Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is meant by an equipotential surface?
उत्तर
The surface of locus of all points at the same potential.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A regular hexagon of side 10 cm has a charge 5 µC at each of its vertices. Calculate the potential at the centre of the hexagon.
The top of the atmosphere is at about 400 kV with respect to the surface of the earth, corresponding to an electric field that decreases with altitude. Near the surface of the earth, the field is about 100 Vm−1. Why then do we not get an electric shock as we step out of our house into the open? (Assume the house to be a steel cage so there is no field inside!)
The discharging current in the atmosphere due to the small conductivity of air is known to be 1800 A on an average over the globe. Why then does the atmosphere not discharge itself completely in due course and become electrically neutral? In other words, what keeps the atmosphere charged?
What are the forms of energy into which the electrical energy of the atmosphere is dissipated during a lightning?
(Hint: The earth has an electric field of about 100 Vm−1 at its surface in the downward direction, corresponding to a surface charge density = −10−9 C m−2. Due to the slight conductivity of the atmosphere up to about 50 km (beyond which it is good conductor), about + 1800 C is pumped every second into the earth as a whole. The earth, however, does not get discharged since thunderstorms and lightning occurring continually all over the globe pump an equal amount of negative charge on the earth.)
Draw the equipotential surfaces due to an electric dipole. Locate the points where the potential due to the dipole is zero.
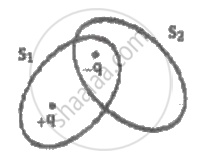
S1 and S2 are the two imaginary surfaces enclosing the charges +q and -q as shown. The electric flux through S1 and S2 are respectively ______.
Equipotentials at a great distance from a collection of charges whose total sum is not zero are approximately.
The diagrams below show regions of equipotentials.
(i) |
(ii)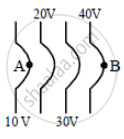 |
(iii) |
(iv) |
A positive charge is moved from A to B in each diagram.
Which of the following is NOT the property of equipotential surface?
Find the equation of the equipotentials for an infinite cylinder of radius r0, carrying charge of linear density λ.
