Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When water droplets merge to form a bigger drop
पर्याय
energy is liberated
energy is absorbed
energy is neither liberated nor absorbed
energy may either be liberated or absorbed depending on the nature of the liquid.
उत्तर
As the water droplets merge to form a single droplet, the surface area decreases. With this decrease in surface area, the surface energy of the resulting drop also decreases. Therefore, extra energy must be liberated from the drop in accordance with the conservation of energy.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The energy of the free surface of a liquid drop is 5π times the surface tension of the liquid. Find the diameter of the drop in C.G.S. system.
Derive Laplace’s law for spherical membrane of bubble due to surface tension.
A uniform vertical tube of circular cross section contains a liquid. The contact angle is 90°. Consider a diameter of the tube lying in the surface of the liquid. The surface to the right of this diameter pulls the surface on the left of it. What keeps the surface on the left in equilibrium?
Frictional force between solids operates even when they do not move with respect to each other. Do we have viscous force acting between two layers even if there is no relative motion?
The properties of a surface are different from those of the bulk liquid because the surface molecules
(a) are smaller than other molecules
(b) acquire charge due to collision from air molecules
(c) find different type of molecules in their range of influence
(d) feel a net force in one direction.
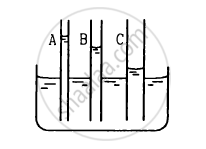
The capillaries shown in figure have inner radii 0.5 mm, 1.0 mm and 1.5 mm respectively. The liquid in the beaker is water. Find the heights of water level in the capillaries. The surface tension of water is 7.5 × 10−2 N m−1.
A capillary tube of radius 0.50 mm is dipped vertically in a pot of water. Find the difference between the pressure of the water in the tube 5.0 cm below the surface and the atmospheric pressure. Surface tension of water = 0.075 N m−1.
Find the surface energy of water kept in a cylindrical vessel of radius 6.0 cm. Surface tension of water = 0.075 J m−2.
Solve the previous problem if the lead piece is fastened on the top surface of the block and the block is to float with its upper surface just dipping into water.
A hollow spherical body of inner and outer radii 6 cm and 8 cm respectively floats half-submerged in water. Find the density of the material of the sphere.
Define surface tension
Water rises to a height of 20 mm in a capillary tube. If the radius made 1/3rd of its previous value, to what height will the water now rise in the tube?
Obtain an expression for the capillary rise or fall using the forces method.
How does surface tension help a plant?
What do you mean by capillarity or capillary action?
What is capillarity?
Two mercury droplets of radii 0.1 cm. and 0.2 cm. collapse into one single drop. What amount of energy is released? The surface tension of mercury T = 435.5 × 10–3 Nm–1.
The excess pressure inside a liquid drop is 500 Nm-2. If the radius of the drop is 2 mm, the surface tension of the liquid is x × 10-3 Nm-1. The value of x is ______.
The surface tension of soap solution is 25 × 10-3 Nm-1. The excess of pressure inside a soap bubble of diameter 1 cm is ______.
