Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Three angles of a quadrilateral are equal. If the fourth angle is 69°; find the measure of equal angles.
उत्तर
Let each equal angle be x°
x + x + x + 69° = 360°
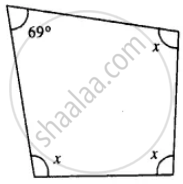
3x = 360°- 69
3x = 291
x = 97°
Each, equal angle = 97°
संबंधित प्रश्न
The perimeter of a parallelogram is 22 cm . If the longer side measures 6.5 cm what is the measure of the shorter side?
ABCD is a parallelogram, AD is produced to E so that DE = DC and EC produced meets AB produced in F. Prove that BF = BC.
Define the following term Quadrilateral .
Define the following term Convex Quadrilateral .
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Interior .
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral has ....... sides.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
The sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is ......
In Fig. 16.19, ABCD is a quadrilateral.
Name a pair of opposite sides.
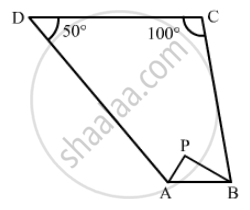
In Fig. 16.21, the bisectors of ∠A and ∠B meet at a point P. If ∠C = 100° and ∠D = 50°, find the measure of ∠APB.
In a convex hexagon, prove that the sum of all interior angle is equal to twice the sum of its exterior angles formed by producing the sides in the same order.
Which of the following quadrilateral is not a rhombus?
In quadrilateral ABCD, side AB is parallel to side DC. If ∠A : ∠D = 1 : 2 and ∠C : ∠B = 4 : 5
(i) Calculate each angle of the quadrilateral.
(ii) Assign a special name to quadrilateral ABCD
From the following figure find;
- x
- ∠ABC
- ∠ACD
In the given figure : ∠b = 2a + 15 and ∠c = 3a + 5; find the values of b and c.
In a quadrilateral ABCD, AO and BO are bisectors of angle A and angle B respectively. Show that:
∠AOB = (∠C + ∠D)
In parallelogram ABCD, ∠A = 90°
(i) What is the measure of angle B.
(ii) Write the special name of the parallelogram.
Observe the figure below and find out their name.
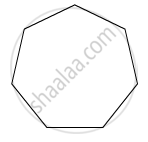
The angles of a pentagon are x°, (x - 10)°, (x + 20)°, (2x - 44)° and (2x - 70)°. Find the angles.
In a pentagon ABCDE, AB || ED and ∠B = 140°, ∠C = 2x° and ∠D = 3x°. Find ∠C and ∠D
If one angle of a cyclic quadrilateral is 75°, then the opposite angle is
Which of the following is not true for a parallelogram?
D and E are the mid-points of the sides AB and AC respectively of ∆ABC. DE is produced to F. To prove that CF is equal and parallel to DA, we need an additional information which is ______.
If the sum of two angles is greater than 180°, then which of the following is not possible for the two angles?
In given figure, What is BD – DE?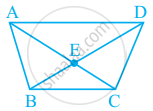
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
AC ⊥ BD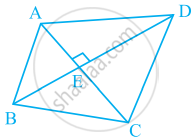
Can we have two obtuse angles whose sum is an acute angle? Why or why not?
Draw a rough sketch of a quadrilateral KLMN. State two pairs of adjacent angles.
