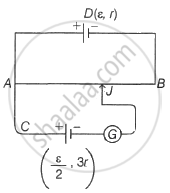
A potentiometer wire AB having length L and resistance 12r is joined to a cell D of emf ε and internal resistance r. A cell C having emt `ε/2` and internal resistance 3r is connected. The length AJ at which the galvanometer as shown in the figure shows no deflection is ______.
Draw neat labelled diagram of potentiometer as voltage divider.
The Figure below shows a potentiometer circuit in which the driver cell D has an emf of 6 V and internal resistance of 2 Ω. The potentiometer wire AB is 10 m long and has a resistance of 28 Ω. The series resistance RS is of 2 Ω.
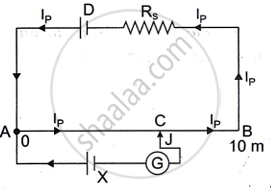
- The current Ip flowing in the potentiometer wire AB when the jockey (J) does not touch the wire AB.
- emf of the cell X if the balancing length AC is 4.5 m.
