Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two discs of the same moment of inertia rotating about their regular axis passing through centre and perpendicular to the plane of the disc with angular velocities ω1 and ω2. They are brought in to contact face to face coinciding with the axis of rotation. The expression for loss of energy during this process is, ______
पर्याय
`1/4I(omega_1 - omega_2)^2`
`I(omega_1 - omega_2)^2`
`1/8I(omega_1 - omega_2)^2`
`1/2I(omega_1 - omega_2)^2`
उत्तर
Two discs of the same moment of inertia rotating about their regular axis passing through centre and perpendicular to the plane of the disc with angular velocities ω1 and ω2. They are brought in to contact face to face coinciding with the axis of rotation. The expression for loss of energy during this process is, `underline(1/4I(omega_1 - omega_2)^2)`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two particles, each of mass m and speed v, travel in opposite directions along parallel lines separated by a distance d. Show that the angular momentum vector of the two particle system is the same whatever be the point about which the angular momentum is taken.
The torque of the weight of any body about any vertical axis is zero. If it always correct?
A body is in translational equilibrium under the action of coplanar forces. If the torque of these forces is zero about a point, is it necessary that it will also be zero about any other point?
Equal torques act on the disc A and B of the previous problem, initially both being at rest. At a later instant, the linear speeds of a point on the rim of A and another point on the rim of B are \[\nu_A\] and \[\nu_B\] respectively. We have
A simple pendulum of length l is pulled aside to make an angle θ with the vertical. Find the magnitude of the torque of the weight ω of the bob about the point of suspension. When is the torque zero?
A cubical block of mass m and edge a slides down a rough inclined plane of inclination θ with a uniform speed. Find the torque of the normal force acting on the block about its centre.
A flywheel of moment of inertia 5⋅0 kg-m2 is rotated at a speed of 60 rad/s. Because of the friction at the axle it comes to rest in 5⋅0 minutes. Find (a) the average torque of the friction (b) the total work done by the friction and (c) the angular momentum of the wheel 1 minute before it stops rotating.
A particle is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to the positive X-axis. The magnitude of its angular momentum with respect to the origin is, ______
A uniform cube of mass m and side a is placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. A vertical force F is applied to the edge as shown in figure. Match the following (most appropriate choice):
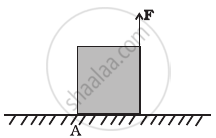
| (a) mg/4 < F < mg/2 | (i) Cube will move up. |
| (b) F > mg/2 | (ii) Cube will not exhibit motion. |
| (c) F > mg | (iii) Cube will begin to rotate and slip at A. |
| (d) F = mg/4 | (iv) Normal reaction effectively at a/3 from A, no motion. |
A solid sphere is rotating in free space. If the radius of the sphere is increased while keeping the mass the same, which one of the following will not be affected?
