Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two particles, each of mass m and speed v, travel in opposite directions along parallel lines separated by a distance d. Show that the angular momentum vector of the two particle system is the same whatever be the point about which the angular momentum is taken.
उत्तर
At a specific moment, two particles are located at points P and Q, as depicted in the diagram provided.
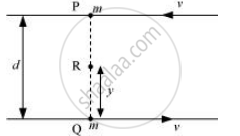
Angular momentum of the system relative to point P:
`vecL_p = mv xx 0 + mv xx d`
= mvd ....(i)
Angular momentum of the system relative to point Q:
`vecL_Q = mv xx d + mv xx 0`
= mvd ....(ii)
Consider a point R, which is at a distance y from point Q, i.e.,
QR = y
∴PR = d – y
Angular momentum of the system relative to point R:
`vecL_R = mvxx(d-y) + mv xx y`
= mvd - mvy + mvy
=mvd ...(iii)
Comparing equation i, ii and iii we get
`vecL_p = vecL_Q = vecL_R` .... (iv)
We infer from equation (iv) that the angular momentum of a system does not depend on the point about which it is taken
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A heavy particle of mass m falls freely near the earth's surface. What is the torque acting on this particle about a point 50 cm east to the line of motion? Does this torque produce any angular acceleration in the particle?
If the resultant torque of all the forces acting on a body is zero about a point, is it necessary that it will be zero about any other point?
A rectangular brick is kept on a table with a part of its length projecting out. It remains at rest if the length projected is slightly less than half the total length but it falls down if the length projected is slightly more than half the total length. Give reason.
A simple pendulum of length l is pulled aside to make an angle θ with the vertical. Find the magnitude of the torque of the weight ω of the bob about the point of suspension. When is the torque zero?
A flywheel of moment of inertia 5⋅0 kg-m2 is rotated at a speed of 60 rad/s. Because of the friction at the axle it comes to rest in 5⋅0 minutes. Find (a) the average torque of the friction (b) the total work done by the friction and (c) the angular momentum of the wheel 1 minute before it stops rotating.
A particle is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to the positive X-axis. The magnitude of its angular momentum with respect to the origin is, ______
Define torque and mention its unit.
State conservation of angular momentum.
A rod of mass 'm' hinged at one end is free to rotate in a horizontal plane. A small bullet of mass m/4 travelling with speed 'u' hits the rod and attaches to it at its centre. Find the angular speed of rotation of rod just after the bullet hits the rod 3. [take length of the rod as 'l']
The magnitude of the torque on a particle of mass 1 kg is 2.5 Nm about the origin. If the force acting on it is 1 N, and the distance of the particle from the origin is 5 m, the angle between the force and the position vector is (in radians) ______.
