Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction in the following case.
Aldol
उत्तर
Aldehydes and ketones having at least one α-hydrogen undergo a reaction in the presence of dilute alkali as catalyst to form β-hydroxy aldehydes (aldol) or β-hydroxy ketones (ketol), respectively. This is known as the aldol reaction.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{\underset{Ethanal}{2CH3-CHO}<=>[dil.NaOH] CH3 - CH - CH2 - CHO ->[\Delta][-H2O]\underset{But-2-enal}{CH3 - CH = CH - CHO}}\\
|\phantom{.....................}\\
\ce{\underset{(Aldol)}{\underset{3-Hydroxybutanal}{OH}}}\phantom{...................}\
\end{array}\]
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..................}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.............................}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{..............}|\phantom{.................................}|\\
\ce{\underset{Propanone}{2CH3 - CO - CH3} <=>[Ba(OH)2] CH3 - C - CH2CO - CH3->[\Delta][-H2O]\underset{(Aldol condensation product)}{\underset{4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one}{CH3 - C = CH - CO - CH3}}}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{\underset{4-Hydroxy-4-methylpentan-2-one}{\underset{(Ketol)}{OH}}}\phantom{................}\
\end{array}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How will you convert ethanal into the following compound?
Butane-1, 3-diol
How will you convert ethanal into the following compound?
But-2-enal
Write structural formulas and names of four possible aldol condensation products from propanal and butanal. In each case, indicate which aldehyde acts as nucleophile and which as electrophile.
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Ethanol to 3-Hydroxybutanal
Give reasons Acetylation of aniline reduces its activation effect.
Why is alpha (α) hydrogen of carbonyl compounds acidic in nature?
Which product is formed when the compound 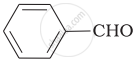 is treated with concentrated aqueous \[\ce{KOH}\] solution?
is treated with concentrated aqueous \[\ce{KOH}\] solution?
Compounds A and C in the following reaction are:
\[\ce{CH3CHO ->[(i) CH3MgBr][(ii) H2O] (A) ->[H2SO4, Δ] (B) ->[Hydroboration oxidation] (C)}\]
Which of the following compounds do not undergo aldol condensation?
(i) \[\ce{CH3 - CHO}\]
(ii) 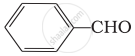
(iii) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{}||\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH3}
\end{array}\]
(iv) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\\
|\phantom{...}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CHO}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{...}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\\
\end{array}\]
What product will be formed on reaction of propanal with 2-methylpropanal in the presence of \[\ce{NaOH}\]? What products will be formed? Write the name of the reaction also.
Assertion: The α-hydrogen atom in carbonyl compounds is less acidic.
Reason: The anion formed after the loss of α-hydrogen atom is resonance stabilised.
Give reasons to support the answer:
Presence of Alpha hydrogen in aldehydes and ketones is essential for aldol condensation.
Which of the following gives aldol con~ensation reaction?
Identify A and B from the following reaction:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}\\
|\phantom{....................}\\
\phantom{}\ce{2CH3 - C = O ->[Ba(OH)2] A ->[Δ] B + H2O}
\end{array}\]
\[\ce{CH3-CH2-CHO ->[dil][alkali] Product}\]
The product in the above reaction is:
Which of the following does not give aldol condensation reaction?
When acetaldehyde is treated with dilute NaOH, the following reaction is observed.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{2CH3 - CHO ->[dil.NaOH] CH3 - CH - CH2 - CHO}\\
\phantom{...............}|\\
\phantom{.................}\ce{OH}
\end{array}\]
- What are the functional groups in the product?
- Can another product be formed during the same reaction? (Deduce the answer by doing atomic audit of reactant and product).
- Is this an addition reaction or condensation reaction?
Write a note on the aldol condensation reaction of acetaldehyde.
