Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is the action of following reagents on glucose?
1. Bromine water
2. Hydroxylamine
उत्तर
1. Action of bromine water on glucose:
The oxidation of glucose wirh bromine water (which is a mild oxidizing agent) gives gluconic acid. This indicates the presence of aldehyde group.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.........}\ce{CHO}\phantom{......................}\ce{COOH}\phantom{.............}\\
\phantom{}|\phantom{............................}|\phantom{......}\\
\ce{(CHOH)4 + [O] ->[Bromine water] (CHOH)4}\\
\phantom{.........}|\phantom{.............................}|\phantom{...............}\\
\phantom{...............}\ce{\underset{\text{Glucose}}{CH2OH}}\phantom{.......................}\ce{\underset{\text{Gluconic acid}}{CH2OH}}\phantom{...............}
\end{array}\]
2. Action of hydroxylamine on glucose:
The reaction of glucose with hydroxylamine gives glucoxime. This indicates the presence of carbonyl group.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{....................}\ce{CHO}\phantom{.........................}\ce{CH = N - OH }\phantom{.............}\\
\phantom{...}|\phantom{............................}|\phantom{......}\\
\ce{(CHOH)4 ->[NH2-OH] (CHOH)4 + H2O}\\
\phantom{.............}|\phantom{.............................}|\phantom{...............}\\
\phantom{................}\ce{\underset{\text{Glucose}}{CH2OH}}\phantom{....................}\ce{\underset{\text{Glucoxime}}{CH2OH}}\phantom{...............}
\end{array}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the structures of A and B in the following reactions
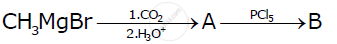
Predict the products of the following reactions:
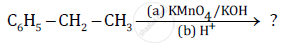
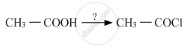
Name the reagents used in the following reactions:

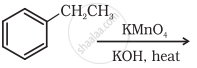
Show how the following compound can be converted to benzoic acid.
Ethylbenzene
Show how the following compound can be converted to benzoic acid.
Acetophenone
An organic compound (A) (molecular formula C8H16O2) was hydrolysed with dilute sulphuric acid to give a carboxylic acid (B) and an alcohol (C). Oxidation of (C) with chromic acid produced (B). (C) on dehydration gives but-1-ene. Write equations for the reactions involved.
How will you prepare the given compound from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
Methyl benzoate
How will you prepare the given compound from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
m-Nitrobenzoic acid
How will you prepare the given compound from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
p-Nitrobenzoic acid
Complete the synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or product.
How is methoxy benzene prepared from carbolic acid?
Name the reagents used in the following reactions:
The functional group present in triacylglycerol is _______.
The reagent which does not react with both, acetone and benzaldehyde.
Which is the most suitable reagent for the following conversion?
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{....................}\ce{O}\phantom{.....................................}\ce{O}\phantom{.}\\
\phantom{....................}||\phantom{......................................}||\phantom{.}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3 - CH = CH - CH2 - C - CH3 -> CH3 - CH = CH - CH2 - C - OH}\phantom{.}
\end{array}\]
Through which of the following reactions number of carbon atoms can be increased in the chain?
(i) Grignard reaction
(ii) Cannizaro’s reaction
(iii) Aldol condensation
(iv) HVZ reaction
Which of the following substance produced acetaldehyde on dry distillation?
The end product Y in the sequence of reaction:
\[\ce{RX ->[CN^-] X ->[NaOH] Y}\] is:
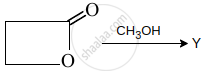
Y is:
Alkaline hydrolysis of C4H8Cl2 gives a compound (A) which on heating with NaOH and I2 produces a yellow precipitate of CHI3. The compound (A) should be ______.
A compound 'X' with molecular formula C3H8O can be oxidised to a compound 'Y' with the molecular formula C3H6O2 'X' is most likely to be ______.
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate words from those given in the brackets:
[stable, low, aldehyde, unstable, 6, 4, ethane, Clemmensen’s, 2, 3, carboxylic acid, high, propane, Rosenmund's]
The primary alcohols are easily oxidised first into ______ and then into ______.
