Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is the action of following reagents on glucose?
1. Bromine water
2. Hydroxylamine
उत्तर
1. Action of bromine water on glucose:
The oxidation of glucose wirh bromine water (which is a mild oxidizing agent) gives gluconic acid. This indicates the presence of aldehyde group.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.........}\ce{CHO}\phantom{......................}\ce{COOH}\phantom{.............}\\
\phantom{}|\phantom{............................}|\phantom{......}\\
\ce{(CHOH)4 + [O] ->[Bromine water] (CHOH)4}\\
\phantom{.........}|\phantom{.............................}|\phantom{...............}\\
\phantom{...............}\ce{\underset{\text{Glucose}}{CH2OH}}\phantom{.......................}\ce{\underset{\text{Gluconic acid}}{CH2OH}}\phantom{...............}
\end{array}\]
2. Action of hydroxylamine on glucose:
The reaction of glucose with hydroxylamine gives glucoxime. This indicates the presence of carbonyl group.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{....................}\ce{CHO}\phantom{.........................}\ce{CH = N - OH }\phantom{.............}\\
\phantom{...}|\phantom{............................}|\phantom{......}\\
\ce{(CHOH)4 ->[NH2-OH] (CHOH)4 + H2O}\\
\phantom{.............}|\phantom{.............................}|\phantom{...............}\\
\phantom{................}\ce{\underset{\text{Glucose}}{CH2OH}}\phantom{....................}\ce{\underset{\text{Glucoxime}}{CH2OH}}\phantom{...............}
\end{array}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
On acid hydrolysis, propane nitrile gives.
How is carbolic acid prepared from chlorobenzene?
Identify ‘A' and ‘B’ in the following reaction :
C6H5MgBr + C02 `(`> ‘A’ `(PCl_5)/()`> ‘B’
Predict the products of the following reactions:
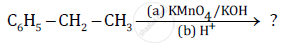
Name the reagents used in the following reactions:

Show how the following compound can be converted to benzoic acid.
Ethylbenzene
Show how the following compound can be converted to benzoic acid.
Bromobenzene
Show how the following compound can be converted to benzoic acid.
Phenylethene (Styrene)
Predict the products formed when cyclohexanecarbaldehyde reacts with the following reagent.
Tollens’ reagent
An organic compound (A) (molecular formula C8H16O2) was hydrolysed with dilute sulphuric acid to give a carboxylic acid (B) and an alcohol (C). Oxidation of (C) with chromic acid produced (B). (C) on dehydration gives but-1-ene. Write equations for the reactions involved.
How will you prepare the given compound from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
Methyl benzoate
How will you prepare the given compound from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
m-Nitrobenzoic acid
How will you prepare the given compound from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
p-Nitrobenzoic acid
Complete the synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or product.
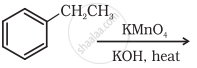
Name the reagents used in the following reactions:
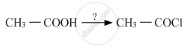
The functional group present in triacylglycerol is _______.
The reagent which does not react with both, acetone and benzaldehyde.
Match the reactions given in Column I with the suitable reagents given in Column II.
| Column I (Reactions) |
Column II (Reagents) |
| (i) Benzophenone Diphenylmethane | (a) \[\ce{LiAlH4}\] |
| (ii) Benzaldehyde 1-Phenylethanol | (b) \[\ce{DIBAL-H}\] |
| (iii) Cyclohexanone Cyclohexanol | (c) \[\ce{Zn(Hg)/Conc. HCl}\] |
| (iv) Phenyl benzoate Benzaldehyde | (d) \[\ce{CH3MgBr}\] |
Substitution of one alkyl group by replacing hydrogen of primary amines
Benzoic acid can be obtained by the oxidation of all of the following EXCEPT ______.
Match List - I with List - II.
| List - I | List - II | ||
| (a) | 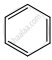 \[\ce{->[CO,HCl][Anhyd. AlCl3/CuCl]}\] \[\ce{->[CO,HCl][Anhyd. AlCl3/CuCl]}\] |
(i) | Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction |
| (b) |
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{O}\phantom{.................}\\ ||\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{R - C - CH3 + NaOX ->} \end{array}\] |
(ii) | Gattermann-Koch reaction |
| (c) | \[\ce{R - CH2 - OH + R'COOH ->[Conc. H2SO4]}\] | (iii) | Haloform reaction |
| (d) | \[\ce{R - CH2COOH ->[(i) X2/Red P][(ii) H2O]}\] | (iv) | Esterification |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
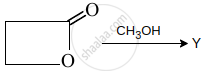
Y is:
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate words from those given in the brackets:
[stable, low, aldehyde, unstable, 6, 4, ethane, Clemmensen’s, 2, 3, carboxylic acid, high, propane, Rosenmund's]
The primary alcohols are easily oxidised first into ______ and then into ______.
